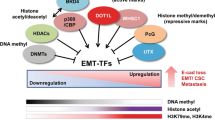
Abstract
Epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) is an essential process for morphogenesis and organ development which reversibly enables polarized epithelial cells to lose their epithelial characteristics and to acquire mesenchymal properties. It is now evident that the aberrant activation of EMT is also a critical mechanism to endow epithelial cancer cells with migratory and invasive capabilities associated with metastatic competence. This dedifferentiation program is mediated by a small cohort of pleiotropic transcription factors which orchestrate a complex array of epigenetic mechanisms for the wide-spread changes in gene expression. Here, we review major epigenetic mechanisms with an emphasis on histone modifications and discuss their implications in EMT and tumor progression. We also highlight mechanisms underlying transcription regulation concerted by various chromatin-modifying proteins and EMT-inducing transcription factors at different molecular layers. Owing to the reversible nature of epigenetic modifications, a thorough understanding of their functions in EMT will not only provide new insights into our knowledge of cancer progression and metastasis, but also facilitate the development of diagnostic and therapeutic strategies for human malignancy.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nieto MA (2011) The ins and outs of the epithelial to mesenchymal transition in health and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 27:347–376. doi:10.1146/annurev-cellbio-092910-154036
Kalluri R (2009) EMT: when epithelial cells decide to become mesenchymal-like cells. J Clin Invest 119(6):1417–1419. doi:10.1172/JCI39675
Kalluri R, Weinberg RA (2009) The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest 119(6):1420–1428. doi:10.1172/JCI39104
Yang J, Weinberg RA (2008) Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: at the crossroads of development and tumor metastasis. Dev Cell 14(6):818–829. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2008.05.009
Ye X, Weinberg RA (2015) Epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity: a central regulator of cancer progression. Trends Cell Biol 25(11):675–686. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2015.07.012
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY, Nieto MA (2009) Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease. Cell 139(5):871–890. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.11.007
Polyak K, Weinberg RA (2009) Transitions between epithelial and mesenchymal states: acquisition of malignant and stem cell traits. Nat Rev Cancer 9(4):265–273. doi:10.1038/nrc2620
Thiery JP, Sleeman JP (2006) Complex networks orchestrate epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7(2):131–142. doi:10.1038/nrm1835
Zheng H, Kang Y (2014) Multilayer control of the EMT master regulators. Oncogene 33(14):1755–1763. doi:10.1038/onc.2013.128
De Craene B, Berx G (2013) Regulatory networks defining EMT during cancer initiation and progression. Nat Rev Cancer 13(2):97–110. doi:10.1038/nrc3447
Peinado H, Olmeda D, Cano A (2007) Snail, Zeb and bHLH factors in tumour progression: an alliance against the epithelial phenotype? Nat Rev Cancer 7(6):415–428. doi:10.1038/nrc2131
Tam WL, Weinberg RA (2013) The epigenetics of epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity in cancer. Nat Med 19(11):1438–1449. doi:10.1038/nm.3336
Onder TT, Gupta PB, Mani SA, Yang J, Lander ES, Weinberg RA (2008) Loss of E-cadherin promotes metastasis via multiple downstream transcriptional pathways. Cancer Res 68(10):3645–3654. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-2938
Schmalhofer O, Brabletz S, Brabletz T (2009) E-cadherin, beta-catenin, and ZEB1 in malignant progression of cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev 28(1–2):151–166. doi:10.1007/s10555-008-9179-y
Casas E, Kim J, Bendesky A, Ohno-Machado L, Wolfe CJ, Yang J (2011) Snail2 is an essential mediator of Twist1-induced epithelial mesenchymal transition and metastasis. Cancer Res 71(1):245–254. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-2330
Dave N, Guaita-Esteruelas S, Gutarra S, Frias A, Beltran M, Peiro S, de Herreros AG (2011) Functional cooperation between Snail1 and twist in the regulation of ZEB1 expression during epithelial to mesenchymal transition. J Biol Chem 286(14):12024–12032. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.168625
Felsenfeld G (2014) A brief history of epigenetics. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a018200
Kouzarides T (2007) Chromatin modifications and their function. Cell 128(4):693–705. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.02.005
Ting AH, McGarvey KM, Baylin SB (2006) The cancer epigenome-components and functional correlates. Genes Dev 20(23):3215–3231. doi:10.1101/gad.1464906
Clapier CR, Cairns BR (2009) The biology of chromatin remodeling complexes. Annu Rev Biochem 78:273–304. doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.77.062706.153223
Wang GG, Allis CD, Chi P (2007) Chromatin remodeling and cancer, Part II: ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling. Trends Mol Med 13(9):373–380. doi:10.1016/j.molmed.2007.07.004
Fujita N, Jaye DL, Kajita M, Geigerman C, Moreno CS, Wade PA (2003) MTA3, a Mi-2/NuRD complex subunit, regulates an invasive growth pathway in breast cancer. Cell 113(2):207–219
Gonzalez-Perez A, Jene-Sanz A, Lopez-Bigas N (2013) The mutational landscape of chromatin regulatory factors across 4623 tumor samples. Genome Biol 14(9):r106. doi:10.1186/gb-2013-14-9-r106
Weissman B, Knudsen KE (2009) Hijacking the chromatin remodeling machinery: impact of SWI/SNF perturbations in cancer. Cancer Res 69(21):8223–8230. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-2166
Sanchez-Tillo E, Lazaro A, Torrent R, Cuatrecasas M, Vaquero EC, Castells A, Engel P, Postigo A (2010) ZEB1 represses E-cadherin and induces an EMT by recruiting the SWI/SNF chromatin-remodeling protein BRG1. Oncogene 29(24):3490–3500. doi:10.1038/onc.2010.102
Jordan NV, Prat A, Abell AN, Zawistowski JS, Sciaky N, Karginova OA, Zhou B, Golitz BT, Perou CM, Johnson GL (2013) SWI/SNF chromatin-remodeling factor Smarcd3/Baf60c controls epithelial-mesenchymal transition by inducing Wnt5a signaling. Mol Cell Biol 33(15):3011–3025. doi:10.1128/MCB.01443-12
Roy N, Malik S, Villanueva KE, Urano A, Lu X, Von Figura G, Seeley ES, Dawson DW, Collisson EA, Hebrok M (2015) Brg1 promotes both tumor-suppressive and oncogenic activities at distinct stages of pancreatic cancer formation. Genes Dev 29(6):658–671. doi:10.1101/gad.256628.114
Kadoch C, Crabtree GR (2015) Mammalian SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complexes and cancer: mechanistic insights gained from human genomics. Sci Adv 1(5):e1500447. doi:10.1126/sciadv.1500447
Bergman Y, Cedar H (2013) DNA methylation dynamics in health and disease. Nat Struct Mol Biol 20(3):274–281. doi:10.1038/nsmb.2518
Cedar H, Bergman Y (2012) Programming of DNA methylation patterns. Annu Rev Biochem 81:97–117. doi:10.1146/annurev-biochem-052610-091920
Sandoval J, Esteller M (2012) Cancer epigenomics: beyond genomics. Curr Opin Genet Dev 22(1):50–55. doi:10.1016/j.gde.2012.02.008
Carmona FJ, Davalos V, Vidal E, Gomez A, Heyn H, Hashimoto Y, Vizoso M, Martinez-Cardus A, Sayols S, Ferreira HJ, Sanchez-Mut JV, Moran S, Margeli M, Castella E, Berdasco M, Stefansson OA, Eyfjord JE, Gonzalez-Suarez E, Dopazo J, Orozco M, Gut IG, Esteller M (2014) A comprehensive DNA methylation profile of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Res 74(19):5608–5619. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-3659
McDonald OG, Wu H, Timp W, Dodsi A, Feinberg AP (2011) Genome-scale epigenetic reprogramming during epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Nat Struct Mol Biol 18(8):867–874. doi:10.1038/nsmb.2084
Lombaerts M, van Wezel T, Philippo K, Dierssen JW, Zimmerman RM, Oosting J, van Eijk R, Eilers PH, van de Water B, Cornelisse CJ, Cleton-Jansen AM (2006) E-cadherin transcriptional downregulation by promoter methylation but not mutation is related to epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer cell lines. Brit J Cancer 94(5):661–671. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6602996
