Abstract
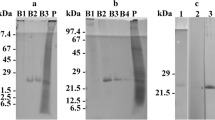
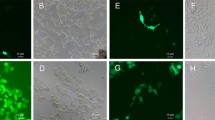
Here, we report the DNA sequence of the rhodopsin gene in the alga Cyanophora paradoxa (Glaucophyta). The primers were designed according to the conserved regions of prokaryotic and eukaryotic rhodopsin-like proteins deposited in the GenBank. The sequence consists of 1,272 bp comprised of 5 introns. The correspondent protein, named Cyanophopsin, showed high identity to rhodopsin-like proteins of Archea, Bacteria, Fungi, and Algae. At the N-terminal, the protein is characterized by a region with no transmembrane α-helices (80 aa), followed by a region with 7α-helices (219 aa) and a shorter 35-aa C-terminal region. The DNA sequence of the N-terminal region was expressed in E. coli and the recombinant purified peptide was used as antigen in hens to obtain polyclonal antibodies. Indirect immunofluorescence in C. paradoxa cells showed a marked labeling of the muroplast (aka cyanelle) membrane.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fathinejad S, Steiner JM, Reipert S, Marchetti M, Allmaier G, Burey SC, Ohnishi N, Fukuzawa H, Loffelhardt W, Bohnert HJ (2008) A carboxysomal carbon-concentrating mechanism in the cyanelles of the “coelacanth” of the algal world, Cyanophora paradoxa? Physiol Plant 133:27–32
Wise RR (2007) The diversity of plastid form and function. In: Wise RR, Hoober JK (eds) The structure and function of plastids. Springer, Netherlands, pp 3–26
Schenk HEA (1994) Cyanophora paradoxa: anagenetic model or missing link of plastid evolution. Endocytobiosis Cell Res 10:87–106
Barsanti L, Gualtieri P (2006) Algae—anatomy, biochemistry and biotechnology. CRC, Taylor & Francis, Boca Raton
Raven JA (2003) Carboxysomes and peptidoglycan walls of cyanelles: possible physiological function. Eur J Phycol 38:47–53
Trench RK, Pool RR, Logan M, Engelland A (1978) Aspects of the Relation between Cyanophora paradoxa (Korschikoff) and its endosymbiotic cyanelles Cyanocyta korschikoffiana (Hall & Claus). I. Growth, ultrastructure, photosynthesis and the obligate nature of the association. Proc R Soc Lond B 202:423–443
Plancke C, Colleoni C, Deschamps P, Dauvillée D, Nakamura Y, Haebel S, Ritte G, Steup M, Buléon A, Putaux JL, Dupeyre D, d’Hulst C, Ral JP, Löffelhardt W, Ball SG (2008) Pathway of cytosolic starch synthesis in the model glaucophyte Cyanophora paradoxa. Eukaryot Cell 7:247–257
Aitken A, Stanier RY (1979) Characterization of peptidoglycan from the cyanelles of Cyanophora paradoxa. J Gen Microbiol 112:219–223
Stirewalt VL, Michalowski CB, Loffelhardt W, Bohnert HJ, Bryant DA (1995) Nucleotide sequence of the cyanelle genome from Cyanophora paradoxa. Plant Mol Biol Rep 13:327–332
Kaneko T, Nakamura Y, Wolk CP, Kuritz T, Sasamoto S, Watanabe A, Iriguchi M, Ishikawa A, Kawashima K, Kimura T, Kishida Y, Kohara M, Matsumoto M, Matsuno A, Muraki A, Nakazaki N, Shimpo S, Sugimoto M, Takazawa M, Yamada M, Yasuda M, Tabata S (2001) Complete genomic sequence of the filamentous nitrogen-fixing cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120. DNA Res 8:205–213
Hader DP (1985) Photomovement in Cyanophora paradoxa. Arch Microbiol 143:100–104
Jung KH (2007) The distinct signalling mechanisms of microbial sensory Rhodopsins in Archaea, Eubacteria and Eukaryaa. Photochem Photobiol 83:63–69
Spudich JL, Yang CS, Jung KH, Spudich EN (2000) Retinylidene proteins: structures and functions from archaea to humans. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 16:365.392
Spudich JL, Jung KH (2005) Microbial rhodopsins: phylogenetic and functional diversity. In: Briggs WR, Spudich JL (eds) Handbook of photosensory receptors. Wiley, Weinheim, pp 1–23
