Abstract
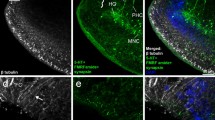
A Chinese praying mantis, Tenodera sinensis, was observed feeding on a living red-spotted newt, Notophthalmus viridescens. Specimens of that newt’s population are known to contain high concentrations of tetrodotoxin (TTX), a specific blocker of voltage-gated sodium channels. After experimental oral administration of a TTX-solution (1 mg/ml) to adult specimens of four mantis species, all survived high TTX concentrations (up to 30.8 μg/g body mass) as revealed by analysis of their body extracts, but they are rapidly killed by intra-abdominal injection of 1 μg TTX. The toxin was found to be gradually excreted with faeces. As demonstrated by monoclonal antibody-based immunohistochemical technique, TTX does not penetrate the mid-gut membrane, since it was localized only in the gut lumen, but not in the epithelial cells. This prevents the toxin to reach its target, the sodium channels of the insect’s nervous system, and enables the mantids to feed on toxic prey without risking poisoning.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Duffey SS (1980) Sequestration of plant natural products by insects. Annu Rev Entomol 25:447–477
Frick C, Wink M (1995) Uptake and sequestration of ouabain and other cardiac glycosides by Danaus plexippus (Lepidoptera: Danaidae): evidence for a carrier-mediated process. J Chem Ecol 21:557–575
Gall BG, Brodie ED III, Brodie ED Jr (2011) Survival and growth of the caddisfly Limnephilus flavastellus after predation on toxic eggs of the rough-skinned newt (Taricha granulosa). Can J Zool 89:483–489
Gall BG, Stokes AN, French SS, Brodie ED III, Brodie ED Jr (2012) Predatory caddisfly larvae sequester tetrodotoxin from their prey, eggs of the rough-skinned newt (Taricha granulosa). J Chem Ecol 38:1351–1357
Hanifin CT (2010) The chemical and evolutionary ecology of tetrodotoxin (TTX) toxicity in terrestrial vertebrates. Mar Drugs 8:577–593
Hanifin CT, Yotsu-Yamashita M, Yasumoto T, Brodie ED III, Brodie ED Jr (1999) Toxicity of dangerous prey: variation of tetrodotoxin levels within and among populations of the newt Taricha granulosa. J Chem Ecol 25:2161–2175
Hanifin CT, Brodie ED III, Brodie ED Jr (2003) Tetrodotoxin levels in eggs of the rough-skinned newt, Taricha granulosa, are correlated with female toxicity. J Chem Ecol 29:1729–1739
Hurlbert SH (1970) Predator responses to the vermillion-spotted newt (Notophthalmus viridescens). J Herpetol 4:47–55
Kao CY (1966) Tetrodotoxin, saxitoxin and their significance in the study of excitation phenomena. Pharmacol Rev 18:997–1049
Kawatsu K, Hamano Y, Yoda T, Terano Y, Shibata T (1997) Rapid and highly sensitive enzyme immunoassay for quantitative determination of tetrodotoxin. Jpn J Med Sci Biol 50:133–150
Kono M, Matsui T, Furukawa K, Takase T, Yamamori K, Kaneda H, Aoki D, Jang J-H, Yotsu-Yamashita M (2008) Examination of transformation among tetrodotoxin and its analogs in the living cultured juvenile puffer fish, kusafugu, Fugu niphobles, by intramuscular administration. Toxicon 52:714–720
Marion ZH, Hay ME (2011) Chemical defense of the eastern newt (Notophthalmus viridescens): variation in efficiency against different consumers and in different habitats. PlOSOne 6(e27581):1–9
Mebs D, Arakawa O, Yotsu-Yamashita M (2010) Tissue distribution of tetrodotoxin in the red-spotted newt Notophthalmus viridescens. Toxicon 55:1353–1357
Narahashi T (1965) The properties of insect axons. Adv Insect Physiol 1:175–256
Narahashi T, Moore JW, Scott WR (1964) Tetrodotoxin blockage of sodium conductance increase in lobster giant axons. J Gen Physiol 47:965–974
Opitz SEW, Müller C (2009) Plant chemistry and insect sequestration. Chemoecology 19:117–154