Reinhold WC, Reimers MA, Maunakea AK, Kim S, Lababidi S, Scherf U, Shankavaram UT, Ziegler MS, Stewart C, Kouros-Mehr H, Cui H, Dolginow D, Scudiero DA, Pommier YG, Munroe DJ, Feinberg AP, Weinstein JN (2007) Detailed DNA methylation profiles of the E-cadherin promoter in the NCI-60 cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther 6(2):391–403. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-0609
Dong C, Wu Y, Yao J, Wang Y, Yu Y, Rychahou PG, Evers BM, Zhou BP (2012) G9a interacts with snail and is critical for snail-mediated E-cadherin repression in human breast cancer. J Clin Invest 122(4):1469–1486. doi:10.1172/JCI57349
Fukagawa A, Ishii H, Miyazawa K, Saitoh M (2015) deltaEF1 associates with DNMT1 and maintains DNA methylation of the E-cadherin promoter in breast cancer cells. Cancer medicine 4(1):125–135. doi:10.1002/cam4.347
Papageorgis P, Lambert AW, Ozturk S, Gao F, Pan H, Manne U, Alekseyev YO, Thiagalingam A, Abdolmaleky HM, Lenburg M, Thiagalingam S (2010) Smad signaling is required to maintain epigenetic silencing during breast cancer progression. Cancer Res 70(3):968–978. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-1872
Tan EJ, Kahata K, Idas O, Thuault S, Heldin CH, Moustakas A (2015) The high mobility group A2 protein epigenetically silences the Cdh1 gene during epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Nucleic Acids Res 43(1):162–178. doi:10.1093/nar/gku1293
Davalos V, Moutinho C, Villanueva A, Boque R, Silva P, Carneiro F, Esteller M (2012) Dynamic epigenetic regulation of the microRNA-200 family mediates epithelial and mesenchymal transitions in human tumorigenesis. Oncogene 31(16):2062–2074. doi:10.1038/onc.2011.383
Vrba L, Jensen TJ, Garbe JC, Heimark RL, Cress AE, Dickinson S, Stampfer MR, Futscher BW (2010) Role for DNA methylation in the regulation of miR-200c and miR-141 expression in normal and cancer cells. PLoS One 5(1):e8697. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0008697
Wiklund ED, Bramsen JB, Hulf T, Dyrskjot L, Ramanathan R, Hansen TB, Villadsen SB, Gao S, Ostenfeld MS, Borre M, Peter ME, Orntoft TF, Kjems J, Clark SJ (2011) Coordinated epigenetic repression of the miR-200 family and miR-205 in invasive bladder cancer. Int J Cancer 128(6):1327–1334. doi:10.1002/ijc.25461
Ning X, Shi Z, Liu X, Zhang A, Han L, Jiang K, Kang C, Zhang Q (2015) DNMT1 and EZH2 mediated methylation silences the microRNA-200b/a/429 gene and promotes tumor progression. Cancer Lett 359(2):198–205. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2015.01.005
Yu Y, Wu J, Guan L, Qi L, Tang Y, Ma B, Zhan J, Wang Y, Fang W, Zhang H (2013) Kindlin 2 promotes breast cancer invasion via epigenetic silencing of the microRNA200 gene family. Int J Cancer 133(6):1368–1379. doi:10.1002/ijc.28151
Ley TJ, Ding L, Walter MJ, McLellan MD, Lamprecht T, Larson DE, Kandoth C, Payton JE, Baty J, Welch J, Harris CC, Lichti CF, Townsend RR, Fulton RS, Dooling DJ, Koboldt DC, Schmidt H, Zhang Q, Osborne JR, Lin L, O’Laughlin M, McMichael JF, Delehaunty KD, McGrath SD, Fulton LA, Magrini VJ, Vickery TL, Hundal J, Cook LL, Conyers JJ, Swift GW, Reed JP, Alldredge PA, Wylie T, Walker J, Kalicki J, Watson MA, Heath S, Shannon WD, Varghese N, Nagarajan R, Westervelt P, Tomasson MH, Link DC, Graubert TA, DiPersio JF, Mardis ER, Wilson RK (2010) DNMT3A mutations in acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 363(25):2424–2433. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1005143
Yan XJ, Xu J, Gu ZH, Pan CM, Lu G, Shen Y, Shi JY, Zhu YM, Tang L, Zhang XW, Liang WX, Mi JQ, Song HD, Li KQ, Chen Z, Chen SJ (2011) Exome sequencing identifies somatic mutations of DNA methyltransferase gene DNMT3A in acute monocytic leukemia. Nat Genet 43(4):309–315. doi:10.1038/ng.788
Yang L, Rau R, Goodell MA (2015) DNMT3A in haematological malignancies. Nat Rev Cancer 15(3):152–165. doi:10.1038/nrc3895
Gao Q, Steine EJ, Barrasa MI, Hockemeyer D, Pawlak M, Fu D, Reddy S, Bell GW, Jaenisch R (2011) Deletion of the de novo DNA methyltransferase Dnmt3a promotes lung tumor progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(44):18061–18066. doi:10.1073/pnas.1114946108
Sansom OJ, Maddison K, Clarke AR (2007) Mechanisms of disease: methyl-binding domain proteins as potential therapeutic targets in cancer. Nat Clin Pract Oncol 4(5):305–315. doi:10.1038/ncponc0812
McCabe MT, Brandes JC, Vertino PM (2009) Cancer DNA methylation: molecular mechanisms and clinical implications. Clin Cancer Res 15(12):3927–3937. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-2784
Koizume S, Tachibana K, Sekiya T, Hirohashi S, Shiraishi M (2002) Heterogeneity in the modification and involvement of chromatin components of the CpG island of the silenced human CDH1 gene in cancer cells. Nucleic Acids Res 30(21):4770–4780
Lai AY, Wade PA (2011) Cancer biology and NuRD: a multifaceted chromatin remodelling complex. Nat Rev Cancer 11(8):588–596. doi:10.1038/nrc3091
Fu J, Qin L, He T, Qin J, Hong J, Wong J, Liao L, Xu J (2011) The TWIST/Mi2/NuRD protein complex and its essential role in cancer metastasis. Cell Res 21(2):275–289. doi:10.1038/cr.2010.118
Xu J, Zhu W, Xu W, Yao W, Zhang B, Xu Y, Ji S, Liu C, Long J, Ni Q, Yu X (2013) Up-regulation of MBD1 promotes pancreatic cancer cell epithelial-mesenchymal transition and invasion by epigenetic down-regulation of E-cadherin. Curr Mol Med 13(3):387–400
Darwanto A, Kitazawa R, Maeda S, Kitazawa S (2003) MeCP2 and promoter methylation cooperatively regulate E-cadherin gene expression in colorectal carcinoma. Cancer Sci 94(5):442–447
Jones J, Wang H, Karanam B, Theodore S, Dean-Colomb W, Welch DR, Grizzle W, Yates C (2014) Nuclear localization of Kaiso promotes the poorly differentiated phenotype and EMT in infiltrating ductal carcinomas. Clin Exp Metastasis 31(5):497–510. doi:10.1007/s10585-014-9644-7
Jones J, Wang H, Zhou J, Hardy S, Turner T, Austin D, He Q, Wells A, Grizzle WE, Yates C (2012) Nuclear Kaiso indicates aggressive prostate cancers and promotes migration and invasiveness of prostate cancer cells. Am J Pathol 181(5):1836–1846. doi:10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.08.008
Wang H, Liu W, Black S, Turner O, Daniel JM, Dean-Colomb W, He QP, Davis M, Yates C (2016) Kaiso, a transcriptional repressor, promotes cell migration and invasion of prostate cancer cells through regulation of miR-31 expression. Oncotarget 7(5):5677–5689. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.6801
Kohli RM, Zhang Y (2013) TET enzymes, TDG and the dynamics of DNA demethylation. Nature 502(7472):472–479. doi:10.1038/nature12750
Williams K, Christensen J, Pedersen MT, Johansen JV, Cloos PA, Rappsilber J, Helin K (2011) TET1 and hydroxymethylcytosine in transcription and DNA methylation fidelity. Nature 473(7347):343–348. doi:10.1038/nature10066
Peinado H, Ballestar E, Esteller M, Cano A (2004) Snail mediates E-cadherin repression by the recruitment of the Sin3A/histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1)/HDAC2 complex. Mol Cell Biol 24(1):306–319
Tsai YP, Chen HF, Chen SY, Cheng WC, Wang HW, Shen ZJ, Song C, Teng SC, He C, Wu KJ (2014) TET1 regulates hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition by acting as a co-activator. Genome Biol 15(12):513. doi:10.1186/s13059-014-0513-0
Auerkari EI (2006) Methylation of tumor suppressor genes p16(INK4a), p27(Kip1) and E-cadherin in carcinogenesis. Oral Oncol 42(1):5–13. doi:10.1016/j.oraloncology.2005.03.016
Corn PG, Smith BD, Ruckdeschel ES, Douglas D, Baylin SB, Herman JG (2000) E-cadherin expression is silenced by 5′ CpG island methylation in acute leukemia. Clin Cancer Res 6(11):4243–4248
Graff JR, Gabrielson E, Fujii H, Baylin SB, Herman JG (2000) Methylation patterns of the E-cadherin 5′ CpG island are unstable and reflect the dynamic, heterogeneous loss of E-cadherin expression during metastatic progression. J Biol Chem 275(4):2727–2732
Nam JS, Ino Y, Kanai Y, Sakamoto M, Hirohashi S (2004) 5-Aza-2′-deoxycytidine restores the E-cadherin system in E-cadherin-silenced cancer cells and reduces cancer metastasis. Clin Exp Metastasis 21(1):49–56
Daskalakis M, Nguyen TT, Nguyen C, Guldberg P, Kohler G, Wijermans P, Jones PA, Lubbert M (2002) Demethylation of a hypermethylated P15/INK4B gene in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome by 5-Aza-2′-deoxycytidine (decitabine) treatment. Blood 100(8):2957–2964. doi:10.1182/blood.V100.8.2957