Mercatelli R, Quercioli F, Barsanti L, Evangelista V, Coltelli P, Passarelli V, Frassanito AM, Gualtieri P (2009) Intramolecular photo-switching and intermolecular energy transfer as primari photoevents in photoreceptive processes: the case of Euglena gracilis. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 385:176–180
Barsanti L, Coltelli P, Evangelista V, Passarelli V, Frassanito AM, Vesentini N, Gualtieri P (2008) Low-resolution characterization of the 3D structure of the Euglena gracilis photoreceptor. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 375:471–476
Barsanti L, Passarelli V, Walne PL, Gualtieri P (2000) The photoreceptor protein of Euglena gracilis. FEBS Lett 482:247–251
Walne PL, Passarelli V, Lenzi P, Barsanti L, Gualtieri P (1995) Isolation of the flagellar swelling and identification of retinal in the phototactic flagellate, Ochromonas danica (Chrysophyceae). J Eukar Microbiol 42:7–11
Robinson KR, Lorenzi R, Ceccarelli N, Gualtieri P (1998) Retinal identification in Pelvetia fastigiata. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 243:776–778
Jung KH, Trivedi DV, Spudich JL (2003) Demonstration of a sensory rhodopsin in eubacteria. Mol Microbiol 47:1513–1522
Okamoto OK, Hastings JW (2003) Novel dinoflagellate clock-related genes identified through microarrays analysis. J Phycol 39:519–526
Sineshchekov OA, Jung KH, Spudich JL (2002) Two rhodopsins mediate phototaxis to low- and high-intensity light in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 25:8689–8694
Sineshchekov OA, Govorunova EG, Jung KH, Zauner S, Maier US, Spudich JL (2005) Rhodopsin-mediated photoreception in cryptophyte flagellates. Biophys J 89:4310–4319
Tsunoda SP, Ewers D, Gazzarrini S, Moroni A, Gradmann D, Hegemann P (2006) H1-pumping rhodopsin from the marine alga Acetabularia. Biophys J 91:1471–1479
Klare JP, Chizhov I, Engelhard M (2008) Microbial rhodopsins: scaffolds for ion pumps, channels, and sensors. Results Probl Cell Differ 45:73–122
Laemmli UK (1979) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Song CS, Yu JH, Bai DH, Hester PY, Kim KH (1985) Antibodies to the alpha-subunit of insulin receptor from eggs of immunized hens. J Immunol 135:3354–3359
Polson A (1990) Isolation of IgY from the yolk of eggs by a chloroform polyethylene glycol procedure. Immunol Investig 19:253–258
Lanyi JK (1997) Mechanism of ion transport across membranes. Bacteriorhodopsin as a prototype for proton pumps. J Biol Chem 272:31209–31212
Wu Q, Krainer AR (1999) AT-AC pre-mRNA splicing mechanisms and conservation of minor introns in voltage-gated ion channel genes. Mol Cell Biol 19:3225–3236
Sato M, Nishikawa T, Kajitani H, Kawano S (2007) Conserved relationship between FtsZ and peptidoglycan in the cyanelles of Cyanophora paradoxa similar to that in bacterial division. Planta 227:177–187
Sato M, Mogi Y, Nishikawa T, Miyamura S, Nagumo T, Kawano S (2009) The dynamic surface of dividing cyanelles and ultrastructure of the region directly below the surface in Cyanophora paradoxa. Planta 229:781–791
Yoon SH, Hackett YD, Ciniglia C, Pinto G, Bhattacharya D (2004) A molecular timeline for the origin of photosynthetic eukaryotes. Mol Biol Evol 21:809–818
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank all the fellows of the “Cooperativa l’Uovo di Colombo” of Viareggio (Italy) for the care they took of our Leghorn hens and Dr. Antonio Barsanti for veterinary assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Frassanito, A.M., Barsanti, L., Passarelli, V. et al. A rhodopsin-like protein in Cyanophora paradoxa: gene sequence and protein immunolocalization. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 67, 965–971 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-009-0225-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-009-0225-x