Pauron D, Barhanin J, Lazdunski M (1985) The voltage-dependent Na+ channel of insect nervous system identified by receptor sites for tetrodotoxin, and scorpion and sea anemone toxins. Biochem Biophys Res. Comm 131:1226–1233
Pelhate M, Sattelle DB (1982) Pharmcological properties of insect axons: a review. J Insect Physiol 28:889–903
Rafter JL, Agrawal AA, Preisser EL (2013) Chinese mantis gut toxic monarch caterpillars: avoidance of prey defence? Ecol Entomol 38:76–82
Reitze M, Nentwig W (1991) Comparative investigations into the feeding ecology of six Mantodea species. Oecologia 86:568–574
Shoji Y, Yotsu-Yamashita M, Miyazawa T, Yasumoto T (2001) Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry of tetrodotoxin and its analogs: liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry, tandem mass spectrometry, and liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Biochem 290:10–17
Snyder W, Evans E (2006) Ecological effects of invasive arthropod generalist predators. Annu Rev Ecol Sytematics 37:95–122
Tsuda K, Ikuma S, Kawamura M, Tachikawa R, Sakai K, Tamura C, Amakasu O (1964) Tetrodotoxin. VII. On the structure of tetrodotoxin and its derivatives. Chem Pharm Bull 12:1357–1374
Yasumoto T, Michishita T (1985) Fluorometric determination of tetrodotoxin by high performance liquid chromatography. Agric Biol Chem 49:3077–3080
Yasumoto T, Yotsu-Yamashita M (1996) Chemical and etiological studies on tetrodotoxin and its analogs. J Toxicol Toxin Rev 15:81–90
Yotsu M, Iorizzi M, Yasumoto T (1990) Distribution of tetrodotoxin, 6-epitetrodotoxin and 11-deoxytetrodotoxin in newts. Toxicon 28:238–241
Yotsu-Yamashita M, Mebs D (2001) The levels of tetrodotoxin and its analogue 6-epitetrodotoxin in the red-spotted newt, Notophthalmus viridescens. Toxicon 39:1261–1263
Yotsu-Yamashita M, Mebs D (2003) Occurrence of 11-oxotetrodotoxin in the red-spotted newt, Notophthalmus viridescens, and further studies on the levels of tetrodotoxin and its analogues in the newt’s efts. Toxicon 41:893–897
Yotsu-Yamashita M, Mebs D, Kwet A, Schneider M (2007) Tetrodotoxin and its analogue 6-epitetrodotoxin in newts (Triturus spp.; Urodela, Salamandridae) from southern Germany. Toxicon 50:306–309
Yotsu-Yamashita M, Gilhen J, Russell RW, Krysko KL, Melaun C, Kurz A, Kauferstein S, Kordis D, Mebs D (2012) Variability of tetrodotoxin and of its analogues in the red-spotted newt, Notophthalmus viridescens (Amphibia: Urodela: Salamandridae). Toxicon 59:257–264
Yotsu-Yamashita M, Abe Y, Kudo Y, Ritson-Williams R, Paul JV, Konoki K, Cho Y, Adachi M, Imazu T, Nishikawa T, Isobe M (2013) First identification of 5,11-dideoxytetrodotoxin in marine animals, and characterization of major fragment ions of tetrodotoxin and its analogs by high resolution ESI-MS/MS. Marine Drugs 11:2799–2813
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Robert S. Mulvihill, National Aviary, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, for making his observation and photos available. Chrstine Elbert performed excellent immunohistochemical work. This work was partially supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) KAKENHI Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (B) no. 26292057 to M.Y.Y.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling Editor: Michael Heethoff.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mebs, D., Yotsu-Yamashita, M. & Arakawa, O. The praying mantis (Mantodea) as predator of the poisonous red-spotted newt Notophthalmus viridescens (Amphibia: Urodela: Salamandridae). Chemoecology 26, 121–126 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00049-016-0211-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00049-016-0211-3