Abstract
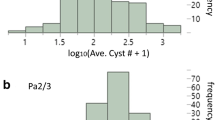
Meloidogyne fallax is an emerging pest in Europe and represents a threat for potato production. We report the mapping of genetic factors controlling a quantitative resistance against M. fallax identified in the Solanum sparsipilum genotype 88S.329.15. When infected, this genotype develops a necrotic reaction at the feeding site of the juveniles and totally prevents their development to the female stage. A “F1” diploid progeny consisting of 128 individuals was obtained using the potato (S. tuberosum) dihaploid genotype BF15 H1 as female progenitor. Sixty-eight hybrid genotypes displayed necrosis at the feeding site of the juveniles and 60 other genotypes showed no defence reaction. This suggested a monogenic control of the resistance. However, when considering the number of nematode females developed in their roots, a continuous distribution was observed for both “necrotic” and “non-necrotic” hybrid genotypes, indicating a polygenic control of the resistance. A linkage map of each parental genotype was constructed using AFLP markers. The necrotic reaction (NR) was mapped as a qualitative trait on chromosome XII of the resistant genotype 88S.329.15. Quantitative trait locus (QTL) analysis for the number of nematode females developed per “F1” plant genotype was performed using the QTL cartographer software. No QTL was detected on the linkage map of the susceptible parent. A QTL explaining 94.5% of the phenotypic variation was mapped on chromosome XII of the resistant progenitor. This QTL, named MfaXIIspl, was mapped in a genomic region collinear to the map position of the Mi-3 gene conferring resistance to Meloidogyne incognita in tomato. It corresponds to the NR locus.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bakker E, Butterbach P, Rouppe van der Voort JNAM, van der Vossen E, van Vliet J, Bakker J, Goverse A (2003) Genetic and physical mapping of homologues of the virus resistance gene Rx1 and the cyst nematode resistance gene Gpa2 in potato. Theor Appl Genet 106:1524–1531
Basten CJ, Weir BS, Zeng ZB (2004) QTL cartographer v 2.0. A reference manual and tutorial for QTL mapping. North Carolina State University, Bioinformatics Research Center, Department of Statistics, Raleigh, North Carolina
Bent AF (1996) Plant disease resistance genes; function meets structure. Plant Cell 8:1757–1771
Berthou F, Palloix A, Mugniéry D (2003) Characterization of virulence in populations of Meloidogyne chitwoodi and evidence for a resistance gene in Capsicum annuum L. line PM 217. Nematology 5:383–390
Boerma HR, Hussey RS (1992) Breeding plant for resistance to nematodes. J Nematol 24:242–252
Botella MA, Parker JE, Frost LN, Bittner-Eddy PD, Beynon JL, Daniel MJ, Holub ER, Jones JDG (1998) Three genes of the Arabidopsis RPP.1 complex resistance locus recognize distinct Perensopora parasitica avirulence determinants. Plant Cell 10:1847–1860
Brown CR, Yang C-P, Mojtahedi H, Santo GS (1996) RFLP analysis of resistance to Columbia root-knot nematode derived from Solanum bulbocastanum in a BC2 population. Theor Appl Genet 92:572–576
Bryan GJ, McLean K, Bradshaw JE, Jong WSD, Phillips M, Castelli L, Waugh R (2002) Mapping QTLs for resistance to the cyst nematode Globodera pallida derived from the wild potato species Solanum vernei. Theor Appl Genet 105:68–77
Caromel B, Mugniéry D, Lefebvre V, Andrejewski S, Ellisèche D, Kerlan MC, Rousselle P, Rousselle-Bourgeois F (2003) Mapping QTLs for resistance against Globodera pallida (Stone) Pa2/3 in a diploid potato progeny originating from Solanum spegazzinii. Theor Appl Genet 106:1517–1523
Caromel B, Mugniéry D, Kerlan MC, Andrzejewski S, Lama N, Dantec JP, Rouaux C, Caranta C, Cavallin P, Ellissèche D, Rousselle-Bourgeois F, Lefebvre V (2004) QTLs for resistance to the cyst nematode Globodera pallida, deriving from Solanum sparsipilum, mapped in resistance gene clusters. In: Solanaceae genome workshop, September, 19–21, 2004, Wageningen, The Netherlands (poster and abstract) p 111
