Abstract
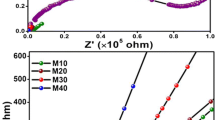
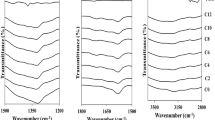
Quasi-solid bioelectrolytes based on hydroxyethyl cellulose (HEC) and sodium iodide (NaI) in three different polar aprotic solvent systems, dimethylformamide (DMF), dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), and dimethylacetamide (DMA), were fabricated and characterized. FTIR studies revealed active solvent-ion interactions in DMF-based electrolytes in comparison to DMA and DMSO. The effect of the solvent system on the crystallinity of HEC gel electrolytes was more significant at low NaI concentration. In each solvent system, the highest ionic conductivity was achieved at 70 wt% NaI and generally DMF-based electrolytes showed higher conductivity than the other solvents. The availability of multiple complexation sites present in DMF is ascribed to improvement in ion mobility and hence conductivity. Rheological analysis was carried out to elucidate the mechanical properties of the gels. Generally, the mechanical strength of the polymer gels was unaffected by the type of solvent.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Varshney PK, Gupta S (2011) Natural polymer-based electrolytes for electrochemical devices: a review. Ionics 17(6):479–483. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-011-0563-1
Di Noto V, Lavina S, Giffin GA, Negro E, Scrosati B (2011) Polymer electrolytes: present, past and future. Electrochimica Acta 57(supplement C):4–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2011.08.048
Wu J, Lan Z, Lin J, Huang M, Huang Y, Fan L, Luo G (2015) Electrolytes in dye-sensitized solar cells. Chem Rev 115(5):2136–2173. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr400675m
Long L, Wang S, Xiao M, Meng Y (2016) Polymer electrolytes for lithium polymer batteries. J Mater Chem A 4(26):10038–10069. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6TA02621D
Ngai KS, Ramesh S, Ramesh K, Juan JC (2016) A review of polymer electrolytes: fundamental, approaches and applications. Ionics 22(8):1259–1279. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-016-1756-4
Song JY, Wang YY, Wan CC (1999) Review of gel-type polymer electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 77(2):183–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-7753(98)00193-1
Sato T, Banno K, Maruo T, Nozu R (2005) New design for a safe lithium-ion gel polymer battery. J Power Sources 152(supplement C):264–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2005.03.212
Nirmale TC, Karbhal I, Kalubarme RS, Shelke MV, Varma AJ, Kale BB (2017) Facile synthesis of unique cellulose triacetate based flexible and high performance gel polymer electrolyte for lithium ion batteries. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(40):34773–34782. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b07020
Ahmad NH, Isa MIN (2016) Characterization of un-plasticized and propylene carbonate plasticized carboxymethyl cellulose doped ammonium chloride solid biopolymer electrolytes. Carbohydr Polym 137:426–432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.10.092
Huang X, Liu Y, Deng J, Yi B, Yu X, Shen P, Tan S (2012) A novel polymer gel electrolyte based on cyanoethylated cellulose for dye-sensitized solar cells. Electrochimica Acta 80:219–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2012.07.014
Ledwon P, Andrade JR, Lapkowski M, Pawlicka A (2015) Hydroxypropyl cellulose-based gel electrolyte for electrochromic devices. Electrochimica Acta 159:227–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2015.01.168
Xiao S, Wang F, Yang Y, Chang Z, Wu Y (2014) An environmentally friendly and economic membrane based on cellulose as a gel polymer electrolyte for lithium ion batteries. RSC Adv 4(1):76–81. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3RA46115G
Mudgil D, Barak S, Khatkar BS (2014) Guar gum: processing, properties and food applications—a review. J Food Sci Technol 51(3):409–418. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-011-0522-x
Chong MY, Numan A, Liew C-W, Ramesh K, Ramesh S (2017) Comparison of the performance of copper oxide and yttrium oxide nanoparticle based hydroxylethyl cellulose electrolytes for supercapacitors. J Appl Polym Sci 134(13):44636. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.44636
Gupta S, Varshney PK (2017) Effect of plasticizer concentration on structural and electrical properties of hydroxyethyl cellulose (HEC)-based polymer electrolyte. Ionics 23(6):1613–1617. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-017-2116-8
Sudhakar YN, Selvakumar M, Bhat DK (2015) Preparation and characterization of phosphoric acid-doped hydroxyethyl cellulose electrolyte for use in supercapacitor. Materials Renewable Sustainable Energy 4(3):10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40243-015-0051-z
Zhang MY, Li MX, Chang Z, Wang YF, Gao J, Zhu YS, Wu YP, Huang W (2017) A sandwich PVDF/HEC/PVDF gel polymer electrolyte for lithium ion battery. Electrochimica Acta 245(supplement C):752–759. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2017.05.154
Li MX, Wang XW, Yang YQ, Chang Z, Wu YP, Holze R (2015) A dense cellulose-based membrane as a renewable host for gel polymer electrolyte of lithium ion batteries. J Membrane Science 476(supplement C):112–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2014.10.056
Ellis BL, Nazar LF (2012) Sodium and sodium-ion energy storage batteries. Current Opinion Solid State Materials Sci 16(4):168–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cossms.2012.04.002
Dell RM (2000) Batteries: fifty years of materials development. Solid State Ionics 134(1):139–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-2738(00)00722-0
