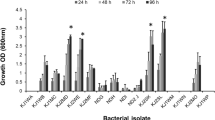
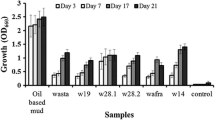
Abstract
In the present study, the efficiency of four different strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and their biosurfactants in the bioremediation process were investigated. The strains were found to be capable of metabolizing a wide range of hydrocarbons (HCs) with preference for high molecular weight aliphatic (ALP) over aromatic (ARO) compounds. After treating with individual bacteria and 11 different consortia, the residual crude oils were quantified and qualitatively analyzed. The bacterial strains degraded ALP, ARO, and nitrogen, sulphur, oxygen (NSO) containing fractions of the crude oil by 73–67.5, 31.8–12.3 and 14.7–7.3%, respectively. Additionally, the viscosity of the residual crude oil reduced from 48.7 to 34.6–39 mPa s. Further, consortium designated as 7 and 11 improved the degradation of ALP, ARO, and NSO HCs portions by 80.4–78.6, 42.7–42.4 and 21.6–19.2%, respectively. Moreover, addition of biosurfactant further increased the degradation performance of consortia by 81.6–80.7, 43.8–42.6 and 22.5–20.7%, respectively. Gas chromatographic analysis confirmed the ability of the individual strains and their consortium to degrade various fractions of crude oil. Experiments with biosurfactants revealed that polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are more soluble in the presence of biosurfactants. Phenanthrene had the highest solubility among the tested PAHs, which further increased as biosurfactant doses raised above their respective critical micelle concentrations (CMC). Furthermore, biosurfactants were able to recover 73.5–63.4% of residual oil from the sludge within their respective CMCs. Hence, selected surfactant-producing bacteria and their consortium could be useful in developing a greener and eco-sustainable way for removing crude oil pollutants from soil.










Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
This manuscript and its additional information files contain all of the data generated or analyzed during the study.
References
Abbasi H, Hamedi MM, Lotfabad TB, Zahiri HS, Sharafi H, Masoomi F, Moosavi-Movahedi AA, Ortiz A, Amanlou M, Noghabi KA (2012) Biosurfactant-producing bacterium, Pseudomonas aeruginosa MA01 isolated from spoiled apples: physicochemical and structural characteristics of isolated biosurfactant. J Biosci Bioeng 113(2):211–219
Abdel-Mawgoud AM, Aboulwafa MM, Hassouna NA (2009) Characterization of rhamnolipid produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolate Bs20. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 157(2):329–345
Abosede EE (2013) Effect of crude oil pollution on some soil physical properties. J Agric Vet Sci 6(3):14–17
Adams PZ, Jackson PP (1996) Bioremediation of oil spill. Theory and Practice. In: Nigeria National Petroleum Corporation Publication, Department of Petroleum Resources, pp 3−10
Adebusoye SA, Ilori MO, Amund OO, Teniola OD, Olatope SO (2007) Microbial degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons in a polluted tropical stream. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 23(8):1149–1159
Ahmed F, Fakhruddin AN (2018) A review on environmental contamination of petroleum hydrocarbons and its biodegradation. J Environ Sci Nat Resour 11(3):1–7. https://doi.org/10.19080/IJESNR.2018.11.555811
Altomare DF, Di Lena M, Porcelli F, Trizio L, Travaglio E, Tutino M, Dragonieri S, Memeo V, De Gennaro G (2013) Exhaled volatile organic compounds identify patients with colorectal cancer. Br J Surg 100(1):144–150. https://doi.org/10.1002/bjs.8942
Alzahrani AM, Rajendran P (2019) Petroleum hydrocarbon and living organisms. In: Ince M, Ince OK (eds) Hydrocarbon pollution and its effect on the environment. IntechOpen. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.86948
Arjoon K, Speight JG (2020) Chemical and physical analysis of a petroleum hydrocarbon contamination on a soil sample to determine its natural degradation feasibility. Inventions 5(3):43. https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions5030043
Balachandran C, Duraipandiyan V, Balakrishna K, Ignacimuthu S (2012) Petroleum and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) degradation and naphthalene metabolism in Streptomyces sp. (ERI-CPDA-1) isolated from oil contaminated soil. Bioresour Technol 112:83–90
Barkay T, Navon-Venezia S, Ron EZ, Rosenberg E (1999) Enhancement of solubilization and biodegradation of polyaromatic hydrocarbons by the bioemulsifier alasan. Appl Environ Microbiol 65(6):2697–2702
