Abstract
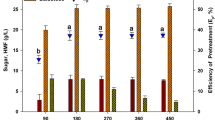
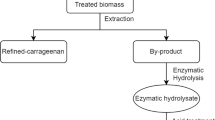
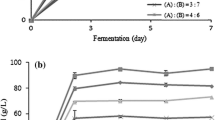
The seaweed industry has developed rapidly over the last decade, and carrageenan is the leading hydrocolloid in the seaweed industry. Approximately 57,500 t of carrageenan is produced annually throughout the world. As a consequence of the increase in carrageenan production, the enormous amount of waste resulting from the carrageenan industry has also increased. This study investigated the possibility of ethanol production using carrageenan solid waste from the carrageenan extraction of Kappaphycus alvarezii, the principal species used in the carrageenan industry. Optimum acid hydrolysis followed by enzymatic hydrolysis enhanced the production of both galactose and glucose. Fermentation of the enzymatic hydrolysate using Saccharomyces cerevisiae ATCC 200062 resulted in an ethanol yield of 13.8 g L−1.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvira P, Tomás-Pejó E, Ballesteros M, Negro MJ (2010) Pretreatment technologies for an efficient bioethanol production process based on enzymatic hydrolysis: a review. Bioresour Technol 101:4851–4861
Bixler HJ, Porse H (2011) A decade of change in the seaweed hydrocolloids industry. J Appl Phycol 23:321–335
Cho Y, Kim H, Kim SK (2013) Bioethanol production from brown seaweed, Undaria pinnatifida, using NaCl acclimated yeast. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 36:713–719
de Góes HG, Reis RP (2012) Temporal variation of the growth, carrageenan yield and quality of Kappaphycus alvarezii (Rhodophyta, Gigartinales) cultivated at Sepetiba bay, southeastern Brazilian coast. J Appl Phycol 24:173–180
Guerrero LA, Maas G, Hogland W (2013) Solid waste management challenges for cities in developing countries. Waste Manag 33:220–232
Hargreaves PI, Barcelos CA, da Costa ACA, Pereira N (2013) Production of ethanol 3G from Kappaphycus alvarezii: evaluation of different process strategies. Bioresour Technol 134:257–263
Hayashi L, De Paula EJ, Chow F (2007) Growth rate and carrageenan analyses in four strains of Kappaphycus alvarezii (Rhodophyta, Gigartinales) farmed in the subtropical waters of São Paulo State, Brazil. J Appl Phycol 19:393–399
Hayashi L, Faria GSM, Nunes BG, Zitta CS, Scariot LA, Rover T, Felix MRL, Bouzon ZL (2011) Effects of salinity on the growth rate, carrageenan yield, and cellular structure of Kappaphycus alvarezii (Rhodophyta, Gigartinales) cultured in vitro. J Appl Phycol 23:439–447
Jol CN, Neiss TG, Penninkhof B, Rudolph B, De Ruiter GA (1999) A novel high-performance anion-exchange chromatographic method for the analysis of carrageenans and agars containing 3,6-anhydrogalactose. Anal Biochem 268:213–222
Khambhaty Y, Mody K, Gandhi MR, Thampy S, Maiti P, Brahmbhatt H, Eswaran K, Ghosh PK (2012) Kappaphycus alvarezii as a source of bioethanol. Bioresour Technol 103:180–185
Marshall RE, Farahbakhsh K (2013) Systems approaches to integrated solid waste management in developing countries. Waste Manag 33:988–1003 3
McHugh DJ (2003) A guide to the seaweed industry, FAO, Rome
Meinita MDN, Kang J-Y, Jeong G-T, Koo H-M, Park S-M, Hong Y-K (2012) Bioethanol production from the acid hydrolysate of the carrageenophyte Kappaphycus alvarezii (cottonii). J Appl Phycol 24:857–862
Meinita MDN, Marhaeni B, Winanto T, Jeong G-T, Khan MNA, Hong Y-K (2013) Comparison of agarophytes (Gelidium, Gracilaria, and Gracilariopsis) as potential resources for bioethanol production. J Appl Phycol 25:1957–1961
Meinita MDN, Marhaeni B, Winanto T, Setyaningsih D, Hong Y-K (2015) Catalytic efficiency of sulfuric and hydrochloric acids for the hydrolysis of Gelidium latifolium (Gelidiales, Rhodophyta) in bioethanol production. J Ind Eng Chem 27:108–114
Meinita MDN, Marhaeni B, Hong Y-K, Jeong G-T (2017a) Enzymatic saccharification of agar waste from Gracilaria verrucosa and Gelidium latifolium for bioethanol production. J Appl Phycol 29:3201–3209
Meinita MDN, Marhaeni B, Oktaviani DF, Jeong G-T, Hong Y-K (2017b) Comparison of bioethanol production from cultivated versus wild Gracilaria verrucosa and Gracilaria gigas. J Appl Phycol 30:143–147
Nunraksa N, Rattanasaensri S, Praiboon J, Chirapart A (2018) Comparison of ethanol production from Gracilaria fisheri and Gracilaria tenuistipitata cultivated in aquaculture system in Thailand. J Appl Phycol 30:3319–3325
Ohno M, Largo DB, Ikumoto T (1994) Growth rate, carrageenan yield and gel properties of cultured kappa- carrageenan producing red alga Kappaphycus alvarezii (Doty) Doty in the subtropical waters of Shikoku, Japan. J Appl Phycol 6:1–5
Pambudi LT, Dyah M, Meinita N, Ariyati RW (2010) Seaweed cultivation in Indonesia: recent status. Mar Biosci Biotechnol 4:6–10
Pereira L, Amado AM, Critchley AT, van de Velde F, Ribeiro-Claro PJA (2009) Identification of selected seaweed polysaccharides (phycocolloids) by vibrational spectroscopy (FTIR-ATR and FT-Raman). Food Hydrocoll 23:1903–1909
Periyasamy C, Anantharaman P, Balasubramanian T, Rao PS (2014) Seasonal variation in growth and carrageenan yield in cultivated Kappaphycus alvarezii (Doty) Doty on the coastal waters of Ramanathapuram district, Tamil Nadu. J Appl Phycol 26:803–810
Porse H, Rudolph B (2017) The seaweed hydrocolloid industry: 2016 updates, requirements, and outlook. J Appl Phycol 29:2187–2200
Sudhakar MP, Jegatheesan A, Poonam C, Perumal K, Arunkumar K (2017) Biosaccharification and ethanol production from spent seaweed biomass using marine bacteria and yeast. Renew Energy 105:133–139
Tan IS, Lee KT (2014) Enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation of seaweed solid wastes for bioethanol production: an optimization study. Energy 78:53–62
Acknowledgments
We thank the Biotechnology Department, College of Fisheries Sciences, Pukyong National University for their collaboration.
Funding
This work was supported by the Ministry of Research, Technology and Higher Education of the Republic of Indonesia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meinita, M.D.N., Marhaeni, B., Jeong, GT. et al. Sequential acid and enzymatic hydrolysis of carrageenan solid waste for bioethanol production: a biorefinery approach. J Appl Phycol 31, 2507–2515 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-019-1755-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-019-1755-8