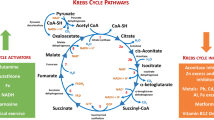
Abstract
Eukaryotic elongation factor-2 kinase (eEF2K), an atypical member of alpha-kinase family, is highly overexpressed in breast, pancreatic, brain, and lung cancers, and associated with poor survival in patients. eEF2K promotes cell proliferation, survival, and aggressive tumor characteristics, leading to tumor growth and progression. While initial studies indicated that eEF2K acts as a negative regulator of protein synthesis by suppressing peptide elongation phase, later studies demonstrated that it has multiple functions and promotes cell cycle, angiogenesis, migration, and invasion as well as induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition through induction of integrin β1, SRC/FAK, PI3K/AKT, cyclin D1, VEGF, ZEB1, Snail, and MMP-2. Under stress conditions such as hypoxia and metabolic distress, eEF2K is activated by several signaling pathways and slows down protein synthesis and helping cells to save energy and survive. In vivo therapeutic targeting of eEF2K by genetic methods inhibits tumor growth in various tumor models, validating it as a potential molecular target. Recent studies suggest that eEF2K plays a role in tumor microenvironment cells by monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) and accumulation of tumor-associated macrophages. Due to its clinical significance and the pivotal role in tumorigenesis and progression, eEF2K is considered as an important therapeutic target in solid tumors. However, currently, there is no specific and potent inhibitor for translation into clinical studies. Here, we aim to systematically review current knowledge regarding eEF2K in tumor biology, microenvironment, and development of eEF2K targeted inhibitors and therapeutics.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashour AA, Abdel-Aziz AA, Mansour AM, Alpay SN, Huo L, Ozpolat B (2014a) Targeting elongation factor-2 kinase (eEF-2K) induces apoptosis in human pancreatic cancer cells. Apoptosis 19:241–258
Bayraktar R, Pichler M, Kanlikilicer P, Ivan C, Bayraktar E, Kahraman N, Aslan B, Oguztuzun S, Ulasli M, Arslan A, Calin G, Lopez-Berestein G, Ozpolat B (2017) MicroRNA 603 acts as a tumor suppressor and inhibits triple-negative breast cancer tumorigenesis by targeting elongation factor 2 kinase. Oncotarget 8:11641–11658
Bircan HA, Gurbuz N, Pataer A, Caner A, Kahraman N, Bayraktar E, Bayraktar R, Erdogan MA, Kabil N, Ozpolat B (2018) Elongation factor-2 kinase (eEF-2K) expression is associated with poor patient survival and promotes proliferation, invasion and tumor growth of lung cancer. Lung Cancer 124:31–39
Leprivier G, Remke M, Rotblat B, Dubuc A, Mateo AR, Kool M, Agnihotri S, El-Naggar A, Yu B, Somasekharan SP, Faubert B, Bridon G, Tognon CE, Mathers J, Thomas R, Li A, Barokas A, Kwok B, Bowden M, Smith S, Wu X, Korshunov A, Hielscher T, Northcott PA, Galpin JD, Ahern CA, Wang Y, McCabe MG, Collins VP, Jones RG, Pollak M, Delattre O, Gleave ME, Jan E, Pfister SM, Proud CG, Derry WB, Taylor MD, Sorensen PH (2013) The eEF2 kinase confers resistance to nutrient deprivation by blocking translation elongation. Cell 153:1064–1079
Zhu H, Song H, Chen G, Yang X, Liu J, Ge Y, Lu J, Qin Q, Zhang C, Xu L, Di X, Cai J, Ma J, Zhang S, Sun X (2017) eEF2K promotes progression and radioresistance of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Radiother Oncol 124:439–447
Ryazanov AG, Shestakova EA, Natapov P (1988) Phosphorylation of elongation factor 2 by EF-2 kinase affects rate of translation. Nature 334:170–173
Ryazanov AG, Pavur KS, Dorovkov MV (1999) Alpha kinases: a new class of protein kinases with a novel catalytic domain. Curr Biol 9:R43–R45