Eden A, Gaudet F, Waghmare A, Jaenisch R (2003) Chromosomal instability and tumors promoted by DNA hypomethylation. Science (New York, NY) 300(5618):455. doi:10.1126/science.1083557
Gaudet F, Hodgson JG, Eden A, Jackson-Grusby L, Dausman J, Gray JW, Leonhardt H, Jaenisch R (2003) Induction of tumors in mice by genomic hypomethylation. Science (New York, NY) 300(5618):489–492. doi:10.1126/science.1083558
Jenuwein T, Allis CD (2001) Translating the histone code. Science (New York, NY) 293(5532):1074–1080. doi:10.1126/science.1063127
Strahl BD, Allis CD (2000) The language of covalent histone modifications. Nature 403(6765):41–45. doi:10.1038/47412
Lee KK, Workman JL (2007) Histone acetyltransferase complexes: one size doesn’t fit all. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8(4):284–295. doi:10.1038/nrm2145
Hao S, He W, Li Y, Ding H, Hou Y, Nie J, Hou FF, Kahn M, Liu Y (2011) Targeted inhibition of beta-catenin/CBP signaling ameliorates renal interstitial fibrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol 22(9):1642–1653. doi:10.1681/ASN.2010101079
Zhou B, Liu Y, Kahn M, Ann DK, Han A, Wang H, Nguyen C, Flodby P, Zhong Q, Krishnaveni MS, Liebler JM, Minoo P, Crandall ED, Borok Z (2012) Interactions between beta-catenin and transforming growth factor-beta signaling pathways mediate epithelial-mesenchymal transition and are dependent on the transcriptional co-activator cAMP-response element-binding protein (CREB)-binding protein (CBP). J Biol Chem 287(10):7026–7038. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.276311
Mizuguchi Y, Specht S, Lunz JG 3rd, Isse K, Corbitt N, Takizawa T, Demetris AJ (2012) Cooperation of p300 and PCAF in the control of microRNA 200c/141 transcription and epithelial characteristics. PLoS One 7(2):e32449. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0032449
Dhasarathy A, Phadke D, Mav D, Shah RR, Wade PA (2011) The transcription factors Snail and Slug activate the transforming growth factor-beta signaling pathway in breast cancer. PLoS One 6(10):e26514. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0026514
Kapoor-Vazirani P, Kagey JD, Powell DR, Vertino PM (2008) Role of hMOF-dependent histone H4 lysine 16 acetylation in the maintenance of TMS1/ASC gene activity. Cancer Res 68(16):6810–6821. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-0141
Liu YN, Lee WW, Wang CY, Chao TH, Chen Y, Chen JH (2005) Regulatory mechanisms controlling human E-cadherin gene expression. Oncogene 24(56):8277–8290. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1208991
Pruitt K, Zinn RL, Ohm JE, McGarvey KM, Kang SH, Watkins DN, Herman JG, Baylin SB (2006) Inhibition of SIRT1 reactivates silenced cancer genes without loss of promoter DNA hypermethylation. PLoS Genet 2(3):e40. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.0020040
Strobl-Mazzulla PH, Bronner ME (2012) A PHD12-Snail2 repressive complex epigenetically mediates neural crest epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. J Cell Biol 198(6):999–1010. doi:10.1083/jcb.201203098
Bansal N, Petrie K, Christova R, Chung CY, Leibovitch BA, Howell L, Gil V, Sbirkov Y, Lee E, Wexler J, Ariztia EV, Sharma R, Zhu J, Bernstein E, Zhou MM, Zelent A, Farias E, Waxman S (2015) Targeting the SIN3A-PF1 interaction inhibits epithelial to mesenchymal transition and maintenance of a stem cell phenotype in triple negative breast cancer. Oncotarget 6(33):34087–34105. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.6048
Tripathi MK, Misra S, Khedkar SV, Hamilton N, Irvin-Wilson C, Sharan C, Sealy L, Chaudhuri G (2005) Regulation of BRCA2 gene expression by the SLUG repressor protein in human breast cells. J Biol Chem 280(17):17163–17171. doi:10.1074/jbc.M501375200
Shi Y, Sawada J, Sui G, el Affar B, Whetstine JR, Lan F, Ogawa H, Luke MP, Nakatani Y, Shi Y (2003) Coordinated histone modifications mediated by a CtBP co-repressor complex. Nature 422(6933):735–738. doi:10.1038/nature01550
Aghdassi A, Sendler M, Guenther A, Mayerle J, Behn CO, Heidecke CD, Friess H, Buchler M, Evert M, Lerch MM, Weiss FU (2012) Recruitment of histone deacetylases HDAC1 and HDAC2 by the transcriptional repressor ZEB1 downregulates E-cadherin expression in pancreatic cancer. Gut 61(3):439–448. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2011-300060
Byles V, Zhu L, Lovaas JD, Chmilewski LK, Wang J, Faller DV, Dai Y (2012) SIRT1 induces EMT by cooperating with EMT transcription factors and enhances prostate cancer cell migration and metastasis. Oncogene 31(43):4619–4629. doi:10.1038/onc.2011.612
Roche J, Nasarre P, Gemmill R, Baldys A, Pontis J, Korch C, Guilhot J, Ait-Si-Ali S, Drabkin H (2013) Global decrease of histone H3K27 acetylation in ZEB1-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition in lung cancer cells. Cancers 5(2):334–356. doi:10.3390/cancers5020334
He J, Shen S, Lu W, Zhou Y, Hou Y, Zhang Y, Jiang Y, Liu H, Shao Y (2016) HDAC1 promoted migration and invasion binding with TCF12 by promoting EMT progress in gallbladder cancer. Oncotarget. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.8740
Zhang X, Yuan Z, Zhang Y, Yong S, Salas-Burgos A, Koomen J, Olashaw N, Parsons JT, Yang XJ, Dent SR, Yao TP, Lane WS, Seto E (2007) HDAC6 modulates cell motility by altering the acetylation level of cortactin. Mol Cell 27(2):197–213. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2007.05.033
Zhang Y, Zhang M, Dong H, Yong S, Li X, Olashaw N, Kruk PA, Cheng JQ, Bai W, Chen J, Nicosia SV, Zhang X (2009) Deacetylation of cortactin by SIRT1 promotes cell migration. Oncogene 28(3):445–460. doi:10.1038/onc.2008.388
Shah P, Gau Y, Sabnis G (2014) Histone deacetylase inhibitor entinostat reverses epithelial to mesenchymal transition of breast cancer cells by reversing the repression of E-cadherin. Breast Cancer Res Treat 143(1):99–111. doi:10.1007/s10549-013-2784-7
Srivastava RK, Kurzrock R, Shankar S (2010) MS-275 sensitizes TRAIL-resistant breast cancer cells, inhibits angiogenesis and metastasis, and reverses epithelial-mesenchymal transition in vivo. Mol Cancer Ther 9(12):3254–3266. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-10-0582
Takai N, Desmond JC, Kumagai T, Gui D, Said JW, Whittaker S, Miyakawa I, Koeffler HP (2004) Histone deacetylase inhibitors have a profound antigrowth activity in endometrial cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 10(3):1141–1149
Ye Y, Xiao Y, Wang W, Yearsley K, Gao JX, Shetuni B, Barsky SH (2010) ERalpha signaling through slug regulates E-cadherin and EMT. Oncogene 29(10):1451–1462. doi:10.1038/onc.2009.433
West AC, Johnstone RW (2014) New and emerging HDAC inhibitors for cancer treatment. J Clin Invest 124(1):30–39. doi:10.1172/JCI69738
Meidhof S, Brabletz S, Lehmann W, Preca BT, Mock K, Ruh M, Schuler J, Berthold M, Weber A, Burk U, Lubbert M, Puhr M, Culig Z, Wellner U, Keck T, Bronsert P, Kusters S, Hopt UT, Stemmler MP, Brabletz T (2015) ZEB1-associated drug resistance in cancer cells is reversed by the class I HDAC inhibitor mocetinostat. EMBO Mol Med 7(6):831–847. doi:10.15252/emmm.201404396
Krumm A, Barckhausen C, Kucuk P, Tomaszowski KH, Loquai C, Fahrer J, Kramer OH, Kaina B, Roos WP (2016) Enhanced histone deacetylase activity in malignant melanoma provokes RAD51 and FANCD2-triggered drug resistance. Cancer Res 76(10):3067–3077. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-2680
Kristensen LS, Nielsen HM, Hansen LL (2009) Epigenetics and cancer treatment. Eur J Pharmacol 625(1–3):131–142. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2009.10.011
Gilbert J, Gore SD, Herman JG, Carducci MA (2004) The clinical application of targeting cancer through histone acetylation and hypomethylation. Clin Cancer Res 10(14):4589–4596. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-03-0297
Gore SD, Baylin S, Sugar E, Carraway H, Miller CB, Carducci M, Grever M, Galm O, Dauses T, Karp JE, Rudek MA, Zhao M, Smith BD, Manning J, Jiemjit A, Dover G, Mays A, Zwiebel J, Murgo A, Weng LJ, Herman JG (2006) Combined DNA methyltransferase and histone deacetylase inhibition in the treatment of myeloid neoplasms. Cancer Res 66(12):6361–6369. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-0080