Bharagava RN, Saxena G, Mulla SI (2020) Introduction to industrial wastes containing organic and inorganic pollutants and bioremediation approaches for environmental management. In: Saxena G, Bharagava R (eds) Bioremediation of industrial waste for environmental safety. Springer, Singapore, pp 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-1891-7_1
Bharali P, Konwar BK (2011) Production and physico-chemical characterization of a biosurfactant produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa OBP1 isolated from petroleum sludge. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 164(8):1444–1460
Bharali P, Singh SP, Yasir B, Nipu D, Konwar BK, Singh CB (2018) Characterization and assessment of biosurfactant producing indigenous hydrocarbonoclastic bacteria: potential application in bioremediation. Nova Biotechnol Chim 17(2):103–114
Brown PJ, Long SM, Spurgeon DJ, Svendsen C, Hankard PK (2004) Toxicological and biochemical responses of the earthworm Lumbricus rubellus to pyrene, a non-carcinogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon. Chemosphere 57(11):1675–1681
Cerniglia CE (1993) Biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Curr Opin Biotechnol 4(3):331–338
Chaerun SK, Tazaki K, Asada R, Kogure K (2005) Interaction between clay minerals and hydrocarbon-utilizing indigenous microorganisms in high concentrations of heavy oil: implications for bioremediation. Clay Miner 40(1):105–114. https://doi.org/10.1180/0009855054010159
Chhatre S, Purohit H, Shanker R, Khanna P (1996) Bacterial consortia for crude oil spill remediation. Water Sci Technol 34(10):187–193
Chirwa EM, Mampholo CT, Fayemiwo OM, Bezza FA (2017) Biosurfactant assisted recovery of the C5–C11 hydrocarbon fraction from oily sludge using biosurfactant producing consortium culture of bacteria. J Environ Manag 196:261–269
Contreras-Ramos SM, Alvarez-Bernal D, Dendooven L (2006) Eisenia fetida increased removal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from soil. Environ Pollut 141(3):396–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2005.08.057
Das P, Mukherjee S, Sen R (2008) Improved bioavailability and biodegradation of a model polyaromatic hydrocarbon by a biosurfactant producing bacterium of marine origin. Chemosphere 72(9):1229–1234
del Mar Sánchez-Peinado M, González-López J, Martínez-Toledo MV, Pozo C, Rodelas B (2010) Influence of linear alkylbenzene sulfonate (LAS) on the structure of Alphaproteobacteria, Actinobacteria, and Acidobacteria communities in a soil microcosm. Environ Sci Pollut Res 17(3):779–790
Déziel E, Lépine F, Dennie D, Boismenu D, Mamer OA, Villemur R (1999) Liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry analysis of mixtures of rhamnolipids produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain 57RP grown on mannitol or naphthalene. Biochim Biophys Acta 1440(2–3):244–252
Déziel E, Lépine F, Milot S, Villemur R (2000) Mass spectrometry monitoring of rhamnolipids from a growing culture of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain 57RP. Biochem Biophys Acta 1485(2–3):145–152
Eddouaouda K, Mnif S, Badis A, Younes SB, Cherif S, Ferhat S, Mhiri N, Chamkha M, Sayadi S (2012) Characterization of a novel biosurfactant produced by Staphylococcus sp. strain 1E with potential application on hydrocarbon bioremediation. J Basic Microbiol 52(4):408–418
Etoumi A, El Musrati I, El Gammoudi B, El Behlil M (2008) The reduction of wax precipitation in waxy crude oils by Pseudomonas species. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 35(11):1241–1245
Ghazali FM, Rahman RN, Salleh AB, Basri M (2004) Biodegradation of hydrocarbons in soil by microbial consortium. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 54(1):61–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2004.02.002
Gudiña EJ, Pereira JF, Rodrigues LR, Coutinho JA, Teixeira JA (2012) Isolation and study of microorganisms from oil samples for application in microbial enhanced oil recovery. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 68:56–64
Guo J, Feng R, Ding Y, Wang R (2014) Applying carbon dioxide, plant growth-promoting rhizobacterium and EDTA can enhance the phytoremediation efficiency of ryegrass in a soil polluted with zinc, arsenic, cadmium and lead. J Environ Manag 141:1–8
Hao R, Lu A, Zeng Y (2004) Effect on crude oil by thermophilic bacterium. Pet Sci Eng 43(3–4):247–258