Kenney JW, Moore CE, Wang X, Proud CG (2014) Eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase, an unusual enzyme with multiple roles. Adv Biol Regul 55:15–27
Liu R, Proud CG (2016) Eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase as a drug target in cancer, and in cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases. Acta Pharmacol Sin 37:285–294
Tavernarakis N (2013) Protein synthesis. In: Vijg J, Campisi J, Lithgow G (eds) The molecular and cellular biology of aging. Gerontological Society of America (GSA) Press, Washington DC
Wang X, Xie J, Proud CG (2017) Eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase (eEF2K) in cancer. Cancers (Basel) 9:162
Moore CE, Mikolajek H, Regufe da Mota S, Wang X, Kenney JW, Werner JM, Proud CG (2015) Elongation factor 2 kinase is regulated by proline hydroxylation and protects cells during hypoxia. Mol Cell Biol 35:1788–1804
Lazarus MB, Levin RS, Shokat KM (2017) Discovery of new substrates of the elongation factor-2 kinase suggests a broader role in the cellular nutrient response. Cell Signal 29:78–83
Kong M, Ditsworth D, Lindsten T, Thompson CB (2009) Alpha4 is an essential regulator of PP2A phosphatase activity. Mol Cell 36:51–60
Reid MA, Wang WI, Rosales KR, Welliver MX, Pan M, Kong M (2013) The B. 55alpha subunit of PP2A drives a p53-dependent metabolic adaptation to glutamine deprivation. Mol Cell 50:200–211
Mihaylova MM, Shaw RJ (2011) The AMPK signalling pathway coordinates cell growth, autophagy and metabolism. Nat Cell Biol 13:1016–1023
Hardie DG, Schaffer BE, Brunet A (2015) AMPK: an energy-sensing pathway with multiple inputs and outputs. Trends Cell Biol 26:190–201
Moore CE, Regufe da Mota S, Mikolajek H, Proud CG (2014) A conserved loop in the catalytic domain of eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase plays a key role in its substrate specificity. Mol Cell Biol 34:2294–2307
Proud CG (2015) Regulation and roles of elongation factor 2 kinase. Biochem Soc Trans 43:328–332
Ryazanov AG (1987) Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent phosphorylation of elongation factor 2. FEBS Lett 214:331–334
Lee K, Alphonse S, Piserchio A, Tavares CD, Giles DH, Wellmann RM, Dalby KN, Ghose R (2016) Structural basis for the recognition of eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase by calmodulin. Structure 24:1441–1451
Kameshima S, Okada M, Ikeda S, Watanabe Y, Yamawaki H (2016) Coordination of changes in expression and phosphorylation of eukaryotic elongation factor 2 (eEF2) and eEF2 kinase in hypertrophied cardiomyocytes. Biochem Biophys Rep 7:218–224
Diggle TA, Seehra CK, Hase S, Redpath NT (1999) Analysis of the domain structure of elongation factor-2 kinase by mutagenesis. FEBS Lett 457:189–192
Pigott CR, Mikolajek H, Moor E, Finn SJ, Phippe CW, Werner JM, Proud CG (2011) Insights into the regulation of eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase and the interplay between its domains. Biochem J 442:105–118
Tavares CDJ, O’Brien JP, Abramczyk O, Devkota AK, Shores KS, Ozpolat B, Dalby K (2012) Calcium/calmodulin stimulates the autophosphorylation of elongation factor 2 kinase on Thr-348 and Ser-500 to regulate its activity and calcium dependence. Biochemistry 51:2232–2245
Pyr Dit Ruys S, Wang X, Smith EM, Herinckx G, Hussain N, Rider MH, Vertommen D, Proud CG (2012) Identification of autophosphorylation sites in eukaryotic elongation factor-2 kinase. Biochem J 442:681–692
Jewell JL, Guan KL (2013) Nutrient signaling to mTOR and cell growth. Trends Biochem Sci 38:233–242
Redpath NT, Foulstone EJ, Proud CG (1996) Regulation of translation elongation factor-2 by insulin via a rapamycin-sensitive signalling pathway. EMBO J 15:2291–2297
