Abstract.
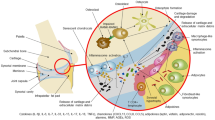
Neutrophils have been implicated in mediating much of the tissue damage associated with chronic inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, where they are involved in destruction of both cartilage and bone. Glucocorticoids are powerful anti-inflammatory agents, often used in the treatment of this autoimmune disease. They exert significant inhibitory effects on neutrophil activation and functions, such as chemotaxis, adhesion, transmigration, apoptosis, oxidative burst, and phagocytosis. The mechanisms by which glucocorticoids exert these effects on neutrophils are unclear. Evidence from studies of inflammation in human subjects and animal models suggests that annexin-I, an endogenous, glucocorticoid-induced protein also known as lipocortin-1, has a pivotal role in modulating neutrophil activation, transmigratory, and phagocytic functions. Furthermore, we present evidence for altered neutrophil functions in rheumatoid arthritis that correspond to a significantly reduced capacity of these cells to bind annexin-I. A proposed novel pathway for glucocorticoid actions on neutrophils involving annexin-I could explain the development of chronic neutrophil activation in diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goulding, N., Euzger, H., Butt, S. et al. Novel pathways for glucocorticoid effects on neutrophils in chronic inflammation. Inflamm. res. 47 (Suppl 3), 158–165 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s000110050310
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s000110050310