Helmy Q, Kardena E, Nurachman Z (2010) Application of biosurfactant produced by Azotobacter vinelandii AV01 for enhanced oil recovery and biodegradation of oil sludge. Int J Civ Environ Eng 10:7–14
Hu G, Feng H, He P, Li J, Hewage K, Sadiq R (2020) Comparative life-cycle assessment of traditional and emerging oily sludge treatment approaches. J Clean Prod 251:119594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119594
Hui K, Tang J, Lu H, Xi B, Qu C, Li J (2020) Status and prospect of oil recovery from oily sludge: a review. Arab J Chem 13(8):6523–6543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2020.06.009
Iloba BN, Jarret IE (2007) Effect of crude oil spills and on the abundance and distribution of soil microartropods at different depths. Int J Zool Res 3(1):24–32
Ji Y, Mao G, Wang Y, Bartlam M (2013) Structural insights into diversity and n-alkane biodegradation mechanisms of alkane hydroxylases. Front Microbiol 4:58. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2013.00058
Jones JG, Edington MA (1968) An ecological survey of hydrocarbon-oxidizing micro-organisms. Microbiology 52(3):381–390
Joseph PJ, Joseph A (2009) Microbial enhanced separation of oil from a petroleum refinery sludge. J Hazard Mater 161(1):522–525
Karlapudi AP, Venkateswarulu TC, Tammineedi J, Kanumuri L, Ravuru BK, ramu Dirisala V, Kodali VP (2018) Role of biosurfactants in bioremediation of oil pollution—a review. Petroleum 4(3):241–249
Koshlaf E, Ball A (2017) Soil bioremediation approaches for petroleum hydrocarbon polluted environments. AIMS Microbiol 3(1):25–49. https://doi.org/10.3934/microbiol.2017.1.25
Krivoshto IN, Richards JR, Albertson TE, Derlet RW (2008) The toxicity of diesel exhaust: implications for primary care. J Am Board Fam Med 21(1):55–62
Kum C, Sekkin S, Kiral F, Akar F (2007) Effects of xylene and formaldehyde inhalations on renal oxidative stress and some serum biochemical parameters in rats. Toxicol Ind Health 23(2):115–120
Lal B, Khanna S (1996) Degradation of crude oil by Acinetobacter calcoaceticus and Alcaligenes odorans. J Appl Bacteriol 81(4):355–362
Leahy JG, Colwell RR (1990) Microbial degradation of hydrocarbons in the environment. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 54(3):305–315
Lee DW, Lee H, Kwon BO, Khim JS, Yim UH, Kim BS, Kim JJ (2018) Biosurfactant-assisted bioremediation of crude oil by indigenous bacteria isolated from Taean beach sediment. Environ Pollut 241:254–264
Lipińska A, Kucharski J, Wyszkowska J (2013) Urease activity in soil contaminated with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Pol J Environ Stud 22(5):1393–1400
Liu H, Xu J, Liang R, Liu J (2014) Characterization of the medium-and long-chain n-alkanes degrading Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain SJTD-1 and its alkane hydroxylase genes. PLoS One 9(8):e105506. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0105506
Liu C, Zhang Y, Sun S, Huang L, Yu L, Liu X, Lai R, Luo Y, Zhang Z, Zhang Z (2018) Oil recovery from tank bottom sludge using rhamnolipids. J Petrol Sci Eng 170:14–20
Liu C, Xu Q, Hu X, Zhang S, Zhang P, You Y (2020) Optimization of process parameters of rhamnolipid treatment of oily sludge based on response surface methodology. ACS Omega 5(45):29333–29341
Lotfabad TB, Shourian M, Roostaazad R, Najafabadi AR, Adelzadeh MR, Noghabi KA (2009) An efficient biosurfactant-producing bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa MR01, isolated from oil excavation areas in south of Iran. Colloids Surf B Biointerface 69(2):183–193
Ma YL, Lu W, Wan LL, Luo N (2015) Elucidation of fluoranthene degradative characteristics in a newly isolated Achromobacter xylosoxidans DN002. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 175:1294–1305
Makkar RS, Cameotra SS, Banat IM (2011) Advances in utilization of renewable substrates for biosurfactant production. AMB Express 1(1):1–9
Mehdi H, Giti E (2008) Investigation of alkane biodegradation using the microtiter plate method and correlation between biofilm formation, biosurfactant production and crude oil biodegradation. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 62(2):170–178
Mishra S, Sarma PM, Lal B (2004) Crude oil degradation efficiency of a recombinant Acinetobacter baumannii strain and its survival in crude oil-contaminated soil microcosm. FEMS Microbiol Lett 235(2):323–331
Monteiro M, Moreira N, Pinto J, Pires-Luís AS, Henrique R, Jerónimo C, Bastos MD, Gil AM, Carvalho M, Guedes de Pinho P (2017) GC-MS metabolomics-based approach for the identification of a potential VOC-biomarker panel in the urine of renal cell carcinoma patients. J Cell Mol Med 21(9):2092–2105. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.13132
