Abstract
Objective
To investigate the signal pathways involved in cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression in chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS).
Methods
The expressions of COX-2, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38MAPK), extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) in nasal mucosa were detected by immunohistological stain and polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Their expressions and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) release were determined by PCR, Western blot and enzyme immunoassay (EIA) in human nasal epithelia (HNE) cells after lipopolysaccharide (LPS) induction, and/or small interfering RNA (siRNA) transfection.
Results
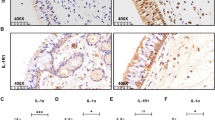
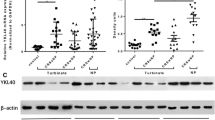
Positive protein expressions of COX-2, p38MAPK, ERK, NF-κB subunits were detected in epithelial and inflammatory cells. Their mRNA levels were significantly higher in CRS than controls (P < 0.05). The expressions varied in time and concentration-dependent manner in LPS-induced HNE cells. COX-2 expression was suppressed by siRNAs of P38MAPK, ERK, and NF-κB; however, COX-2-specific siRNA had no blocking effect on them. SiRNAs of P38MAPK or ERK could block NF-κB, but NF-κB-specific siRNA had no blocking effect on the former. SiRNA of p38MAPK, or ERK did not inhibit each other.
Conclusion
Upregulation of COX-2 expression suggested its role as a mediator in CRS. ERK and p38MAPK pathways were involved in signaling COX-2 through NF-κB pathway.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pérez-Novo CA, Watelet JB, Claeys C, Van Cauwenberge P, Bachert C. Prostaglandin, leukotriene, and lipoxin balance in chronic rhinosinusitis with and without nasal polyposis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005;115:1189–96.
Guilemany JM, Roca-Ferrer J, Mullol J. Cyclooxygenases and the pathogenesis of chronic rhinosinusitis and nasal polyposis. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2008;8:219–26.
Wood LG, Gibson PG, Garg ML. Biomarkers of lipid peroxidation, airway inflammation and asthma. Eur Respir J. 2003;21:177–86.
Sastre B, Fernández-Nieto M, Mollá R, López E, Lahoz C, Sastre J, et al. Increased prostaglandin E2 levels in the airway of patients with eosinophilic bronchitis. Allergy. 2008;63:58–66.
Zhang H, Ching S, Chen Q, Li Q, An Y, Quan N. Localized inflammation in peripheral tissue signals the CNS for sickness response in the absence of interleukin-1 and cyclooxygenase-2 in the blood and brain. Neuroscience. 2008;157:895–907.
Coon D, Gulati A, Cowan C, He J. The role of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) in inflammatory bone resorption. J Endod. 2007;33:432–6.
Brechter AB, Lerner UH. Bradykinin potentiates cytokine-induced prostaglandin biosynthesis in osteoblasts by enhanced expression of cyclooxygenase 2, resulting in increased RANKL expression. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56:910–23.
Chen YL, Hu CS, Lin FY, Chen YH, Sheu LM, Ku HH, et al. Salvianolic acid B attenuates cyclooxygenase-2 expression in vitro in LPS-treated human aortic smooth muscle cells and in vivo in the apolipoprotein-E-deficient mouse aorta. J Cell Biochem. 2006;98:618–31.
Petrovic N, Knight DA, Bomalaski JS, Thompson PJ, Misso NL. Concomitant activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase and induction of COX-2 stimulates maximum prostaglandin E2 synthesis in human airway epithelial cells. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2006;81:126–35.
Ahn EK, Yoon HK, Jee BK, Ko HJ, Lee KH, Kim HJ, et al. COX-2 expression and inflammatory effects by diesel exhaust particles in vitro and in vivo. Toxicol Lett. 2008;176:178–87.
Shiraishi Y, Asano K, Niimi K, Fukunaga K, Wakaki M, Kagyo J, et al. Cyclooxygenase-2/prostaglandin D2/CRTH2 pathway mediates double-stranded RNA-induced enhancement of allergic airway inflammation. J Immunol. 2008;180:541–9.
Kondoh K, Torii S, Nishida E. Control of MAP kinase signaling to the nucleus. Chromosoma. 2005;114:86–91.
Burgermeister E, Seger R. MAPK kinases as nucleo-cytoplasmic shuttles for PPARgamma. Cell Cycle. 2007;6:1539–48.
Zhang Z, Reenstra W, Weiner DJ, Louboutin JP, Wilson JM. The p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway is coupled to Toll-like receptor 5 to mediate gene regulation in response to Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in human airway epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 2007;75:5985–92.
Lee SJ, Lim KT. Inhibitory effect of 30-kDa phytoglycoprotein on expression of TNF-alpha and COX-2 via activation of PKCalpha and ERK 1/2 in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 2008;317:151–9.
Xu F, Xu Z, Zhang R, Wu Z, Lim JH, Koga T, et al. Nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae induces COX-2 and PGE2 expression in lung epithelial cells via activation of p38 MAPK and NF-kappa B. Respir Res. 2008;9:16.
