Abstract
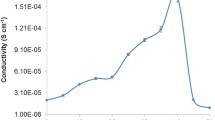
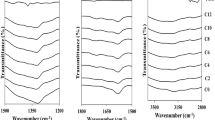
The present work investigates the ionic conductivity as well as its transport properties of carboxymethyl cellulose–NH4Br plasticized with various weight percentage of glycerol for solid biopolymer electrolytes (SBEs) prepared by solution-casting technique. It was shown from the FTIR analysis that the complexation transpires at C=O and C–O− from COO− of CMC upon the addition of glycerol into the SBEs system. The highest room temperature ionic conductivity of ~10−3 S cm−1 was achieved at 6 wt.% of glycerol owing to the broadening in the amorphous state as demonstrated in the XRD analysis. The conductivity-temperature plots were found to be in good agreement with the conventional Arrhenius relationship. It was further shown that the conducting element is mainly due to the protonation of H+ where ionic mobility and diffusion coefficient was found to contribute towards the enhancement in the ionic conductivity of SBEs system.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rudhziah S, Rani MSA, Ahmad A, Mohamed NS, Kaddami H (2015) Potential of blend of kappa-carrageenan and cellulose derivatives for green polymer electrolyte application. Ind Crop Prod 72:133–141
Wright PV (1975) Electrical conductivity in ionic complexes of poly (ethylene oxide). Polym Int 7(5):319–327
Armand MB, Chabagno JM, Duclot M (1978) Second international meeting on solid electrolytes. St Andrews, Scotland
Aziz NN (2010) Proton conducting polymer electrolytes of methylcellulose doped ammonium fluoride: conductivity and ionic transport studies. Int J Phys Sci 5:748–752
Avellaneda CO, Vieira DF, Al-Kahlout A, Heusing S, Leite ER, Pawlicka A, Aegerter MA (2008) All solid-state electrochromic devices with gelatin-based electrolyte. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 92:228–233
Nithya S, Selvasekarapandian S, Karthikeyan S, Inbavalli D, Sikkinthar S, Sanjeeviraja C (2014) AC impedance studies on proton-conducting PAN: NH4SCN polymer electrolytes. Ionics 20:1391–1398
Ramlli MA, Isa MIN (2014) Conductivity study of carboxyl methyl cellulose solid biopolymer electrolytes (SBE) doped with ammonium fluoride. Res J Recent Sci 3:59–66
Ahmad NH, Isa MIN (2015) Structural and ionic conductivity studies of CMC based polymerelectrolyte doped with NH4Cl. Adv Mater Res 1107:247–252
Rozali MLH, Isa MIN (2014) Electrical behaviour of carboxy methyl cellulose doped adipic acid solid biopolymer electrolyte. International Journal of Material Science 4:59
Shukur MF, Ithnin R, Kadir MFZ (2014) Electrical characterization of corn starch-LiOAc electrolytes and application in electrochemical double layer capacitor. Electrochim Acta 136:204–216
Rani MSA, Rudhziah S, Ahmad A, Mohamed NS (2014) Biopolymer electrolyte based on derivatives of cellulose from kenaf bast fiber. Polymers 6:2371–2385
Nik Aziz NA, Idris NK, Isa MIN (2010) Solid polymer electrolytes based on methylcellulose: FTIR and ionic conductivity studies. Int J Polym Anal Charact 15:319–327
Samsudin AS, Lai HM, Isa MIN (2014) Biopolymer materials based carboxymethyl cellulose as a proton conducting biopolymer electrolyte for application in rechargeable proton battery. Electrochim Acta 129:1–13
Kamarudin KH, Isa MIN (2013) Structural and DC ionic conductivity studies of carboxy methylcellulose doped with ammonium nitrate as solid polymer electrolytes. Int J Phys Sci 8:1581–1587
Chai MN, Isa MIN (2013) The oleic acid composition effect on the carboxymethyl cellulose based biopolymer electrolyte. J Cryst Process Technol 3:14
Chai MN, Isa MIN (2011) Carboxyl methylcellulose solid polymer electrolytes: ionic conductivity and dielectric study. J Curr Eng Res 1:23–27