Jiang GM, Wang HS, Zhang F, Zhang KS, Liu ZC, Fang R, Wang H, Cai SH, Du J (2012) Histone deacetylase inhibitor induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transitions via up-regulation of Snail facilitates cancer progression. Biochim Biophys Acta 1833(3):663–671. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2012.12.002
Kong D, Ahmad A, Bao B, Li Y, Banerjee S, Sarkar FH (2012) Histone deacetylase inhibitors induce epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in prostate cancer cells. PLoS One 7(9):e45045. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0045045
Martin C, Zhang Y (2005) The diverse functions of histone lysine methylation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6(11):838–849. doi:10.1038/nrm1761
Butler JS, Dent SY (2013) The role of chromatin modifiers in normal and malignant hematopoiesis. Blood 121(16):3076–3084. doi:10.1182/blood-2012-10-451237
Zhang L, Deng L, Chen F, Yao Y, Wu B, Wei L, Mo Q, Song Y (2014) Inhibition of histone H3K79 methylation selectively inhibits proliferation, self-renewal and metastatic potential of breast cancer. Oncotarget 5(21):10665–10677. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.2496
Cho MH, Park JH, Choi HJ, Park MK, Won HY, Park YJ, Lee CH, Oh SH, Song YS, Kim HS, Oh YH, Lee JY, Kong G (2015) DOT1L cooperates with the c-Myc-p300 complex to epigenetically derepress CDH1 transcription factors in breast cancer progression. Nat Commun 6:7821. doi:10.1038/ncomms8821
Gao Y, Zhao Y, Zhang J, Lu Y, Liu X, Geng P, Huang B, Zhang Y, Lu J (2016) The dual function of PRMT1 in modulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cellular senescence in breast cancer cells through regulation of ZEB1. Sci Rep 6:19874. doi:10.1038/srep19874
Shi Y, Lan F, Matson C, Mulligan P, Whetstine JR, Cole PA, Casero RA, Shi Y (2004) Histone demethylation mediated by the nuclear amine oxidase homolog LSD1. Cell 119(7):941–953. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2004.12.012
Hojfeldt JW, Agger K, Helin K (2013) Histone lysine demethylases as targets for anticancer therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov 12(12):917–930. doi:10.1038/nrd4154
Lee MG, Wynder C, Cooch N, Shiekhattar R (2005) An essential role for CoREST in nucleosomal histone 3 lysine 4 demethylation. Nature 437(7057):432–435. doi:10.1038/nature04021
Shi YJ, Matson C, Lan F, Iwase S, Baba T, Shi Y (2005) Regulation of LSD1 histone demethylase activity by its associated factors. Mol Cell 19(6):857–864. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2005.08.027
Lin Y, Wu Y, Li J, Dong C, Ye X, Chi YI, Evers BM, Zhou BP (2010) The SNAG domain of Snail1 functions as a molecular hook for recruiting lysine-specific demethylase 1. EMBO J 29(11):1803–1816. doi:10.1038/emboj.2010.63
Wang Y, Zhang H, Chen Y, Sun Y, Yang F, Yu W, Liang J, Sun L, Yang X, Shi L, Li R, Li Y, Zhang Y, Li Q, Yi X, Shang Y (2009) LSD1 is a subunit of the NuRD complex and targets the metastasis programs in breast cancer. Cell 138(4):660–672. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.05.050
Metzger E, Wissmann M, Yin N, Muller JM, Schneider R, Peters AH, Gunther T, Buettner R, Schule R (2005) LSD1 demethylates repressive histone marks to promote androgen-receptor-dependent transcription. Nature 437(7057):436–439. doi:10.1038/nature04020
Wang J, Scully K, Zhu X, Cai L, Zhang J, Prefontaine GG, Krones A, Ohgi KA, Zhu P, Garcia-Bassets I, Liu F, Taylor H, Lozach J, Jayes FL, Korach KS, Glass CK, Fu XD, Rosenfeld MG (2007) Opposing LSD1 complexes function in developmental gene activation and repression programmes. Nature 446(7138):882–887. doi:10.1038/nature05671
Teng YC, Lee CF, Li YS, Chen YR, Hsiao PW, Chan MY, Lin FM, Huang HD, Chen YT, Jeng YM, Hsu CH, Yan Q, Tsai MD, Juan LJ (2013) Histone demethylase RBP2 promotes lung tumorigenesis and cancer metastasis. Cancer Res 73(15):4711–4721. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-3165
Cao J, Liu Z, Cheung WK, Zhao M, Chen SY, Chan SW, Booth CJ, Nguyen DX, Yan Q (2014) Histone demethylase RBP2 is critical for breast cancer progression and metastasis. Cell Rep 6(5):868–877. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2014.02.004
Liang X, Zeng J, Wang L, Shen L, Ma X, Li S, Wu Y, Ma L, Ci X, Guo Q, Jia M, Shen H, Sun Y, Liu Z, Liu S, Li W, Yu H, Chen C, Jia J (2015) Histone demethylase RBP2 promotes malignant progression of gastric cancer through TGF-beta1-(p-Smad3)-RBP2-E-cadherin-Smad3 feedback circuit. Oncotarget 6(19):17661–17674. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.3756
Li Q, Shi L, Gui B, Yu W, Wang J, Zhang D, Han X, Yao Z, Shang Y (2011) Binding of the JmjC demethylase JARID1B to LSD1/NuRD suppresses angiogenesis and metastasis in breast cancer cells by repressing chemokine CCL14. Cancer Res 71(21):6899–6908. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-1523
Enkhbaatar Z, Terashima M, Oktyabri D, Tange S, Ishimura A, Yano S, Suzuki T (2013) KDM5B histone demethylase controls epithelial-mesenchymal transition of cancer cells by regulating the expression of the microRNA-200 family. Cell Cycle (Georgetown, Tex) 12(13):2100–2112. doi:10.4161/cc.25142
Tang B, Qi G, Tang F, Yuan S, Wang Z, Liang X, Li B, Yu S, Liu J, Huang Q, Wei Y, Zhai R, Lei B, Yu H, Jiao X, He S (2015) JARID1B promotes metastasis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition via PTEN/AKT signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncotarget 6(14):12723–12739. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.3713
Mozzetta C, Boyarchuk E, Pontis J, Ait-Si-Ali S (2015) Sound of silence: the properties and functions of repressive Lys methyltransferases. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 16(8):499–513. doi:10.1038/nrm4029
Chen MW, Hua KT, Kao HJ, Chi CC, Wei LH, Johansson G, Shiah SG, Chen PS, Jeng YM, Cheng TY, Lai TC, Chang JS, Jan YH, Chien MH, Yang CJ, Huang MS, Hsiao M, Kuo ML (2010) H3K9 histone methyltransferase G9a promotes lung cancer invasion and metastasis by silencing the cell adhesion molecule Ep-CAM. Cancer Res 70(20):7830–7840. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-0833
Liu S, Ye D, Guo W, Yu W, He Y, Hu J, Wang Y, Zhang L, Liao Y, Song H, Zhong S, Xu D, Yin H, Sun B, Wang X, Liu J, Wu Y, Zhou BP, Zhang Z, Deng J (2015) G9a is essential for EMT-mediated metastasis and maintenance of cancer stem cell-like characters in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 6(9):6887–6901. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.3159
Dong C, Wu Y, Wang Y, Wang C, Kang T, Rychahou PG, Chi YI, Evers BM, Zhou BP (2013) Interaction with Suv39H1 is critical for Snail-mediated E-cadherin repression in breast cancer. Oncogene 32(11):1351–1362. doi:10.1038/onc.2012.169
Zhang H, Cai K, Wang J, Wang X, Cheng K, Shi F, Jiang L, Zhang Y, Dou J (2014) MiR-7, inhibited indirectly by lincRNA HOTAIR, directly inhibits SETDB1 and reverses the EMT of breast cancer stem cells by downregulating the STAT3 pathway. Stem Cells (Dayton, Ohio) 32(11):2858–2868. doi:10.1002/stem.1795
Regina C, Compagnone M, Peschiaroli A, Lena A, Annicchiarico-Petruzzelli M, Piro MC, Melino G, Candi E (2016) Setdb1, a novel interactor of DeltaNp63, is involved in breast tumorigenesis. Oncotarget. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.7089
Ceol CJ, Houvras Y, Jane-Valbuena J, Bilodeau S, Orlando DA, Battisti V, Fritsch L, Lin WM, Hollmann TJ, Ferre F, Bourque C, Burke CJ, Turner L, Uong A, Johnson LA, Beroukhim R, Mermel CH, Loda M, Ait-Si-Ali S, Garraway LA, Young RA, Zon LI (2011) The histone methyltransferase SETDB1 is recurrently amplified in melanoma and accelerates its onset. Nature 471(7339):513–517. doi:10.1038/nature09806
Fei Q, Shang K, Zhang J, Chuai S, Kong D, Zhou T, Fu S, Liang Y, Li C, Chen Z, Zhao Y, Yu Z, Huang Z, Hu M, Ying H, Chen Z, Zhang Y, Xing F, Zhu J, Xu H, Zhao K, Lu C, Atadja P, Xiao ZX, Li E, Shou J (2015) Histone methyltransferase SETDB1 regulates liver cancer cell growth through methylation of p53. Nat Commun 6:8651. doi:10.1038/ncomms9651
Rodriguez-Paredes M, Martinez de Paz A, Simo-Riudalbas L, Sayols S, Moutinho C, Moran S, Villanueva A, Vazquez-Cedeira M, Lazo PA, Carneiro F, Moura CS, Vieira J, Teixeira MR, Esteller M (2014) Gene amplification of the histone methyltransferase SETDB1 contributes to human lung tumorigenesis. Oncogene 33(21):2807–2813. doi:10.1038/onc.2013.239