Diggle TA, Subkhankulova T, Lilley KS, Shikotra N, Willis AE, Redpath NT (2001) Phosphorylation of elongation factor-2 kinase on serine 499 by cAMP-dependent protein kinase induces Ca2+/ calmodulin-independent activity. Biochem J 353:621–626
Proud CG (2013) mTORC1 regulates the efficiency and cellular capacity for protein synthesis. Biochem Soc Trans 41:923–926
Wang X, Regufe da Mota S, Liu R, Moore CE, Xie J, Lanucara F, Agarwala U, Pyr Dit Ruys S, Vertommen D, Rider MH, Eyers CE, Proud CG (2014a) Eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase activity is controlled by multiple inputs from oncogenic signaling. Mol Cell Biol 34:4088–4103
Wang X, Li W, Williams M, Terada N, Alessi DR, Proud CG (2001) Regulation of elongation factor 2 kinase by p90RSK1 and p70 S6 kinase. EMBO J 20:4370–4379
Hardie DG (2014) AMP-activated protein kinase: maintaining energy homeostasis at the cellular and whole-body levels. Annu Rev Nutr 34:31–55
Browne GJ, Finn SG, Proud CG (2004) Stimulation of the AMP-activated protein kinase leads to activation of eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase and to its phosphorylation at a novel site, serine 398. J Biol Chem 279:12220–12231
Johanns M, Ruys SPD, Houddane A, Vertommen D, Herinckx G, Hue L, Proud CG, Rider MH (2017) Direct and indirect activation of eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase by AMP-activated protein kinase. Cell Signal 36:212–221
Zona S, Bella L, Burton MJ, Nestal de Moraes G, Lam EW (2014) FOXM1: an emerging master regulator of DNA damage response and genotoxic agent resistance. Biochim Biophys Acta 1839:1316–1322
Hamurcu Z, Ashour A, Kahraman N, Ozpolat B (2016) FOXM1 regulates expression of eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase and promotes proliferation, invasion and tumorgenesis of human triple negative breast cancer cells. Oncotarget 7:16619–16635
Calin GA, Croce CM (2006) MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer 6:857–866
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA, Downing JR, Jacks T, Horvitz HR, Golub TR (2005) MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature 435:834–838
Schwarzenbach H, Nishida N, Calin GA, Pantel K (2014) Clinical relevance of circulating cell-free microRNAs in cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 11:145–156
Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack FJ (2006) Oncomirs - microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 6:259–269
Pillai RS (2005) MicroRNA function: multiple mechanisms for a tiny RNA? RNA 11:1753–1761
Chen B, Li H, Zeng X, Yang P, Liu X, Zhao X, Liang S (2012) Roles of microRNA on cancer cell metabolism. J Transl Med 10:228
Bayraktar R, Ivan C, Bayraktar E, Kanlikilicer P, Kabil NN, Kahraman N, Mokhlis HA, Karakas D, Rodriguez-Aguayo C, Arslan A, Sheng J, Wong S, Lopez-Berestein G, Calin GA, Ozpolat B (2018) Dual suppressive effect of miR-34a on the FOXM1/eEF2-kinase axis regulates triple-negative breast cancer growth and invasion. Clin Cancer Res 24:4225–4241
Shi Q, Xu X, Liu Q, Luo F, Shi J, He X (2016) MicroRNA-877 acts as a tumor suppressor by directly targeting eEF2K in renal cell carcinoma. Oncol Lett 11:1474–1480
Wu H, Zhu H, Liu DX, Niu TK, Ren X, Patel R, Hait WN, Yang JM (2009) Silencing of elongation factor-2 kinase potentiates the effect of 2-deoxy-D-glucose against human glioma cells through blunting of autophagy. Cancer Res 69:2453–2460
Tekedereli I, Alpay SN, Tavares CD, Cobanoglu ZE, Kaoud TS, Sahin I, Sood AK, Lopez-Berestein G, Dalby KN, Ozpolat B (2012) Targeted silencing of elongation factor 2 kinase suppresses growth and sensitizes tumors to doxorubicin in an orthotopic model of breast cancer. PLoS One 7:e41171