Müller MM, Kügler JH, Henkel M, Gerlitzki M, Hörmann B, Pöhnlein M, Syldatk C, Hausmann R (2012) Rhamnolipids—next generation surfactants? J Biotechnol 162(4):366–380
Mulligan CN (2005) Environmental applications for biosurfactants. Environ Pollut 133(2):183–198
Mulligan CN, Gibbs BF (2004) Types, production and applications of biosurfactants. Proc Indian Acad Sci Part B 70(1):31–56
Muriel-Millán LF, Rodríguez-Mejía JL, Godoy-Lozano EE, Rivera-Gómez N, Gutierrez-Rios RM, Morales-Guzmán D, Trejo-Hernández MR, Estradas-Romero A, Pardo-López L (2019) Functional and genomic characterization of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain isolated from the southwestern Gulf of Mexico reveals an enhanced adaptation for long-chain alkane degradation. Front Mar Sci 6:572. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2019.00572
Naik PR, Sakthivel N (2006) Functional characterization of a novel hydrocarbonoclastic Pseudomonas sp. strain PUP6 with plant-growth-promoting traits and antifungal potential. Res Microbiol 157(6):538–546
Odukoya J, Lambert R, Sakrabani R (2019) Understanding the impacts of crude oil and its induced abiotic stresses on agrifood production: a review. Horticulturae 5(2):47. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae5020047
Ordinioha B, Brisibe S (2013) The human health implications of crude oil spills in the Niger delta, Nigeria: an interpretation of published studies. Niger Med J J Niger Med Assoc 54(1):10–16. https://doi.org/10.4103/0300-1652.108887
Peng G, Hakim M, Broza YY, Billan S, Abdah-Bortnyak R, Kuten A, Tisch U, Haick H (2010) Detection of lung, breast, colorectal, and prostate cancers from exhaled breath using a single array of nanosensors. Br J Cancer 103(4):542–551. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6605810
Perfumo A, Banat IM, Canganella F, Marchant R (2006) Rhamnolipid production by a novel thermophilic hydrocarbon-degrading Pseudomonas aeruginosa AP02-1. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72(1):132–138
Pi Y, Meng L, Bao M, Sun P, Lu J (2016) Degradation of crude oil and relationship with bacteria and enzymatic activities in laboratory testing. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 106:106–116
Primeia S, Inoue C, Chien MF (2020) potential of biosurfactants’ production on degrading heavy oil by bacterial consortia obtained from tsunami-induced oil-spilled beach areas in Miyagi, Japan. J Mar Sci Eng 8(8):577. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8080577
Queiroga CL, Nascimento LR, Serra GE (2003) Evaluation of paraffins biodegradation and biosurfactant production by Bacillus subtilis in the presence of crude oil. Brazil J Microbiol 34(4):321–324
Ren H, Zhou S, Wang B, Peng L, Li X (2020) Treatment mechanism of sludge containing highly viscous heavy oil using biosurfactant. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 585:124117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.124117
Riihimäki V, Savolainen K (1980) Human exposure to m-xylene. Kinetics and acute effects on the central nervous system. Ann Occup Hyg 23(4):411–422
Rudyk S (2018) Relationships between SARA fractions of conventional oil, heavy oil, natural bitumen and residues. Fuel 216:330–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2017.12.001
Saadoun IM (2015) Impact of oil spills on marine life. In: Larramendy M, Soloneski S (eds) Emerging pollutants in the environment-current and further implications. Intech, Croatia, pp 75–104. https://doi.org/10.5772/60455
Saikia RR, Deka S (2013) Removal of hydrocarbon from refinery tank bottom sludge employing microbial culture. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20(12):9026–9033. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1888-2
Salihu A, Abdulkadir I, Almustapha MN (2009) An investigation for potential development on biosurfactants. Biotechnol Mol Biol Rev 4(5):111–117
Shao Z, Wang W (2013) Enzymes and genes involved in aerobic alkane degradation. Front Microbiol 4:116. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2013.00116
Sharma SL, Pant A (2000) Biodegradation and conversion of alkanes and crude oil by a marine Rhodococcus. Biodegradation 11(5):289–294
She YH, Zhang F, Xia JJ, Kong SQ, Wang ZL, Shu FC, Hu JM (2011) Investigation of biosurfactant-producing indigenous microorganisms that enhance residue oil recovery in an oil reservoir after polymer flooding. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 163(2):223–234