Wu PC, Lu JW, Yang JY, Lin IH, Ou DL, Lin YH, Chou KH, Huang WF, Wang WP, Huang YL, Hsu C, Lin LI, Lin YM, Shen CK, Tzeng TY (2014) H3K9 histone methyltransferase, KMT1E/SETDB1, cooperates with the SMAD2/3 pathway to suppress lung cancer metastasis. Cancer Res 74(24):7333–7343. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-3572
Di Croce L, Helin K (2013) Transcriptional regulation by Polycomb group proteins. Nat Struct Mol Biol 20(10):1147–1155. doi:10.1038/nsmb.2669
Margueron R, Reinberg D (2011) The polycomb complex PRC2 and its mark in life. Nature 469(7330):343–349. doi:10.1038/nature09784
Yu H, Simons DL, Segall I, Carcamo-Cavazos V, Schwartz EJ, Yan N, Zuckerman NS, Dirbas FM, Johnson DL, Holmes SP, Lee PP (2012) PRC2/EED-EZH2 complex is up-regulated in breast cancer lymph node metastasis compared to primary tumor and correlates with tumor proliferation in situ. PLoS One 7(12):e51239. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0051239
Herranz N, Pasini D, Diaz VM, Franci C, Gutierrez A, Dave N, Escriva M, Hernandez-Munoz I, Di Croce L, Helin K, Garcia de Herreros A, Peiro S (2008) Polycomb complex 2 is required for E-cadherin repression by the Snail1 transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol 28(15):4772–4781. doi:10.1128/MCB.00323-08
Hou Z, Peng H, Ayyanathan K, Yan KP, Langer EM, Longmore GD, Rauscher FJ 3rd (2008) The LIM protein AJUBA recruits protein arginine methyltransferase 5 to mediate SNAIL-dependent transcriptional repression. Mol Cell Biol 28(10):3198–3207. doi:10.1128/MCB.01435-07
Langer EM, Feng Y, Zhaoyuan H, Rauscher FJ 3rd, Kroll KL, Longmore GD (2008) Ajuba LIM proteins are snail/slug corepressors required for neural crest development in Xenopus. Dev Cell 14(3):424–436. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2008.01.005
Xia R, Jin FY, Lu K, Wan L, Xie M, Xu TP, De W, Wang ZX (2015) SUZ12 promotes gastric cancer cell proliferation and metastasis by regulating KLF2 and E-cadherin. Tumour Biol 36(7):5341–5351. doi:10.1007/s13277-015-3195-7
Malouf GG, Taube JH, Lu Y, Roysarkar T, Panjarian S, Estecio MR, Jelinek J, Yamazaki J, Raynal NJ, Long H, Tahara T, Tinnirello A, Ramachandran P, Zhang XY, Liang S, Mani SA, Issa JP (2013) Architecture of epigenetic reprogramming following Twist1-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Genome Biol 14(12):R144. doi:10.1186/gb-2013-14-12-r144
Chaffer CL, Marjanovic ND, Lee T, Bell G, Kleer CG, Reinhardt F, D’Alessio AC, Young RA, Weinberg RA (2013) Poised chromatin at the ZEB1 promoter enables breast cancer cell plasticity and enhances tumorigenicity. Cell 154(1):61–74. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2013.06.005
Yang H, Mizzen CA (2009) The multiple facets of histone H4-lysine 20 methylation. Biochem Cell Biol 87(1):151–161. doi:10.1139/O08-131
Yang F, Sun L, Li Q, Han X, Lei L, Zhang H, Shang Y (2012) SET8 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and confers TWIST dual transcriptional activities. EMBO J 31(1):110–123. doi:10.1038/emboj.2011.364
Hou L, Li Q, Yu Y, Li M, Zhang D (2016) SET8 induces epithelialmesenchymal transition and enhances prostate cancer cell metastasis by cooperating with ZEB1. Mol Med Rep 13(2):1681–1688. doi:10.3892/mmr.2015.4733
Fraga MF, Ballestar E, Villar-Garea A, Boix-Chornet M, Espada J, Schotta G, Bonaldi T, Haydon C, Ropero S, Petrie K, Iyer NG, Perez-Rosado A, Calvo E, Lopez JA, Cano A, Calasanz MJ, Colomer D, Piris MA, Ahn N, Imhof A, Caldas C, Jenuwein T, Esteller M (2005) Loss of acetylation at Lys16 and trimethylation at Lys20 of histone H4 is a common hallmark of human cancer. Nat Genet 37(4):391–400. doi:10.1038/ng1531
Shinchi Y, Hieda M, Nishioka Y, Matsumoto A, Yokoyama Y, Kimura H, Matsuura S, Matsuura N (2015) SUV420H2 suppresses breast cancer cell invasion through down regulation of the SH2 domain-containing focal adhesion protein tensin-3. Exp Cell Res 334(1):90–99. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2015.03.010
Dhar SS, Lee SH, Kan PY, Voigt P, Ma L, Shi X, Reinberg D, Lee MG (2012) Trans-tail regulation of MLL4-catalyzed H3K4 methylation by H4R3 symmetric dimethylation is mediated by a tandem PHD of MLL4. Genes Dev 26(24):2749–2762. doi:10.1101/gad.203356.112
Ibrahim R, Matsubara D, Osman W, Morikawa T, Goto A, Morita S, Ishikawa S, Aburatani H, Takai D, Nakajima J, Fukayama M, Niki T, Murakami Y (2014) Expression of PRMT5 in lung adenocarcinoma and its significance in epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Hum Pathol 45(7):1397–1405. doi:10.1016/j.humpath.2014.02.013
Yao R, Jiang H, Ma Y, Wang L, Wang L, Du J, Hou P, Gao Y, Zhao L, Wang G, Zhang Y, Liu DX, Huang B, Lu J (2014) PRMT7 induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and promotes metastasis in breast cancer. Cancer Res 74(19):5656–5667. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-0800
Tee AE, Ling D, Nelson C, Atmadibrata B, Dinger ME, Xu N, Mizukami T, Liu PY, Liu B, Cheung B, Pasquier E, Haber M, Norris MD, Suzuki T, Marshall GM, Liu T (2014) The histone demethylase JMJD1A induces cell migration and invasion by up-regulating the expression of the long noncoding RNA MALAT1. Oncotarget 5(7):1793–1804. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.1785
Shi L, Sun L, Li Q, Liang J, Yu W, Yi X, Yang X, Li Y, Han X, Zhang Y, Xuan C, Yao Z, Shang Y (2011) Histone demethylase JMJD2B coordinates H3K4/H3K9 methylation and promotes hormonally responsive breast carcinogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(18):7541–7546. doi:10.1073/pnas.1017374108
Zhao L, Li W, Zang W, Liu Z, Xu X, Yu H, Yang Q, Jia J (2013) JMJD2B promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition by cooperating with beta-catenin and enhances gastric cancer metastasis. Clin Cancer Res 19(23):6419–6429. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-0254
Bjorkman M, Ostling P, Harma V, Virtanen J, Mpindi JP, Rantala J, Mirtti T, Vesterinen T, Lundin M, Sankila A, Rannikko A, Kaivanto E, Kohonen P, Kallioniemi O, Nees M (2012) Systematic knockdown of epigenetic enzymes identifies a novel histone demethylase PHF8 overexpressed in prostate cancer with an impact on cell proliferation, migration and invasion. Oncogene 31(29):3444–3456. doi:10.1038/onc.2011.512
Kim JH, Sharma A, Dhar SS, Lee SH, Gu B, Chan CH, Lin HK, Lee MG (2014) UTX and MLL4 coordinately regulate transcriptional programs for cell proliferation and invasiveness in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 74(6):1705–1717. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-1896
Zha L, Cao Q, Cui X, Li F, Liang H, Xue B, Shi H (2016) Epigenetic regulation of E-cadherin expression by the histone demethylase UTX in colon cancer cells. Med Oncol 33(3):21. doi:10.1007/s12032-016-0734-z
Choi HJ, Park JH, Park M, Won HY, Joo HS, Lee CH, Lee JY, Kong G (2015) UTX inhibits EMT-induced breast CSC properties by epigenetic repression of EMT genes in cooperation with LSD1 and HDAC1. EMBO Rep 16(10):1288–1298. doi:10.15252/embr.201540244
Ramadoss S, Chen X, Wang CY (2012) Histone demethylase KDM6B promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Biol Chem 287(53):44508–44517. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.424903
Greiner D, Bonaldi T, Eskeland R, Roemer E, Imhof A (2005) Identification of a specific inhibitor of the histone methyltransferase SU(VAR)3-9. Nat Chem Biol 1(3):143–145. doi:10.1038/nchembio721
Lakshmikuttyamma A, Scott SA, DeCoteau JF, Geyer CR (2010) Reexpression of epigenetically silenced AML tumor suppressor genes by SUV39H1 inhibition. Oncogene 29(4):576–588. doi:10.1038/onc.2009.361
Chang Y, Zhang X, Horton JR, Upadhyay AK, Spannhoff A, Liu J, Snyder JP, Bedford MT, Cheng X (2009) Structural basis for G9a-like protein lysine methyltransferase inhibition by BIX-01294. Nat Struct Mol Biol 16(3):312–317. doi:10.1038/nsmb.1560
Kubicek S, O’Sullivan RJ, August EM, Hickey ER, Zhang Q, Teodoro ML, Rea S, Mechtler K, Kowalski JA, Homon CA, Kelly TA, Jenuwein T (2007) Reversal of H3K9me2 by a small-molecule inhibitor for the G9a histone methyltransferase. Mol Cell 25(3):473–481. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2007.01.017
Vedadi M, Barsyte-Lovejoy D, Liu F, Rival-Gervier S, Allali-Hassani A, Labrie V, Wigle TJ, Dimaggio PA, Wasney GA, Siarheyeva A, Dong A, Tempel W, Wang SC, Chen X, Chau I, Mangano TJ, Huang XP, Simpson CD, Pattenden SG, Norris JL, Kireev DB, Tripathy A, Edwards A, Roth BL, Janzen WP, Garcia BA, Petronis A, Ellis J, Brown PJ, Frye SV, Arrowsmith CH, Jin J (2011) A chemical probe selectively inhibits G9a and GLP methyltransferase activity in cells. Nat Chem Biol 7(8):566–574. doi:10.1038/nchembio.599