Ashour AA, Gurbuz N, Alpay SN, Abdel-Aziz AA, Mansour AM, Huo L, Ozpolat B (2014b) Elongation factor-2 kinase regulates TG2/β1 integrin/Src/uPAR pathway and epithelial-mesenchymal transition mediating pancreatic cancer cells invasion. J Cell Mol Med 18:2235–2251
Huang L, Xu AM, Liu W (2015) Transglutaminase 2 in cancer. Am J Cancer Res 5:2756–2776
Akar U, Ozpolat B, Mehta K, Fok J, Kondo Y, Lopez-Berestein G (2007) Tissue transglutaminase inhibits autophagy in pancreatic cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res 5:241–249
Zhang Y, Cheng Y, Zhang L, Ren X, Huber-Keener KJ, Lee S, Yun J, Wang HG, Yang JM (2011) Inhibition of eEF-2 kinase sensitizes human glioma cells to TRAIL and down-regulates Bcl-xL expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 414:129–134
He C, Klionsky DJ (2009) Regulation mechanisms and signaling pathways of autophagy. Annu Rev Genet 43:67–93
Filomeni G, De Zio D, Cecconi F (2015) Oxidative stress and autophagy: the clash between damage and metabolic needs. Cell Death Differ 22:377–388
Hamurcu Z, Delibaşı N, Geçene S, Şener EF, Dönmez-Altuntaş H, Özkul Y, Canatan H, Ozpolat B (2018) Targeting LC3 and Beclin-1 autophagy genes suppresses proliferation, survival, migration and invasion by inhibition of Cyclin-D1 and uPAR/Integrin β1/Src signaling in triple negative breast cancer cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 144:415–430
Xie CM, Liu XY, Sham KW, Lai JM, Cheng CH (2014) Silencing of EEF2K (eukaryotic elongation factor-2 kinase) reveals AMPK-ULK1-dependent autophagy in colon cancer cells. Autophagy 10:1495–1508
Laplante M, Sabatini DM (2012) mTOR signaling in growth control and disease. Cell 149:274–293
Shimobayashi M, Hall MN (2014) Making new contacts: the mTOR network in metabolism and signalling crosstalk. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 15:155–162
Shimobayashi M, Hall MN (2016) Multiple amino acid sensing inputs to mTORC1. Cell Res 26:7–20
Heberle AM, Prentzell MT, van Eunen K, Bakker BM, Grellscheid SN, Thedieck K (2015) Molecular mechanisms of mTOR regulation by stress. Mol Cell Oncol 2:e970489
Egan D, Kim J, Shaw R, Guan KL (2011) The autophagy initiating kinase ULK1 is regulated via opposing phosphorylation by AMPK and mTOR. Autophagy 7:643–644
Lindqvist LM, Tandoc K, Topisirovic I, Furic L (2018) Cross-talk between protein synthesis, energy metabolism and autophagy in cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev 48:104–111
Rabanal-Ruiz Y, Otten EG, Korolchuk VI (2017) mTORC1 as the main gateway to autophagy. Essays Biochem 61:565–584
Xu J, Ji J, Yan XH (2012) Cross-talk between AMPK and mTOR in regulating energy balance. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 52:373–381
Kim J, Kundu M, Viollet B, Guan KL (2011) AMPK and mTOR regulate autophagy through direct phosphorylation of Ulk1. Nat Cell Biol 13:132–141
Wu H, Yang JM, Jin S, Zhang H, Hait WN (2006) Elongation factor-2 kinase regulates autophagy in human glioblastoma cells. Cancer Res 66:3015–3023
Cheng Y, Ren X, Zhang Y, Shan Y, Huber-Keener KJ, Zhang L, Kimball SR, Harvey H, Jefferson LS, Yang JM (2013) Integrated regulation of autophagy and apoptosis by EEF2K controls cellular fate and modulates the efficacy of curcumin and velcade against tumor cells. Autophagy 9:208–219
Pinto JA, Rolfo C, Raez LE, Prado A, Araujo JM, Bravo L, Fajardo W, Morante ZD, Aguilar A, Neciosup SP, Mas LA, Bretel D, Balko JM, Gomez HL (2017) In silico evaluation of DNA damage inducible transcript 4 gene (DDIT4) as prognostic biomarker in several malignancies. Sci Rep 7:1526
Sun D, Zhu L, Zhao Y, Jiang Y, Chen L, Yu Y, Ouyang L (2018) Fluoxetine induces autophagic cell death via eEF2K-AMPK-mTOR-ULK complex axis in triple negative breast cancer. Cell Prolif 51:e12402