Siddiqui S, Adams WA (2002) The fate of diesel hydrocarbons in soils and their effect on the germination of perennial ryegrass. Environ Toxicol 17(1):49–62. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.10032
Sierra-Garcia IN, de Oliveira VM (2013) Microbial hydrocarbon degradation: efforts to understand biodegradation in petroleum reservoirs. In: Chamy R, Rosenkranz F (eds) Biodegradation−engineering and technology, vol 10, p 55920. IntechOpen, London. https://doi.org/10.5772/55920
Smits TH, Balada SB, Witholt B, Van Beilen JB (2002) Functional analysis of alkane hydroxylases from gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria. J Bacteriol 184(6):1733–1742
Urum K, Pekdemir T (2004) Evaluation of biosurfactants for crude oil contaminated soil washing. Chemosphere 57(9):1139–1150
Viamajala S, Peyton BM, Richards LA, Petersen JN (2007) Solubilization, solution equilibria, and biodegradation of PAH’s under thermophilic conditions. Chemosphere 66(6):1094–1106
Vinas M, Grifoll M, Sabaté J, Solanas AM (2002) Biodegradation of a crude oil by three microbial consortia of different origins and metabolic capabilities. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 28(5):252–260
Wang C, Chen S, Wang Z (2014) Electrophysiological follow-up of patients with chronic peripheral neuropathy induced by occupational intoxication with n-hexane. Cell Biochem Biophys 70(1):579–585
Wongsa P, Tanaka M, Ueno A, Hasanuzzaman M, Yumoto I, Okuyama H (2004) Isolation and characterization of novel strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Serratia marcescens possessing high efficiency to degrade gasoline, kerosene, diesel oil, and lubricating oil. Curr Microbiol 49(6):415–422
Wyrwas B, Chrzanowski Ł, Ławniczak Ł, Szulc A, Cyplik P, Białas W, Szymański A, Hołderna-Odachowska A (2011) Utilization of Triton X-100 and polyethylene glycols during surfactant-mediated biodegradation of diesel fuel. J Hazard Mater 197:97–103
Yan P, Lu M, Yang Q, Zhang HL, Zhang ZZ, Chen R (2012) Oil recovery from refinery oily sludge using a rhamnolipid biosurfactant-producing Pseudomonas. Bioresour Technol 116:24–28
Yasin G, Bhanger MI, Ansari TM, Naqvi SM, Ashraf M, Ahmad K, Talpur FN (2013) Quality and chemistry of crude oils. J Pet Technol Altern Fuels 4(3):53–63. https://doi.org/10.5897/JPTAF12.025
Yin H, Qiang J, Jia Y, Ye J, Peng H, Qin H, Zhang N, He B (2009) Characteristics of biosurfactant produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa S6 isolated from oil-containing wastewater. Process Biochem 44(3):302–308
Yu Y, Zhang Y, Zhao N, Guo J, Xu W, Ma M, Li X (2020) Remediation of crude oil-polluted soil by the bacterial rhizosphere community of Suaeda Salsa revealed by 16S rRNA genes. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17(5):1471. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17051471
Zhan X, Wu W, Zhou L, Liang J, Jiang T (2010) Interactive effect of dissolved organic matter and phenanthrene on soil enzymatic activities. J Environ Sci 22(4):607–614
Zhang GL, Wu YT, Qian XP, Meng Q (2005) Biodegradation of crude oil by Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the presence of rhamnolipids. J Zhejiang Univ Sci Biol 6(8):725–730. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2005.B0725
Zhang X, Liu Z, Luc NT, Yu Q, Liu X, Liang X (2016) Impacts of soil petroleum contamination on nutrient release during litter decomposition of Hippophae rhamnoides. Environ Sci Proc Impact 18(3):398–405
Funding
PB acknowledges ONGC, India for the fellowship and funding the research (Sanction number: ONGCA/CHAIRS/PU/2010-Dated 31-03-2010 for the year 2009–2014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PB, YB, AR, ND, PM designed the experiments, analyzed the data. PB, YB, AR, ND, PM, conducted most of the experiments. VS, AT, VV, PDN, BKK provided the experimental materials and performed few experiments. PB, BKK, YB, AT, VS, AR wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
The authors agreed and gave their permission for the manuscript to be published.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bharali, P., Bashir, Y., Ray, A. et al. Bioprospecting of indigenous biosurfactant-producing oleophilic bacteria for green remediation: an eco-sustainable approach for the management of petroleum contaminated soil. 3 Biotech 12, 13 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-021-03068-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-021-03068-0