Pan MR, Hsu MC, Chen LT, Hung WC (2015) G9a orchestrates PCL3 and KDM7A to promote histone H3K27 methylation. Sci Rep 5:18709. doi:10.1038/srep18709
Finley A, Copeland RA (2014) Small molecule control of chromatin remodeling. Chem Biol 21(9):1196–1210. doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2014.07.024
Lv T, Yuan D, Miao X, Lv Y, Zhan P, Shen X, Song Y (2012) Over-expression of LSD1 promotes proliferation, migration and invasion in non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS One 7(4):e35065. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0035065
Ferrari-Amorotti G, Fragliasso V, Esteki R, Prudente Z, Soliera AR, Cattelani S, Manzotti G, Grisendi G, Dominici M, Pieraccioli M, Raschella G, Chiodoni C, Colombo MP, Calabretta B (2013) Inhibiting interactions of lysine demethylase LSD1 with snail/slug blocks cancer cell invasion. Cancer Res 73(1):235–245. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-1739
Wang L, Chang J, Varghese D, Dellinger M, Kumar S, Best AM, Ruiz J, Bruick R, Pena-Llopis S, Xu J, Babinski DJ, Frantz DE, Brekken RA, Quinn AM, Simeonov A, Easmon J, Martinez ED (2013) A small molecule modulates Jumonji histone demethylase activity and selectively inhibits cancer growth. Nat Commun 4:2035. doi:10.1038/ncomms3035
Gale M, Sayegh J, Cao J, Norcia M, Gareiss P, Hoyer D, Merkel JS, Yan Q (2016) Screen-identified selective inhibitor of lysine demethylase 5A blocks cancer cell growth and drug resistance. Oncotarget. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.9539
Robinson PJ, An W, Routh A, Martino F, Chapman L, Roeder RG, Rhodes D (2008) 30 nm chromatin fibre decompaction requires both H4-K16 acetylation and linker histone eviction. J Mol Biol 381(4):816–825. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2008.04.050
Shogren-Knaak M, Ishii H, Sun JM, Pazin MJ, Davie JR, Peterson CL (2006) Histone H4-K16 acetylation controls chromatin structure and protein interactions. Science (New York, NY) 311(5762):844–847. doi:10.1126/science.1124000
Filippakopoulos P, Picaud S, Mangos M, Keates T, Lambert JP, Barsyte-Lovejoy D, Felletar I, Volkmer R, Muller S, Pawson T, Gingras AC, Arrowsmith CH, Knapp S (2012) Histone recognition and large-scale structural analysis of the human bromodomain family. Cell 149(1):214–231. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2012.02.013
Shi J, Vakoc CR (2014) The mechanisms behind the therapeutic activity of BET bromodomain inhibition. Mol Cell 54(5):728–736. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2014.05.016
Shi J, Wang Y, Zeng L, Wu Y, Deng J, Zhang Q, Lin Y, Li J, Kang T, Tao M, Rusinova E, Zhang G, Wang C, Zhu H, Yao J, Zeng YX, Evers BM, Zhou MM, Zhou BP (2014) Disrupting the interaction of BRD4 with diacetylated Twist suppresses tumorigenesis in basal-like breast cancer. Cancer Cell 25(2):210–225. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2014.01.028
Wagner T, Robaa D, Sippl W, Jung M (2014) Mind the methyl: methyllysine binding proteins in epigenetic regulation. Chem Med Chem 9(3):466–483. doi:10.1002/cmdc.201300422
Maison C, Almouzni G (2004) HP1 and the dynamics of heterochromatin maintenance. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5(4):296–304. doi:10.1038/nrm1355
Bua DJ, Kuo AJ, Cheung P, Liu CL, Migliori V, Espejo A, Casadio F, Bassi C, Amati B, Bedford MT, Guccione E, Gozani O (2009) Epigenome microarray platform for proteome-wide dissection of chromatin-signaling networks. PLoS One 4(8):e6789. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0006789
Kokura K, Sun L, Bedford MT, Fang J (2010) Methyl-H3K9-binding protein MPP8 mediates E-cadherin gene silencing and promotes tumour cell motility and invasion. EMBO J 29(21):3673–3687. doi:10.1038/emboj.2010.239
Quinn AM, Bedford MT, Espejo A, Spannhoff A, Austin CP, Oppermann U, Simeonov A (2010) A homogeneous method for investigation of methylation-dependent protein-protein interactions in epigenetics. Nucleic Acids Res 38(2):e11. doi:10.1093/nar/gkp899
Nady N, Krichevsky L, Zhong N, Duan S, Tempel W, Amaya MF, Ravichandran M, Arrowsmith CH (2012) Histone recognition by human malignant brain tumor domains. J Mol Biol 423(5):702–718. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2012.08.022
Tang M, Shen H, Jin Y, Lin T, Cai Q, Pinard MA, Biswas S, Tran Q, Li G, Shenoy AK, Tongdee E, Lin S, Gu Y, Law BK, Zhou L, McKenna R, Wu L, Lu J (2013) The malignant brain tumor (MBT) domain protein SFMBT1 is an integral histone reader subunit of the LSD1 demethylase complex for chromatin association and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. J Biol Chem 288(38):27680–27691. doi:10.1074/jbc.M113.482349
Wysocka J, Swigut T, Milne TA, Dou Y, Zhang X, Burlingame AL, Roeder RG, Brivanlou AH, Allis CD (2005) WDR5 associates with histone H3 methylated at K4 and is essential for H3 K4 methylation and vertebrate development. Cell 121(6):859–872. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2005.03.036
Couture JF, Collazo E, Trievel RC (2006) Molecular recognition of histone H3 by the WD40 protein WDR5. Nat Struct Mol Biol 13(8):698–703. doi:10.1038/nsmb1116
Ruthenburg AJ, Wang W, Graybosch DM, Li H, Allis CD, Patel DJ, Verdine GL (2006) Histone H3 recognition and presentation by the WDR5 module of the MLL1 complex. Nat Struct Mol Biol 13(8):704–712. doi:10.1038/nsmb1119
Wu MZ, Tsai YP, Yang MH, Huang CH, Chang SY, Chang CC, Teng SC, Wu KJ (2011) Interplay between HDAC3 and WDR5 is essential for hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Mol Cell 43(5):811–822. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2011.07.012
Margueron R, Justin N, Ohno K, Sharpe ML, Son J, Drury WJ 3rd, Voigt P, Martin SR, Taylor WR, De Marco V, Pirrotta V, Reinberg D, Gamblin SJ (2009) Role of the polycomb protein EED in the propagation of repressive histone marks. Nature 461(7265):762–767. doi:10.1038/nature08398
Dhayalan A, Rajavelu A, Rathert P, Tamas R, Jurkowska RZ, Ragozin S, Jeltsch A (2010) The Dnmt3a PWWP domain reads histone 3 lysine 36 trimethylation and guides DNA methylation. J Biol Chem 285(34):26114–26120. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.089433
Collins RE, Northrop JP, Horton JR, Lee DY, Zhang X, Stallcup MR, Cheng X (2008) The ankyrin repeats of G9a and GLP histone methyltransferases are mono- and dimethyllysine binding modules. Nat Struct Mol Biol 15(3):245–250. doi:10.1038/nsmb.1384
Huang Y, Fang J, Bedford MT, Zhang Y, Xu RM (2006) Recognition of histone H3 lysine-4 methylation by the double tudor domain of JMJD2A. Science (New York, NY) 312(5774):748–751. doi:10.1126/science.1125162
Delmore JE, Issa GC, Lemieux ME, Rahl PB, Shi J, Jacobs HM, Kastritis E, Gilpatrick T, Paranal RM, Qi J, Chesi M, Schinzel AC, McKeown MR, Heffernan TP, Vakoc CR, Bergsagel PL, Ghobrial IM, Richardson PG, Young RA, Hahn WC, Anderson KC, Kung AL, Bradner JE, Mitsiades CS (2011) BET bromodomain inhibition as a therapeutic strategy to target c-Myc. Cell 146(6):904–917. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2011.08.017
Filippakopoulos P, Qi J, Picaud S, Shen Y, Smith WB, Fedorov O, Morse EM, Keates T, Hickman TT, Felletar I, Philpott M, Munro S, McKeown MR, Wang Y, Christie AL, West N, Cameron MJ, Schwartz B, Heightman TD, La Thangue N, French CA, Wiest O, Kung AL, Knapp S, Bradner JE (2010) Selective inhibition of BET bromodomains. Nature 468(7327):1067–1073. doi:10.1038/nature09504
Loven J, Hoke HA, Lin CY, Lau A, Orlando DA, Vakoc CR, Bradner JE, Lee TI, Young RA (2013) Selective inhibition of tumor oncogenes by disruption of super-enhancers. Cell 153(2):320–334. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2013.03.036
Hu Y, Zhou J, Ye F, Xiong H, Peng L, Zheng Z, Xu F, Cui M, Wei C, Wang X, Wang Z, Zhu H, Lee P, Zhou M, Jiang B, Zhang DY (2015) BRD4 inhibitor inhibits colorectal cancer growth and metastasis. Int J Mol Sci 16(1):1928–1948. doi:10.3390/ijms16011928
James LI, Barsyte-Lovejoy D, Zhong N, Krichevsky L, Korboukh VK, Herold JM, MacNevin CJ, Norris JL, Sagum CA, Tempel W, Marcon E, Guo H, Gao C, Huang XP, Duan S, Emili A, Greenblatt JF, Kireev DB, Jin J, Janzen WP, Brown PJ, Bedford MT, Arrowsmith CH, Frye SV (2013) Discovery of a chemical probe for the L3MBTL3 methyllysine reader domain. Nat Chem Biol 9(3):184–191. doi:10.1038/nchembio.1157