Charcosset A, Gallais A (1996) Estimation of the contribution of quantitative trait loci (QTL) to the variance of quantitative trait by means of genetic markers. Theor Appl Genet 93:1193–1201
Choi K, Burrow MD, Church G, Burrow G, Paterson AH, Simpson CE, Starr JL (1999) Genetics and mechanism of resistance to Meloidogyne arenaria in peanut germplasm. J Nematol 31:283–290
Cousins P, Walker A (2002) Genetics of resistance to Meloidogyne incognita in crosses of grape rootstocks. Theor Appl Genet 105:802–807
Daher S, Gillet S, Mugniéry D, Marzin, H (1996) Discovery in France and characteristics of the Dutch variant of Meloidogyne chitwoodi. In: Third international congress of nematology 07.-12. 07. 1996, La Guadeloupe, Program and Abstract, 188 pp
Daykin ME, Hussey RS (1985) Staining and histopathological techniques in Nematology. In: Baker KR, Carter CC, Sasser JN (eds) An advanced treatise on Meloidogyne. Volume II: methodology, pp 39–48
Djian-Caporalino C, Pijarowski L, Fazari A, Samson M, Gaveau L, O’Byrne C, Lefebvre V, Caranta C, Palloix A, Abad P (2001) High-resolution genetic mapping of the pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) resistance loci Me3 and Me4 conferring heat-stable resistance to root-knot nematodes (Meloidogyne spp.). Theor Appl Genet 103:592–600
Foot MA (1977) Laboratory rearing of potato cyst nematodes; a method suitable for pathotyping and biological studies. NZ J Agric 4:183–186
Gilbert JC, McGuire DC (1956) Inheritance of resistance to severe root-knot from Meloidogyne incognita in commercial type tomatoes. Proc Am Soc Hortic Sci 63:437–442
Grattapaglia D, Sederoff R (1994) Genetic linkage map of Eucalyptus grandis and Eucalyptus urophylla using a pseudo-testcross: mapping strategy and RAPD markers. Genetics 137:1121–1137
Grube RC, Radwanski ER, Jahn M (2000) Comparative genetics of disease resistance within the Solanaceae. Genetics 155:873–887
Hammond-Kosack KE, Jones JDG (1997) Plant disease resistance genes. Annu Rev Phytopathol 48:575–607
Hendy H, DalmassoA, Cardin MC (1985) Differences in resistant Capsicum annuum attacked by different Meloidogyne species. Nematologica 31:72–78
Janssen GJW, Verkerk-Bakker B, Van Norel A, Janssen R (1996) Resistance to Meloidogyne hapla, M. fallax and M. chitwoodi in wild tuber-bearing Solanum spp. Euphytica 92:287–294
Janssen GJW, Van Norel A, Janssen R, Hoogendoorn J (1997) Dominant and additive resistance to the root knot nematodes Meloidogyne chitwoodi and M. fallax in Central American Solanum species. Theor Appl Genet 94:692–700
Kanyuka K, Bendahmane A, Rouppe van der Voort JNAM, van der Vossen EAG, Baulcomb DC (1999) Mapping of intra-locus duplications and introgressed DNA: aids to map-based cloning of genes from complex genomes illustrated by physical analysis of the Rx locus in tetraploid potato. Theor Appl Genet 98:679–689
Karssen G (1996) Description of Meloidogyne fallax n. sp. (Nematoda: Heteroderidae), a root-knot nematode from the Netherlands. Fundam Appl Nematol 19:593–597
Kosambi DD (1944) The estimation of map distances from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12:172–175
Kouassi AB, Kerlan M-C, Sobczak M, Dantec J-P, Rouaux C, Ellissèche D, Mugniéry D (2004) Resistance to the root-knot nematode Meloidogyne fallax in Solanum sparsipilum: analysis of the mechanisms. Nematology 6(3):389–400
Kreike CM, De Koning JRA, Vinke JH, Van Ooijen JW, Stiekema WJ (1994) Quantitatively inherited resistance to Globodera pallida is dominated by one major locus in Solanum spegazzinii. Theor Appl Genet 88:764–769
Lincoln SE, Daly M, Lander E (1992) Constructing genetic maps with MAPMAKER/EXP 3.0. Whitehead Institute for Biochemical Research, Technical report, 3rd edn, Cambridge, Massachusetts
Michelmore RW, Meyers BC (1998) Clusters of resistance genes in plants evolve by divergent selection and a birth-and-death process. Genome Res 8:1113–1130