Pandey M, Joshi GM, Ghosh NN (2016) Electrical performance of lithium ion based polymer electrolyte with polyethylene glycol and polyvinyl alcohol network. Int J Polym Mater 65:759–768
Flora XH, Ulaganathan M, Rajendran S (2013) Role of different plasticizers in li-ion conducting poly (acrylonitrile)-poly (methyl methacrylate) hybrid polymer electrolyte. Int J Polym Mater 62:737–742
Isa MIN, Samsudin AS (2016) Potential study of biopolymer-based carboxymethylcellulose electrolytes system for solid-state battery application. Int J Polym Mater 65:561–567
Mishra K, Hashmi SA, Rai DK (2013) Investigations on poly (ethylene oxide)+ NH4PF6 solid polymer electrolyte system. Int J Polym Mater 62(13):663–670
Noor MM, Careem MA, Majid SR, Arof AK (2011) Characterisation of plasticised PVDF–HFP polymer electrolytes. Mater Res Innov 15(2):157–160
Vroman I, Tighzert L (2009) Biodegradable polymers. Materials 2(2):307–344
Samsudin AS, Isa MIN (2014) Conductivity and transport properties study of plasticized carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) based solid biopolymer electrolytes (SBE). Adv Mater Res 856:118–122
Pradhan DK, Choudhary RNP, Samantaray BK, Karan NK, Katiyar RS (2007) Int. J. Electrochem Sci 2:861–871
Majid SR, Arof AK (2007) Electrical behavior of proton-conducting chitosan-phosphoric acid-based electrolytes. Physica B 390:209–215
Chai MN, Isa MIN (2014) Electrical study of plasticized carboxy methylcellulose based solid polymer electrolyte. Int J Phys Sci 9:397–401
Samsudin AS, Isa MIN (2015) Conduction mechanism of enhanced CMC-NH4Br biopolymer electrolytes. Adv Mater Res 1108:27
Starkey SR, Frech R (1997) Plasticizer interactions with polymer and salt in propylene carbonate-poly (acrylonitrile)-lithium triflate. Electrochim Acta 42(3):471–474
Zainuddin NK, Samsudin AS (2017) Influence of polyethylene glycol (PEG) in CMC-NH4BR based polymer electrolytes: conductivity and electrical study. Makara. J Technol 21(1):37–42
Chai MN, Isa MIN (2015) Structural study of plasticized carboxy methylcellulose based solid biopolymer electrolyte. Adv Mater Res 1107:242–246
Chelli R, Procacci P, Cardini G, Califano S (1999) Glycerol condensed phases part II. A molecular dynamics study of the conformational structure and hydrogen bonding. Phys Chem Chem Phys 1(5):879–885
Pagliaro M, Rossi M (2010) Glycerol: properties and production. The future of glycerol 7
Shukur MF, Ithnin R, MFZ K (2016, 1113) Ionic conductivity and dielectric properties of potato starch-magnesium acetate biopolymer electrolytes: the effect of glycerol and 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride. Ionics:22
Sonnati MO, Amigoni S, de Givenchy EPT, Darmanin T, Choulet O, Guittard F (2013) Glycerol carbonate as a versatile building block for tomorrow: synthesis, reactivity, properties and applications. Green Chem 15(2):283–306
Samsudin AS, Isa MIN (2012) Structural and ionic transport study on CMC doped NH4Br: a new types of biopolymer electrolytes. J Appl Sci 12:174–179
Samsudin AS, Isa MIN (2012) Structural and electrical properties of carboxy methylcellulose-dodecyltrimethyl ammonium bromide-based biopolymer electrolytes system. Int J Polym Mater 61:30–40
Pushmalar V, Langford SJ, Ahmad M, Lim YY (2006) Optimization of reaction conditions for preparing carboxymethyl cellulose from sago waste. Carbohydr Polym 64:312–318
Samsudin AS, Khairul WM, Isa MIN (2012) Characterization on the potential of carboxy methylcellulose for application as proton conducting biopolymer electrolytes. J Non-Cryst 358:1104–1112
Biswal DR, Singh RP (2004) Characterisation of carboxymethyl cellulose and polyacrylamide graft copolymer. Carbohyd Polym 57:379–387