Ogata S, Kubota Y, Yamashiro T, Takeuchi H, Ninomiya T, Suyama Y, et al. Signaling pathways regulating IL-1alpha-induced COX-2 expression. J Dent Res. 2007;86:186–91.
Yan X, Hao Q, Mu Y, Timani KA, Ye L, Zhu Y, et al. Nucleocapsid protein of SARS-CoV activates the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 by binding directly to regulatory elements for nuclear factor-kappa B and CCAAT/enhancer binding protein. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2006;38:1417–28.
Nie M, Pang L, Inoue H, Knox AJ. Transcriptional regulation of cyclooxygenase 2 by bradykinin and interleukin-1beta in human airway smooth muscle cells: involvement of different promoter elements, transcription factors, and histone h4 acetylation. Mol Cell Biol. 2003;23:9233–44.
Chun KS, Surh YJ. Signal transduction pathways regulating cyclooxygenase-2 expression: potential molecular targets for chemoprevention. Biochem Pharmacol. 2004;68:1089–100.
Owens JM, Shroyer KR, Kingdom TT. Expression of cyclooxygenase and lipoxygenase enzymes in nasal polyps of aspirin-sensitive and aspirin-tolerant patients. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2006;132:579–87.
Yano M, Matsumura T, Senokuchi T, Ishii N, Murata Y, Taketa K, et al. Statins activate peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma through extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent cyclooxygenase-2 expression in macrophages. Circ Res. 2007;100:1442–51.
Duggan SV, Lindstrom T, Iglesias T, Bennett PR, Mann GE, Bartlett SR. Role of atypical protein kinase C isozymes and NF-kappaB in IL-1beta-induced expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in human myometrial smooth muscle cells. J Cell Physiol. 2007;210:637–43.
Zhou HY, Shin EM, Guo LY, Youn UJ, Bae K, Kang SS, et al. Anti-inflammatory activity of 4-methoxyhonokiol is a function of the inhibition of iNOS and COX-2 expression in RAW 264.7 macrophages via NF-kappaB, JNK and p38 MAPK inactivation. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008;586:340–9.
Tsoyi K, Kim HJ, Shin JS, Kim DH, Cho HJ, Lee SS, et al. HO-1 and JAK-2/STAT-1 signals are involved in preferential inhibition of iNOS over COX-2 gene expression by newly synthesized tetrahydroisoquinoline alkaloid, CKD712, in cells activated with lipopolysacchride. Cell Signal. 2008;20:1839–47.
Kim YD, Kwon EJ, Park DW, Song SY, Yoon SK, Baek SH. Interleukin-1beta induces MUC2 and MUC5AC synthesis through cyclooxygenase-2 in NCI-H292 cells. Mol Pharmacol. 2002;62:1112–8.
Park GY, Christman JW. Involvement of cyclooxygenase-2 and prostaglandins in the molecular pathogenesis of inflammatory lung diseases. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2006;290:L797–805.
Hisatsune J, Yamasaki E, Nakayama M, Shirasaka D, Kurazono H, Katagata Y, et al. Helicobacter pylori VacA enhances prostaglandin E2 production through induction of cyclooxygenase 2 expression via a p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase/activating transcription factor 2 cascade in AZ-521 cells. Infect Immun. 2007;75:4472–81.
Chang MS, Chen BC, Yu MT, et al. Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate upregulates cyclooxygenase-2 expression in human pulmonary epithelial cells via Ras, Raf-1, ERK, and NF-kappaB, but not p38 MAPK, pathways. Cell Signal. 2005;17:299–310.
Yan SR, Joseph RR, Wang J, Stadnyk AW. Differential pattern of inflammatory molecule regulation in intestinal epithelial cells stimulated with IL-1. J Immunol. 2006;177:5604–11.
Patel KM, Wright KL, Whittaker P, Chakravarty P, Watson ML, Ward SG. Differential modulation of COX-2 expression in A549 airway epithelial cells by structurally distinct PPAR (gamma) agonists: evidence for disparate functional effects which are independent of NF-(kappa) B and PPAR (gamma). Cell Signal. 2005;17:1098–110.
He D, Natarajan V, Stern R, Gorshkova IA, Solway J, Spannhake EW, et al. Lysophosphatidic acid-induced transactivation of epidermal growth factor receptor regulates cyclo-oxygenase-2 expression and prostaglandin E(2) release via C/EBPbeta in human bronchial epithelial cells. Biochem J. 2008;412:153–62.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a research grant from the Postdoctoral Science Foundation of China (20080430442) and National Nature Science Foundation of China (30772412).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: J. A. Di Battista.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Zhang, Q., Li, Y. et al. Involvement of mitogen-activated protein kinases and nuclear factor kappa B pathways in signaling COX-2 expression in chronic rhinosinusitis. Inflamm. Res. 58, 649–658 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-009-0030-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-009-0030-x