Moore CE, Wang X, Xie J, Pickford J, Barron J, Regufe da Mota S, Versele M, Proud CG (2016) Elongation factor 2 kinase promotes cell survival by inhibiting protein synthesis without inducing autophagy. Cell Signal 28:284–293
Karakas D, Kahraman N, Bayraktar R, Kabil N, Ulukaya E, Dere E, Lopez-Berestein G, Ozpolat B (2018) Identification of microenvironmental regulation and therapeutic targeting of ongenic EF-2 kinase in pancreatic cancer. (Conference paper). Abstracts of the 25th Biennial Congress of the European Association for Cancer Research, Amsterdam. doi: https://doi.org/10.1136/esmoopen-2018-EACR25.803
Xie J, Shen K, Lenchine RV, Gethings LA, Trim PJ, Snel MF, Zhou Y, Kenney JW, Kamei M, Kochetkova M, Wang X, Proud CG (2018) Eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase upregulates the expression of proteins implicated in cell migration and cancer cell metastasis. Int J Cancer 142:1865–1877
Zhou Y, Li Y, Xu S, Lu J, Zhu Z, Chen S, Tan Y, He P, Xu J, Proud CG, Xie J, Shen K (2019) Eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase promotes angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma via PI3K/Akt and STAT3. Int J Cancer 146:1383–1395
Asik E, Kahraman N, Guray T, Volkan M, Lopez-Berestein G, Ozpolat B (2017) Eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase (eEF-2K) is a novel therapeutic target in BRCA1+ mutated breast cancer. (Conference paper). Cancer Res 77(13 Supplement):1125–1125
Cheng Y, Ren X, Zhang Y, Patel R, Sharma A, Wu H, Robertson GP, Yan L, Rubin E, Yang JM (2011) eEF-2 kinase dictates cross-talk between autophagy and apoptosis induced by Akt inhibition, thereby modulating cytotoxicity of novel Akt inhibitor MK-2206. Cancer Res 71:2654–2663
Hui L, Chen Y (2015) Tumor microenvironment: sanctuary of the devil. Cancer Lett 368:7–13
Chen F, Zhuang X, Lin L, Yu P, Wang Y, Shi Y, Hu G, Sun Y (2015) New horizons in tumor microenvironment biology: challenges and opportunities. BMC Med 13:45
Witz IP (2008) Tumor-microenvironment interactions: dangerous liaisons. Adv Cancer Res 100:203–229
Li LY (2010) Tumor microenvironment: bidirectional interactions between cancer cells and normal cells. Protein Cell 1:702–705
Balkwill FR, Capasso M, Hagemann T (2012) The tumor microenvironment at a glance. J Cell Sci 125:5591–5596
Quail DF, Joyce JA (2013) Microenvironmental regulation of tumor progression and metastasis. Nat Med 19:1423–1437
Hanahan D, Coussens LM (2012) Accessories to the crime: functions of cells recruited to the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Cell 21:309–322
Williams CB, Yeh ES, Soloff AC (2016) Tumor-associated macrophages: unwitting accomplices in breast cancer malignancy. NPJ Breast Cancer 2:15025
Naito Y, Yoshioka Y, Yamamoto Y, Ochiya T (2017) How cancer cells dictate their microenvironment: present roles of extracellular vesicles. Cell Mol Life Sci 74:697–713
Kanter JE (2017) Monocyte recruitment versus macrophage proliferation in atherosclerosis. Circ Res 121:1109–1110
Mantovani A, Bottazzi B, Colotta F, Sozzani S, Ruco L (1992) The origin and function of tumor-associated macrophages. Immunol Today 13:265–270
Mantovani A, Marchesi F, Malesci A, Laghi L, Allavena P (2017) Tumour-associated macrophages as treatment targets in oncology. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 14:399–416
Biswas SK, Mantovani A (2010) Macrophage plasticity and interaction with lymphocyte subsets: cancer as a paradigm. Nat Immunol 11:889–896
Tian W, Wang L, Yuan L, Duan W, Zhao W, Wang S, Zhang Q (2016) A prognostic risk model for patients with triple negative breast cancer based on stromal natural killer cells, tumor-associated macrophages and growth-arrest specific protein 6. Cancer Sci 107:882–889
