Abstract
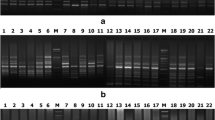
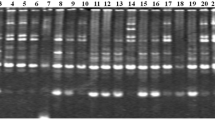
Random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) is an efficient tool to detect DNA polymorphisms and to distinguish different clones and cultivars. We have applied the RAPD technique to distinguish, starting from a single rice seed, among some Italian rice cultivars from market and from National Institute for research on food and nutrition, Italy. We also estimated the genomic similarity among the rice cultivars object of this study taking advantage of the amplification patterns. Despite the low genomic variability among Italian rice cultivars, RAPD technique allowed us to distinguish among them. This indicates that RAPD can be used routinely to verify the identity of Italian rice cultivars in order to prevent fraudulent commercial activity.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CTAB:
-
Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide
- MVSP:
-
Multivariate statistical package for windows
- NL:
-
Nei and Li’s similarity index
- PTB:
-
Phenacyl tiazolium bromide
- RAPD:
-
Random amplified polymorphic DNA
- UPGMA:
-
Unweighted pair group method using arithmetic average
References
Strasburger E, Noll F, Schenck H (2004) Trattato di botanica. Delfino Antonio Editore, Rome
Spada A, Mantegazza R, Biloni M, Caporali E, Sala F (2004) Plant Breed 123:105–111
Ko HL, Cowan DC, Henry RJ, Graham GC, Blakeney AB, Lewin LG (1994) Euphytica 80:179–189
Di Bernardo G, Galderisi U, Cipollaro M, Cascino A (2005) Biotechnol Prog 21:546–549
Galderisi U, Cipollaro M, Di Bernardo G, De Masi L, Galano G, Cascino A (1999) Plant Cell Rep 18:652–655
Micheli MR, Bova R (1997) Fingerprinting methods based on arbitrarily primed PCR. Springer, New York
Welsh J, Mc Clelland M (1990) Nucleic Acids Res 18:7213–7218
Galderisi U, Cipollaro M, Di Bernardo G, De Masi L, Galano G, Cascino A (1999) HortScience 34:1263–1265
Fukuoka S, Hosaka K, Kamijima O (1992) Jpn J Genet 67:243–252
Verma SK, Khanna V, Singh N (1999) Electrophoresis 20:1786–1789
Yu LX, Nguyen HT (1994) Theor Appl Genet 87:668–672
Virk PS, Zhu J, Newbury HJ, Bryan GJ, Jackson MT, Ford-Lloyd BV (2000) Euphytica 112:275–284
Raghunathachari P, Khanna VK, Singh US, Singh NK (2000) Curr Sci 79:994–998
Virk PS, Newbury HJ, Jackson MT, Ford-Lloyd BV (1995) Theor Appl Genet 90:1049–1055
Nei M, Li WH (1979) Proc Natl Acad Sci 76:5269–5273
Kovach WL (1999) MVSP-A multivariate statistical package for windows, ver3.1 Kovach Computing Services, Pentraeth, Wales, UK
Rooney LW, Serna-Saldivar S (1987) In: Corn chemistry and technology. American Association of Cereal Chemist, Inc., St Paul
Acknowledgments
This study is dedicated to the memory of Prof. Antonino Cascino, who passed away on April 6th 2008. We are greatly indebted to Mrs. M.R. Cipollaro and Mrs O. Matarazzo for their administrative assistance, and to Jean Ann Gilder (Scientific Communication sas) for text editing and to Prof. Robert G. Milne (Institute of Plant Virology, CNR, Torino, Italy) for his constructive criticism in revising the manuscript. This research was supported by the National Institute for research on food and nutrition (INRAN) Progetto qualità alimentare to A.C. (2006) and partially by Fondo Integrativo Speciale per la Ricerca (FISR), Tracciabilità genetica per la qualità e sicurezza della filiera della carne e quantizzazione di Organismi Geneticamente Modificati (2005–2009) to M.C.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cirillo, A., Del Gaudio, S., Di Bernardo, G. et al. Molecular characterization of Italian rice cultivars. Eur Food Res Technol 228, 875–881 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-008-1000-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-008-1000-1