Stuckey JI, Dickson BM, Cheng N, Liu Y, Norris JL, Cholensky SH, Tempel W, Qin S, Huber KG, Sagum C, Black K, Li F, Huang XP, Roth BL, Baughman BM, Senisterra G, Pattenden SG, Vedadi M, Brown PJ, Bedford MT, Min J, Arrowsmith CH, James LI, Frye SV (2016) A cellular chemical probe targeting the chromodomains of Polycomb repressive complex 1. Nat Chem Biol 12(3):180–187. doi:10.1038/nchembio.2007
Suganuma T, Workman JL (2008) Crosstalk among Histone Modifications. Cell 135(4):604–607. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2008.10.036
Nishioka K, Chuikov S, Sarma K, Erdjument-Bromage H, Allis CD, Tempst P, Reinberg D (2002) Set9, a novel histone H3 methyltransferase that facilitates transcription by precluding histone tail modifications required for heterochromatin formation. Genes Dev 16(4):479–489. doi:10.1101/gad.967202
Wang H, Cao R, Xia L, Erdjument-Bromage H, Borchers C, Tempst P, Zhang Y (2001) Purification and functional characterization of a histone H3-lysine 4-specific methyltransferase. Mol Cell 8(6):1207–1217
Smallwood A, Esteve PO, Pradhan S, Carey M (2007) Functional cooperation between HP1 and DNMT1 mediates gene silencing. Genes Dev 21(10):1169–1178. doi:10.1101/gad.1536807
Norwood LE, Moss TJ, Margaryan NV, Cook SL, Wright L, Seftor EA, Hendrix MJ, Kirschmann DA, Wallrath LL (2006) A requirement for dimerization of HP1Hsalpha in suppression of breast cancer invasion. J Biol Chem 281(27):18668–18676. doi:10.1074/jbc.M512454200
Chang Y, Sun L, Kokura K, Horton JR, Fukuda M, Espejo A, Izumi V, Koomen JM, Bedford MT, Zhang X, Shinkai Y, Fang J, Cheng X (2011) MPP8 mediates the interactions between DNA methyltransferase Dnmt3a and H3K9 methyltransferase GLP/G9a. Nat Commun 2:533. doi:10.1038/ncomms1549
Sampath SC, Marazzi I, Yap KL, Sampath SC, Krutchinsky AN, Mecklenbrauker I, Viale A, Rudensky E, Zhou MM, Chait BT, Tarakhovsky A (2007) Methylation of a histone mimic within the histone methyltransferase G9a regulates protein complex assembly. Mol Cell 27(4):596–608. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2007.06.026
Chang Y, Horton JR, Bedford MT, Zhang X, Cheng X (2011) Structural insights for MPP8 chromodomain interaction with histone H3 lysine 9: potential effect of phosphorylation on methyl-lysine binding. J Mol Biol 408(5):807–814. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2011.03.018
Li J, Li Z, Ruan J, Xu C, Tong Y, Pan PW, Tempel W, Crombet L, Min J, Zang J (2011) Structural basis for specific binding of human MPP8 chromodomain to histone H3 methylated at lysine 9. PLoS One 6(10):e25104. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0025104
Sun L, Kokura K, Izumi V, Koomen JM, Seto E, Chen J, Fang J (2015) MPP8 and SIRT1 crosstalk in E-cadherin gene silencing and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. EMBO Rep 16(6):689–699. doi:10.15252/embr.201439792
Moore KE, Carlson SM, Camp ND, Cheung P, James RG, Chua KF, Wolf-Yadlin A, Gozani O (2013) A general molecular affinity strategy for global detection and proteomic analysis of lysine methylation. Mol Cell 50(3):444–456. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2013.03.005
Kapoor-Vazirani P, Kagey JD, Vertino PM (2011) SUV420H2-mediated H4K20 trimethylation enforces RNA polymerase II promoter-proximal pausing by blocking hMOF-dependent H4K16 acetylation. Mol Cell Biol 31(8):1594–1609. doi:10.1128/MCB.00524-10
Cheng X, Blumenthal RM (2010) Coordinated chromatin control: structural and functional linkage of DNA and histone methylation. Biochemistry 49(14):2999–3008. doi:10.1021/bi100213t
Epsztejn-Litman S, Feldman N, Abu-Remaileh M, Shufaro Y, Gerson A, Ueda J, Deplus R, Fuks F, Shinkai Y, Cedar H, Bergman Y (2008) De novo DNA methylation promoted by G9a prevents reprogramming of embryonically silenced genes. Nat Struct Mol Biol 15(11):1176–1183. doi:10.1038/nsmb.1476
Esteve PO, Chin HG, Smallwood A, Feehery GR, Gangisetty O, Karpf AR, Carey MF, Pradhan S (2006) Direct interaction between DNMT1 and G9a coordinates DNA and histone methylation during replication. Genes Dev 20(22):3089–3103. doi:10.1101/gad.1463706
Fuks F (2005) DNA methylation and histone modifications: teaming up to silence genes. Curr Opin Genet Dev 15(5):490–495. doi:10.1016/j.gde.2005.08.002
Schotta G, Ebert A, Krauss V, Fischer A, Hoffmann J, Rea S, Jenuwein T, Dorn R, Reuter G (2002) Central role of Drosophila SU(VAR)3-9 in histone H3-K9 methylation and heterochromatic gene silencing. EMBO J 21(5):1121–1131. doi:10.1093/emboj/21.5.1121
Vire E, Brenner C, Deplus R, Blanchon L, Fraga M, Didelot C, Morey L, Van Eynde A, Bernard D, Vanderwinden JM, Bollen M, Esteller M, Di Croce L, de Launoit Y, Fuks F (2006) The polycomb group protein EZH2 directly controls DNA methylation. Nature 439(7078):871–874. doi:10.1038/nature04431
Otani J, Nankumo T, Arita K, Inamoto S, Ariyoshi M, Shirakawa M (2009) Structural basis for recognition of H3K4 methylation status by the DNA methyltransferase 3A ATRX-DNMT3-DNMT3L domain. EMBO Rep 10(11):1235–1241. doi:10.1038/embor.2009.218
Zhang Y, Jurkowska R, Soeroes S, Rajavelu A, Dhayalan A, Bock I, Rathert P, Brandt O, Reinhardt R, Fischle W, Jeltsch A (2010) Chromatin methylation activity of Dnmt3a and Dnmt3a/3L is guided by interaction of the ADD domain with the histone H3 tail. Nucleic Acids Res 38(13):4246–4253. doi:10.1093/nar/gkq147
Yang MH, Wu MZ, Chiou SH, Chen PM, Chang SY, Liu CJ, Teng SC, Wu KJ (2008) Direct regulation of TWIST by HIF-1alpha promotes metastasis. Nat Cell Biol 10(3):295–305. doi:10.1038/ncb1691
Yang MH, Hsu DS, Wang HW, Wang HJ, Lan HY, Yang WH, Huang CH, Kao SY, Tzeng CH, Tai SK, Chang SY, Lee OK, Wu KJ (2010) Bmi1 is essential in Twist1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Cell Biol 12(10):982–992. doi:10.1038/ncb2099
Cao Q, Yu J, Dhanasekaran SM, Kim JH, Mani RS, Tomlins SA, Mehra R, Laxman B, Cao X, Yu J, Kleer CG, Varambally S, Chinnaiyan AM (2008) Repression of E-cadherin by the polycomb group protein EZH2 in cancer. Oncogene 27(58):7274–7284. doi:10.1038/onc.2008.333
Kalakonda N, Fischle W, Boccuni P, Gurvich N, Hoya-Arias R, Zhao X, Miyata Y, Macgrogan D, Zhang J, Sims JK, Rice JC, Nimer SD (2008) Histone H4 lysine 20 monomethylation promotes transcriptional repression by L3MBTL1. Oncogene 27(31):4293–4304. doi:10.1038/onc.2008.67
Li Z, Nie F, Wang S, Li L (2011) Histone H4 Lys 20 monomethylation by histone methylase SET8 mediates Wnt target gene activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(8):3116–3123. doi:10.1073/pnas.1009353108
Bartel DP (2009) MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 136(2):215–233. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.002
Kim VN, Han J, Siomi MC (2009) Biogenesis of small RNAs in animals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10(2):126–139. doi:10.1038/nrm2632
Abba ML, Patil N, Leupold JH, Allgayer H (2016) MicroRNA Regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition. J Clin Med. doi:10.3390/jcm5010008
Brabletz S, Brabletz T (2010) The ZEB/miR-200 feedback loop—a motor of cellular plasticity in development and cancer? EMBO Rep 11(9):670–677. doi:10.1038/embor.2010.117
Bracken CP, Gregory PA, Khew-Goodall Y, Goodall GJ (2009) The role of microRNAs in metastasis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cell Mol Life Sci 66(10):1682–1699. doi:10.1007/s00018-009-8750-1
Gregory PA, Bracken CP, Bert AG, Goodall GJ (2008) MicroRNAs as regulators of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cell Cycle (Georgetown, Tex) 7(20):3112–3118
Korpal M, Lee ES, Hu G, Kang Y (2008) The miR-200 family inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer cell migration by direct targeting of E-cadherin transcriptional repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. J Biol Chem 283(22):14910–14914. doi:10.1074/jbc.C800074200
Park SM, Gaur AB, Lengyel E, Peter ME (2008) The miR-200 family determines the epithelial phenotype of cancer cells by targeting the E-cadherin repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. Genes Dev 22(7):894–907. doi:10.1101/gad.1640608