Yusof YM, Illias HA, Shukur MF, Kadir MFZ (2017) Characterization of starch-chitosan blend-based electrolyte doped with ammonium iodide for application in proton batteries. Ionics 23(3):681–697
Ramlli MA, Maksud MA, Isa MIN (2017) Characterization of polyethylene glycol plasticized carboxymethyl cellulose-ammonium fluoride solid biopolymer electrolytes. AIP Conf Proc 1826:020001
Kumar M, Tiwari T, Srivastava N (2012) Electrical transport behaviour of bio-polymer electrolyte system: potato starch+ ammonium iodide. Carbohyd Polym 88:54–60
Arof AK, Shuhaimi NEA, Alias NA, Kufian MZ, Majid SR (2010) Application of chitosan/iota-carrageenan polymer electrolytes in electrical double layer capacitor (EDLC). J Solid State Electr 14:2145–2152
Winie T, Ramesh S, Arof AK (2009) Studies on the structure and transport properties of hexanoyl chitosan-based polymer electrolytes. Physica B 404:4308–4311
Yusof YM, Majid NA, Kasmani RM, Illias HA, Kadir MFZ (2014) The effect of plasticization on conductivity and other properties of starch/chitosan blend biopolymer electrolyte incorporated with ammonium iodide. Mol Cryst Liq Cryst 603:73–88
Vijaya N, Selvasekarapandian S, Nithya H, Sanjeeviraja C (2015) Proton conducting polymer electrolyte based on poly (N-vinyl pyrrolidone) doped with ammonium iodide. Int J electroactive Mater 3:20–27
Pandey K, Asthana N, Dwivedi MM, Chaturvedi, SK (2013) Effect of plasticizers on structural and dielectric behaviour of [PEO + (NH4)2C4H8(COO)2] polymer electrolyte. J Polym 2013:752596
Shukur MF, Azmi MS, Zawawi SMM, Majid NA, Illias HA, Kadir MFZ (2013) Conductivity studies of biopolymer electrolytes based on chitosan incorporated with NH4Br. Phys Scr 2013:014049
Ramya CS, Selvasekarapandian S, Savitha T, Hirankumar G, Baskaran R, Angelo PC (2006) Conductivity and thermal behavior of proton conducting polymer electrolyte based on poly (N-vinyl pyrrolidone). Eur Polym J 42:2672–2677
Hema M, Selvasekerapandian S, Sakunthala A, Arunkumar D, Nithya H (2008) Structural, vibrational and electrical characterization of PVA–NH4Br polymer electrolyte system. Physica B 403:2740–2747
Shukur MF, Kadir MFZ (2015) Electrical and transport properties of NH4Br-doped cornstarch-based solid biopolymer electrolyte. Ionics 21:111–124
GM W, Lin SJ, Yang CC (2006) Preparation and characterization of PVA/PAA membranes for solid polymer electrolytes. J Membrane Sci 275:127–133
Shuhaimi NEA, Teo LP, Woo HJ, Majid SR, Arof AK (2012) Electrical double-layer capacitors with plasticized polymer electrolyte based on methyl cellulose. Polym Bull 69:807–826
Rajendran S, Sivakumar M, Subadevi R (2004) Investigations on the effect of various plasticizers in PVA–PMMA solid polymer blend electrolytes. Mater Lett 58:641–649
Qian X, Gu N, Cheng Z, Yang X, Wang E, Dong S (2001) Impedance study of (PEO) 10 LiClO 4–Al2O3 composite polymer electrolyte with blocking electrodes. Electrochim Acta 46:1829–1836
Stephan AM, Thirunakaran R, Renganathan NG, Sundaram V, Pitchumani S, Muniyandi N, Gangadharan R, Ramamoorthy P (1999) J Power Sources 81:752–758
Teo LP, Buraidah MH, Nor AFM, Majid SR (2012) Conductivity and dielectric studies of Li2SnO3. Ionics 18:655–665
Ramya CS, Selvasekarapandian S, Hirankumar G, Savitha T, Angelo PC (2008) Investigation on dielectric relaxations of PVP–NH 4 SCN polymer electrolyte. J Non-Cryst Solids 354:1494–1502
Ramesh S, Arof AK (2001) Ionic conductivity studies of plasticized poly (vinyl chloride) polymer electrolytes. Mater Sci Eng B 85:11–15
Chai MN, Isa MIN (2016) Novel proton conducting solid bio-polymer electrolytes based on carboxymethyl cellulose doped with oleic acid and plasticized with glycerol. Sci Rep 6
Gondaliya N, Kanchan DK, Sharma P, Jayswal MS (2012) Dielectric and electric properties of plasticized PEO-AgCF3SO3-SiO2 nanocomposite polymer electrolyte system. Polym Composite 33:2195–2200