Rouppe van der Voort JNAM, van Zandvoort P, van Eck HJ, Folkertsma R, Hutten RCB, Draaistra J, Gommers FJ, Jacobsen E, Helder J, Bakker J (1997a) Use of allele specificity of comigrating AFLP markers to align genetic maps from different potato genotypes. Mol Gen Genet 255:438–447
Rouppe van der Voort JNAM, Wolters P, Folkertsma R, Hutten R, van Zandvoort P, Vinke H, Kanyuka K, Bendahmane A, Jacobsen E, Janssen R, Bakker J (1997b) Mapping the cyst nematode resistance locus Gpa2 in potato using a strategy based on comigrating AFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 95:874–880
Rouppe van der Voort JNAM, Lindeman W, Folkertsma R, Hutten RCB, Overmars H, Van der Vossen E, Jacobsen E, Bakker J (1998) A QTL for broad-spectrum resistance to cyst nematode species (Globodera spp.) maps to a resistance gene cluster in potato. Theor Appl Genet 96:654–661
Rouppe van der Voort JNAM, Janssen GJW, Overmars H, van Zandvoort PM, van Norel A, Scholten OE, Janssen R, Bakker J (1999a) Development of a PCR-based selection assay for root-knot nematode resistance (Rmc1) by a comparative analysis of the Solanum bulbocastanum and S. tuberosum genome. Euphytica 106:187–195
Rouppe van der Voort JNAM, Kanyuka K, van der Vossen E, Bendahmane A, Mooijman P, Klein-Lankhorst R, Stiekema W, Baulcombe D, Bakker J (1999b) Tight physical linkage of the nematode resistance gene Gpa2 and the virus resistance gene Rx on a single segment introgressed from the wild species Solanum tuberosum subsp. andigena CPC 1673 into cultivated potato. Mol Plant–Microbe Interact 12:197–206
Rouppe van der Voort JNAM, van der Vossen E, Bakker E, Overmars H, van Zandvoort P, Hutten R, Klein Lankhorst R, Bakker J (2000) Two additive QTLs conferring broad-spectrum resistance in potato to Globodera pallida are localized on resistance gene clusters. Theor Appl Genet 101:1122–1130
SAS Institute Inc (1989) SAS technical report P-179, additional SAS/STAT procedures, release 6.03. Cary, North Carolina
Thabuis A, Lefebvre V, Bernard G, Daubèze AM, Phaly T, Pochard E, Palloix A (2004) Phenotypic and molecular evaluation of a recurrent selection program for a polygenic resistance to Phytophtora capsici in pepper. Theor Appl Genet 109:342–351
Trudgill DL, Blok VC (2001) Apomictic, polyphagous root-knot nematodes: exceptionally successful and damaging biotrophic root pathogens. Annu Rev Phytopathol 39:53–77
Van der Vossen EAG, Rouppe van der Voort JNAM, Kanyuka K, Bendahmane A, Sandbrink H, Baulcombe DC, Bakker J, Stiekema WJ, Klein-Lankhorst RM (2000) Homologues of a single resistance-gene cluster in potato confer resistance to distinct pathogens: a virus and a nematode. Plant J 23:567–576
Vos P, Hogers R, Bleeker M, Reijans M, Van de Lee T, Hornes M, Frijters A, Pot J, Peleman J, Kuiper M, Zabeau M (1995) AFLP: a new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Res 23:4407–4414
Yaghoobi J, Kaloshian I, Wen Y, Williamson VM (1995) Mapping a new nematode resistance locus in Lycopersicon peruvianum. Theor Appl Genet 91:457–464
Yin TM, DiFazio SP, Gunter LE, Riemenschneider D, Tuskan GA (2004) Large-scale heterospecific segregation distortion in Populus revealed by a dense genetic map. Theor Appl Genet 109(3):451–463
Zijlstra C, Lever AEM, Uenk BJ, Van Silhout CH (1995) Differences between ITS regions of isolates of root-knot nematodes Meloidogyne hapla and M. chitwoodi. Phytopathology 25:1231–1237
Acknowledgements
This work is a part of the European Union funded project QLRT-1999-01462 (acronym DREAM). The authors are thankful to Dr. Olivier Plantard for his useful critical advises on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by G. Wenzel
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bakari, K.A., Marie-Claire, K., Bernard, C. et al. A major gene mapped on chromosome XII is the main factor of a quantitatively inherited resistance to Meloidogyne fallax in Solanum sparsipilum . Theor Appl Genet 112, 699–707 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-005-0173-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-005-0173-2