Bracken CP, Gregory PA, Kolesnikoff N, Bert AG, Wang J, Shannon MF, Goodall GJ (2008) A double-negative feedback loop between ZEB1-SIP1 and the microRNA-200 family regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Res 68(19):7846–7854. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-1942
Burk U, Schubert J, Wellner U, Schmalhofer O, Vincan E, Spaderna S, Brabletz T (2008) A reciprocal repression between ZEB1 and members of the miR-200 family promotes EMT and invasion in cancer cells. EMBO Rep 9(6):582–589. doi:10.1038/embor.2008.74
Gregory PA, Bert AG, Paterson EL, Barry SC, Tsykin A, Farshid G, Vadas MA, Khew-Goodall Y, Goodall GJ (2008) The miR-200 family and miR-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal transition by targeting ZEB1 and SIP1. Nat Cell Biol 10(5):593–601. doi:10.1038/ncb1722
Xia H, Ng SS, Jiang S, Cheung WK, Sze J, Bian XW, Kung HF, Lin MC (2010) miR-200a-mediated downregulation of ZEB2 and CTNNB1 differentially inhibits nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell growth, migration and invasion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 391(1):535–541. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.11.093
Eades G, Yao Y, Yang M, Zhang Y, Chumsri S, Zhou Q (2011) miR-200a regulates SIRT1 expression and epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT)-like transformation in mammary epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 286(29):25992–26002. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.229401
Iliopoulos D, Lindahl-Allen M, Polytarchou C, Hirsch HA, Tsichlis PN, Struhl K (2010) Loss of miR-200 inhibition of Suz12 leads to polycomb-mediated repression required for the formation and maintenance of cancer stem cells. Mol Cell 39(5):761–772. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2010.08.013
Shimono Y, Zabala M, Cho RW, Lobo N, Dalerba P, Qian D, Diehn M, Liu H, Panula SP, Chiao E, Dirbas FM, Somlo G, Pera RA, Lao K, Clarke MF (2009) Downregulation of miRNA-200c links breast cancer stem cells with normal stem cells. Cell 138(3):592–603. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.07.011
Varambally S, Cao Q, Mani RS, Shankar S, Wang X, Ateeq B, Laxman B, Cao X, Jing X, Ramnarayanan K, Brenner JC, Yu J, Kim JH, Han B, Tan P, Kumar-Sinha C, Lonigro RJ, Palanisamy N, Maher CA, Chinnaiyan AM (2008) Genomic loss of microRNA-101 leads to overexpression of histone methyltransferase EZH2 in cancer. Science (New York, NY) 322(5908):1695–1699. doi:10.1126/science.1165395
Zheng M, Jiang YP, Chen W, Li KD, Liu X, Gao SY, Feng H, Wang SS, Jiang J, Ma XR, Cen X, Tang YJ, Chen Y, Lin YF, Tang YL, Liang XH (2015) Snail and Slug collaborate on EMT and tumor metastasis through miR-101-mediated EZH2 axis in oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 6(9):6797–6810. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.3180
Kim NH, Kim HS, Li XY, Lee I, Choi HS, Kang SE, Cha SY, Ryu JK, Yoon D, Fearon ER, Rowe RG, Lee S, Maher CA, Weiss SJ, Yook JI (2011) A p53/miRNA-34 axis regulates Snail1-dependent cancer cell epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Cell Biol 195(3):417–433. doi:10.1083/jcb.201103097
Kim T, Veronese A, Pichiorri F, Lee TJ, Jeon YJ, Volinia S, Pineau P, Marchio A, Palatini J, Suh SS, Alder H, Liu CG, Dejean A, Croce CM (2011) p53 regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition through microRNAs targeting ZEB1 and ZEB2. J Exp Med 208(5):875–883. doi:10.1084/jem.20110235
Dong P, Karaayvaz M, Jia N, Kaneuchi M, Hamada J, Watari H, Sudo S, Ju J, Sakuragi N (2013) Mutant p53 gain-of-function induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition through modulation of the miR-130b-ZEB1 axis. Oncogene 32(27):3286–3295. doi:10.1038/onc.2012.334
Ma L, Young J, Prabhala H, Pan E, Mestdagh P, Muth D, Teruya-Feldstein J, Reinhardt F, Onder TT, Valastyan S, Westermann F, Speleman F, Vandesompele J, Weinberg RA (2010) miR-9, a MYC/MYCN-activated microRNA, regulates E-cadherin and cancer metastasis. Nat Cell Biol 12(3):247–256. doi:10.1038/ncb2024
Drasin DJ, Guarnieri AL, Neelakantan D, Kim J, Cabrera JH, Wang CA, Zaberezhnyy V, Gasparini P, Cascione L, Huebner K, Tan AC, Ford HL (2015) TWIST1-Induced miR-424 Reversibly Drives Mesenchymal Programming while Inhibiting Tumor Initiation. Cancer Res 75(9):1908–1921. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-2394
Neves R, Scheel C, Weinhold S, Honisch E, Iwaniuk KM, Trompeter HI, Niederacher D, Wernet P, Santourlidis S, Uhrberg M (2010) Role of DNA methylation in miR-200c/141 cluster silencing in invasive breast cancer cells. BMC Res Notes 3:219. doi:10.1186/1756-0500-3-219
Schmitz SU, Grote P, Herrmann BG (2016) Mechanisms of long noncoding RNA function in development and disease. Cell Mol Life Sci. doi:10.1007/s00018-016-2174-5
Tsai MC, Manor O, Wan Y, Mosammaparast N, Wang JK, Lan F, Shi Y, Segal E, Chang HY (2010) Long noncoding RNA as modular scaffold of histone modification complexes. Science (New York, NY) 329(5992):689–693. doi:10.1126/science.1192002
Gupta RA, Shah N, Wang KC, Kim J, Horlings HM, Wong DJ, Tsai MC, Hung T, Argani P, Rinn JL, Wang Y, Brzoska P, Kong B, Li R, West RB, van de Vijver MJ, Sukumar S, Chang HY (2010) Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR reprograms chromatin state to promote cancer metastasis. Nature 464(7291):1071–1076. doi:10.1038/nature08975
Prensner JR, Iyer MK, Sahu A, Asangani IA, Cao Q, Patel L, Vergara IA, Davicioni E, Erho N, Ghadessi M, Jenkins RB, Triche TJ, Malik R, Bedenis R, McGregor N, Ma T, Chen W, Han S, Jing X, Cao X, Wang X, Chandler B, Yan W, Siddiqui J, Kunju LP, Dhanasekaran SM, Pienta KJ, Feng FY, Chinnaiyan AM (2013) The long noncoding RNA SChLAP1 promotes aggressive prostate cancer and antagonizes the SWI/SNF complex. Nat Genet 45(11):1392–1398. doi:10.1038/ng.2771
Hou P, Zhao Y, Li Z, Yao R, Ma M, Gao Y, Zhao L, Zhang Y, Huang B, Lu J (2014) LincRNA-ROR induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and contributes to breast cancer tumorigenesis and metastasis. Cell Death Dis 5:e1287. doi:10.1038/cddis.2014.249
Orom UA, Derrien T, Beringer M, Gumireddy K, Gardini A, Bussotti G, Lai F, Zytnicki M, Notredame C, Huang Q, Guigo R, Shiekhattar R (2010) Long noncoding RNAs with enhancer-like function in human cells. Cell 143(1):46–58. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2010.09.001
Gumireddy K, Li A, Yan J, Setoyama T, Johannes GJ, Orom UA, Tchou J, Liu Q, Zhang L, Speicher DW, Calin GA, Huang Q (2013) Identification of a long non-coding RNA-associated RNP complex regulating metastasis at the translational step. EMBO J 32(20):2672–2684. doi:10.1038/emboj.2013.188
Richards EJ, Zhang G, Li ZP, Permuth-Wey J, Challa S, Li Y, Kong W, Dan S, Bui MM, Coppola D, Mao WM, Sellers TA, Cheng JQ (2015) Long non-coding RNAs (LncRNA) regulated by transforming growth factor (TGF) beta: LncRNA-hit-mediated TGFbeta-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition in mammary epithelia. J Biol Chem 290(11):6857–6867. doi:10.1074/jbc.M114.610915
Dhamija S, Diederichs S (2016) From junk to master regulators of invasion: lncRNA functions in migration. EMT and metastasis. Int J Cancer 139(2):269–280. doi:10.1002/ijc.30039
Fischer KR, Durrans A, Lee S, Sheng J, Li F, Wong ST, Choi H, El Rayes T, Ryu S, Troeger J, Schwabe RF, Vahdat LT, Altorki NK, Mittal V, Gao D (2015) Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition is not required for lung metastasis but contributes to chemoresistance. Nature 527(7579):472–476. doi:10.1038/nature15748
Zheng X, Carstens JL, Kim J, Scheible M, Kaye J, Sugimoto H, Wu CC, LeBleu VS, Kalluri R (2015) Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition is dispensable for metastasis but induces chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer. Nature 527(7579):525–530. doi:10.1038/nature16064
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Grant from the National Cancer Institute (R01CA172774) to J Fang. This work was also supported in part by Core Facilities at the H. Lee Moffitt Cancer Center & Research Institute, an NCI designated Comprehensive Cancer Center.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, L., Fang, J. Epigenetic regulation of epithelial–mesenchymal transition. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 73, 4493–4515 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-016-2303-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-016-2303-1