Fang WB, Yao M, Brummer G, Acevedo D, Alhakamy N, Berkland C, Cheng N (2016) Targeted gene silencing of CCL2 inhibits triple negative breast cancer progression by blocking cancer stem cell renewal and M2 macrophage recruitment. Oncotarget 7:49349–49367
Wang H, Zhang Q, Kong H, Zeng Y, Hao M, Yu T, Peng J, Xu Z, Chen J, Shi H (2014b) Monocyte chemotactic protein-1 expression as a prognosic biomarker in patients with solid tumor: a meta analysis. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 7:3876–3886
Kitamura T, Qian BZ, Soong D, Cassetta L, Noy R, Sugano G, Kato Y, Li J, Pollard JW (2015) CCL2-induced chemokine cascade promotes breast cancer metastasis by enhancing retention of metastasis-associated macrophages. J Exp Med 212:1043–1059
Mitchem JB, Brennan DJ, Knolhoff BL, Belt BA, Zhu Y, Sanford DE, Belaygorod L, Carpenter D, Collins L, Piwnica-Worms D, Hewitt S, Udupi GM, Gallagher WM, Wegner C, West BL, Wang-Gillam A, Goedegebuure P, Linehan DC, DeNardo DG (2013) Targeting tumor-infiltrating macrophages decreases tumor-initiating cells, relieves immunosuppression, and improves chemotherapeutic responses. Cancer Res 73:1128–1141
Chen JH, Riazy M, Smith EM, Proud CG, Steinbrecher UP, Duronio V (2009) Oxidized LDL-mediated macrophage survival involves elongation factor-2 kinase. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 29:92–98
Zhang P, Riazy M, Gold M, Tsai SH, McNagny K, Proud C, Duronio V (2014) Impairing eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase activity decreases atherosclerotic plaque formation. Can J Cardiol 30:1684–1688
Xu Z, Zhao L, Yang X, Ma S, Ge Y, Liu Y, Liu S, Shi J, Zheng D (2016) Mmu-miR-125b overexpression suppresses NO production in activated macrophages by targeting eEF2K and CCNA2. BMC Cancer 16:252
Li S, Sun Y, Gao D (2013) Role of the nervous system in cancer metastasis. Oncol Lett 5:1101–1111
Kayahara M, Nakagawara H, Kitagawa H, Ohta T (2007) The nature of neural invasion by pancreatic cancer. Pancreas 35:218–223
Seifert P, Benedic M, Effert P (2002) Nerve fibers in tumors of the human urinary bladder. Virchows Arch 440:291–297
Ventura S, Pennefather J, Mitchelson F (2002) Cholinergic innervation and function in the prostate gland. Pharmacol Ther 94:93–112
Mitchell BS, Schumacher U, Stauber VV, Kaiserling E (1994) Are breast tumours innervated? Immunohistological investigations using antibodies against the neuronal marker protein gene product 9.5 (PGP 9.5) in benign and malignant breast lesions. Eur J Cancer 30A:1100–1103
Seifert P, Spitznas M (2002) Axons in human choroidal melanoma suggest the participation of nerves in the control of these tumors. Am J Ophthalmol 133:711–713
Jobling P, Pundavela J, Oliveira SM, Roselli S, Walker MM, Hondermarck H (2015) Nerve-cancer cell cross-talk: a novel promoter of tumor progression. Cancer Res 75:1777–1781
Connolly E, Braunstein S, Formenti S, Schneider RJ (2006) Hypoxia inhibits protein synthesis through a 4E-BP1 and elongation factor 2 kinase pathway controlled by mTOR and uncoupled in breast cancer cells. Mol Cell Biol 26:3955–3965
Kenney JW, Genheden M, Moon KM, Wang X, Foster LJ, Proud CG (2015) Eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase regulates the synthesis of microtubule-related proteins in neurons. J Neurochem 136:276–284
Neri D, Supuran CT (2011) Interfering with pH regulation in tumours as a therapeutic strategy. Nat Rev Drug Discov 10:767–777
Xie J, Mikolajek H, Pigott CR, Hooper KJ, Mellows T, Moore CE, Mohammed H, Werner JM, Thomas GJ, Proud CG (2015) Molecular mechanism for the control of eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase by pH: role in cancer cell survival. Mol Cell Biol 35:1805–1824