Osman Z, Md Isa KB, Ahmad A, Othman L (2010) A comparative study of lithium and sodium salts in PAN-based ion conducting polymer electrolytes. Ionics 16(5):431–435. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-009-0410-9
Vondrák J, Reiter J, Velická J, Sedlařı́ková M (2004) PMMA-based aprotic gel electrolytes. Solid State Ionics 170(1):79–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2003.08.060
Zhang B, Zhou Y, Li X, Wang J, Li G, Yun Q, Wang X (2014) Li+−molecule interactions of lithium tetrafluoroborate in propylene carbonate + N,N-dimethylformamide mixtures: an FTIR spectroscopic study. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy 124(Supplement C):40–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2014.01.001
Verbovy DM, Smagala TG, Brynda MA, Fawcett WR (2006) A FTIR study of ion-solvent interactions in N,N-dimethylacetamide. J Molecular Liquids 129(1):13–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2006.08.008
Kloss AA, Fawcett WR (1998) ATR-FTIR studies of ionic solvation and ion-pairing in dimethyl sulfoxide solutions of the alkali metal nitrates. J Chem Soc Faraday Trans 94(11):1587–1591. https://doi.org/10.1039/A800427G
Klemm D, Heublein B, Fink H-P, Bohn A (2005) Cellulose: fascinating biopolymer and sustainable raw material. Angewandte Chemie 44(22):3358–3303. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200460587
He R, Kyu T (2016) Effect of plasticization on ionic conductivity enhancement in relation to glass transition temperature of crosslinked polymer electrolyte membranes. Macromolecules 49(15):5637–5648. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.macromol.6b00918
Dissanayake MAKL, Thotawatthage CA, Senadeera GKR, Bandara TMWJ, WJMJSR J, Mellander BE (2012) Efficiency enhancement by mixed cation effect in dye-sensitized solar cells with PAN based gel polymer electrolyte. J Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry 246:29–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2012.06.023
Yusuf SNF, Azzahari AD, Yahya R, Majid SR, Careem MA, Arof AK (2016) From crab shell to solar cell: a gel polymer electrolyte based on N-phthaloylchitosan and its application in dye-sensitized solar cells. RSC Adv 6(33):27714–27724. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA04188D
Yusuf SNF, Azzahari AD, Selvanathan V, Yahya R, Careem MA, Arof AK (2017) Improvement of N-phthaloylchitosan based gel polymer electrolyte in dye-sensitized solar cells using a binary salt system. Carbohydrate Polymers 157:938–944. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.10.032
Shukur MF, Ibrahim FM, Majid NA, Ithnin R, Kadir MFZ (2013) Electrical analysis of amorphous corn starch-based polymer electrolyte membranes doped with LiI. Phys Scr 88(2):025601. https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-8949/88/02/025601
Yang YQ, Chang Z, Li MX, Wang XW, Wu YP (2015) A sodium ion conducting gel polymer electrolyte. Solid State Ionics 269(supplement C):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2014.11.015
Xue Y (2017) Electrochemical and mechanical properties of sodium-ion conducting cross-linked polymer gel electrolyte, vol 12. doi:https://doi.org/10.20964/2017.11.56
Vanitha D, Bahadur SA, Nallamuthu N, Athimoolam S, Manikandan A (2017) Electrical impedance studies on sodium ion conducting composite blend polymer electrolyte. J Inorg Organomet Polym Mater 27(1):257–265. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-016-0468-6
Kumar D, Hashmi SA (2010) Ionic liquid based sodium ion conducting gel polymer electrolytes. Solid State Ionics 181(8):416–423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2010.01.025
Zebardastan N, Khanmirzaei MH, Ramesh S, Ramesh K (2017) Presence of NaI in PEO/PVdF-HFP blend based gel polymer electrolytes for fabrication of dye-sensitized solar cells. Materials Sci Semiconductor Processing 66(supplement C):144–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2017.04.016
Subban RHY, Arof AK (1996) Sodium iodide added chitosan electrolyte film for polymer batteries. Phys Scr 53(3):382–384. https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-8949/53/3/021
Rani M, Rudhziah S, Ahmad A, Mohamed N (2014) Biopolymer electrolyte based on derivatives of cellulose from kenaf bast fiber. Polymers 6(9):2371–2385. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym6092371
Yue L, Xie Y, Zheng Y, He W, Guo S, Sun Y, Zhang T, Liu S (2017) Sulfonated bacterial cellulose/polyaniline composite membrane for use as gel polymer electrolyte. Composites Sci Technol 145(supplement C):122–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2017.04.002
Kavanagh GM, Ross-Murphy SB (1998) Rheological characterisation of polymer gels. Progress Polymer Sci 23(3):533–562. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0079-6700(97)00047-6
Stoppe N, Horn R (2017) How far are rheological parameters from amplitude sweep tests predictable using common physicochemical soil properties? J Phys Conf Ser 790(1). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/790/1/012032
Mezger TG (2011) The rheology handbook: for users of rotational and oscillatory rheometers. Vincentz Network, Hannover
Funding
This work is supported by the University of Malaya through FG031-17AFR grant. V. Selvanathan is grateful to the Ministry of Higher Education (MOHE), Malaysia, for the MyBrainSc scholarship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Selvanathan, V., Halim, M.N.A., Azzahari, A.D. et al. Effect of polar aprotic solvents on hydroxyethyl cellulose-based gel polymer electrolyte. Ionics 24, 1955–1964 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-018-2455-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-018-2455-0