Ramesh S, Yahaya AH, Arof AK (2002) Effect of dibutyl phthalate as plasticizer on high-molecular weight poly (vinyl chloride)–lithium tetraborate-based solid polymer electrolytes. Solid State Ionics 152:291–294
Pradhan DK, Choudhary RNP, Samantaray BK (2009) Studies of dielectric and electrical properties of plasticized polymer nanocomposite electrolytes. Mater Chem Phys 115:557–561
Samsudin AS, Isa MIN (2014) Study of the ionic conduction mechanism based on carboxymethyl cellulose biopolymer electrolytes. J Korean Phys Soc 65:1441–1447
Kadir MFZ, Majid SR, Arof AK (2010) Plasticized chitosan–PVA blend polymer electrolyte based proton battery. Electrochim Acta 55:1475–1482
Achari VB, Reddy TJR, Sharma AK, Rao VN (2007) Electrical, optical, and structural characterization of polymer blend (PVC/PMMA) electrolyte films. Ionics 13:349–354
Shuhaimi NEA, Teo LP, Majid SR, Arof AK (2010) Transport studies of NH 4 NO 3 doped methyl cellulose electrolyte. Synth Met 160:1040–1044
Samsudin AS, Isa MIN (2102) Characterization of carboxy methylcellulose doped with DTAB as new types of biopolymer electrolytes. Bull Mater Sci 35:1123–1131
Sivakumar M, Subadevi R, Rajendran S, NL W, Lee JY (2006) Electrochemical studies on [(1− x) PVA–xPMMA] solid polymer blend electrolytes complexed with LiBF4. Mater Chem Phys 97:330–336
Cowie JMG, Spence GH (1998) Ion conduction in macroporous polyethylene film doped with electrolytes. Solid State Ionics 109:139–144
Schantz S, Torell LM (1993) Evidence of dissolved ions and ion pairs in dilute poly (propylene oxide)-salt solutions. Solid State Ionics 60:47–53
Selvasekarapandian S, Hirankumar G, Kawamura J, Kuwata N, Hattori T (2005) 1 H solid state NMR studies on the proton conducting polymer electrolytes. Mater Lett 59:2741–2745
Hafiza MN, Bashirah ANA, Bakar NY, Isa MIN (2014) Electrical properties of carboxyl methylcellulose/chitosan dual-blend green polymer doped with ammonium bromide. Int J Polym Anal Ch 19:151–158
Ahmad NHB, Isa MIN (2015) Proton conducting solid polymer electrolytes based carboxymethyl cellulose doped ammonium chloride: ionic conductivity and transport studies. Int J Plast Technol 19:47–55
Salleh NS, Aziz SB, Aspanut Z, Kadir MFZ (2016) Electrical impedance and conduction mechanism analysis of biopolymer electrolytes based on methyl cellulose doped with ammonium iodide. Ionics 22:2157–2167
Missan HPS, Chu PP, Sekhon SS (2006) Ion conduction mechanism in non-aqueous polymer electrolytes based on oxalic acid: effect of plasticizer and polymer. J Power Sources 158:1472–1479
Rao M, Geng X, Liao Y, Hu S, Li W (2012) Preparation and performance of gel polymer electrolyte based on electrospun polymer membrane and ionic liquid for lithium ion battery. J Membrane Sci 399:37–42
Chai MN, Ramlli MA, Isa MIN (2013) Proton conductor of propylene carbonate–plasticized carboxyl methylcellulose–based solid polymer electrolyte. Int J Polym Anal Ch 18:297–302
Ramesh S, Ng KY (2009) Characterization of polymer electrolytes based on high molecular weight PVC and Li 2SO4. Curr Appl Phy 9:329–332
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank MOHE for FRGS Grant (RDU170115), Faculty Industrial Science & Technology, Universiti Malaysia Pahang for the technical and research support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rasali, N.M.J., Samsudin, A.S. Ionic transport properties of protonic conducting solid biopolymer electrolytes based on enhanced carboxymethyl cellulose - NH4Br with glycerol. Ionics 24, 1639–1650 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-017-2318-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-017-2318-0