Yamaguchi H, Matsushita M, Nairn AC, Kuriyan J (2001) Crystal structure of the atypical protein kinase domain of a TRP channel with phosphotransferase activity. Mol Cell 7:1047–1057
Ye Q, Crawley SW, Yang Y, Cote GP, Jia Z (2010) Crystal structure of the alpha-kinase domain of dictyostelium myosin heavy chain kinase A. Sci Signal 3:ra17
De Gassart A, Demaria O, Panes R, Zaffalon L, Ryazanov AG, Gilliet M, Martinon F (2016) Pharmacological eEF2K activation promotes cell death and inhibits cancer progression. EMBO Rep 17:1471–1484
Gschwendt M, Müller HJ, Kielbassa K, Zang R, Kittstein W, Rincke G, Marks F (1994a) Rottlerin, a novel protein kinase inhibitor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 199:93–98
Gschwendt M, Kittstein W, Marks F (1994b) Elongation factor-2 kinase: effective inhibition by the novel protein kinase inhibitor rottlerin and relative insensitivity towards staurosporine. FEBS Lett 338:85–88
Davies SP, Reddy H, Caivano M, Cohen P (2000) Specificity and mechanism of action of some commonly used protein kinase inhibitors. Biochem J 351:95–105
Cho SI, Koketsu M, Ishihara H, Matsushita M, Nairn AC, Fukazawa H, Uehara Y (2000) Novel compounds, ‘1,3-selenazine derivatives’ as specific inhibitors of eukaryotic elongation factor-2 kinase. Biochim Biophys Acta 1475:207–215
Hori H, Nagasawa H, Ishibashi M, Uto Y, Hirata A, Saijo K, Ohkura K, Kirk KL, Uehara Y (2002) TX-1123: an antitumor 2-hydroxyarylidene-4-cyclopentene-1,3-dione as a protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor having low mitochondrial toxicity. Bioorg Med Chem 10:3257–3265
Arora S, Yang JM, Kinzy TG, Utsumi R, Okamoto T, Kitayama T, Ortiz PA, Hait WN (2003) Identification and characterization of an inhibitor of eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase against human cancer cell lines. Cancer Res 63:6894–6899
Chen Z, Gopalakrishnan SM, Bui MH, Soni NB, Warrior U, Johnson EF, Donnelly JB, Glaser KB (2011) 1-Benzyl-3-cetyl-2-methylimidazolium iodide (NH125) induces phosphorylation of eukaryotic elongation factor-2 (eEF2): a cautionary note on the anticancer mechanism of an eEF2 kinase inhibitor. J Biol Chem 286:43951–43958
Devkota AK, Tavares CD, Warthaka M, Abramczyk O, Marshall KD, Kaoud TS, Gorgulu K, Ozpolat B, Dalby KN (2012) Investigating the kinetic mechanism of inhibition of elongation factor 2 kinase by NH125: evidence of a common in vitro artifact. Biochemistry 51:2100–2112
Lockman JW, Reeder MD, Suzuki K, Ostanin K, Hoff R, Bhoite L, Austin H, Baichwal VJ, Willardsen JA (2010) Inhibition of eEF2-K by thieno[2,3-b]pyridine analogues. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 20:2283–2286
Guo Y, Zhao Y, Wang G, Chen Y, Jiang Y, Ouyang L, Liu B (2018) Design, synthesis and structure-activity relationship of a focused library of β-phenylalanine derivatives as novel eEF2K inhibitors with apoptosis-inducing mechanisms in breast cancer. Eur J Med Chem 143:402–418
Faller WJ, Jackson TJ, Knight JR, Ridgway RA, Jamieson T, Karim SA, Jones C, Radulescu S, Huels DJ, Myant KB, Dudek KM, Casey HA, Scopelliti A, Cordero JB, Vidal M, Pende M, Ryazanov AG, Sonenberg N, Meyuhas O, Hall MN, Bushell M, Willis AE, Sansom OJ (2015) mTORC1-mediated translational elongation limits intestinal tumour initiation and growth. Nature 517:497–500
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karakas, D., Ozpolat, B. Eukaryotic elongation factor-2 kinase (eEF2K) signaling in tumor and microenvironment as a novel molecular target. J Mol Med 98, 775–787 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-020-01917-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-020-01917-8