Abstract
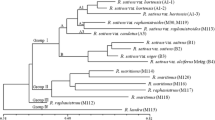
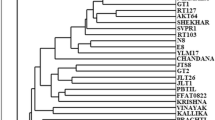
A set of accessions of Oryza sativa from the International Rice Research Institute (Philippines) that included known and suspected duplicates as well as closely related germplasm has been subjected to RAPD analysis. The number of primers, the number of polymorphic bands and the total number of bands were determined that will allow the accurate discrimination of these categories of accessions, including the identification of true and suspected duplicates. Two procedures have been described that could be employed on a more general basis for identifying duplicates in genetic resources collections, and further discussion on the values of such activities is presented.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Campos LP, Raelson JV, Grant WF (1994) Genome relationships among Lotus species based on random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD). Theor Appl Genet 88:417–422
Demeke T, Adams RP, Chibbar R (1992) Potential taxonomic use of random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) — a case study in Brassica. Theor Appl Genet 84:990–994
Howell EC, Newbury HJ, Swennen RL, Withers LA, Ford-Lloyd BV (1994) The use of RAPD for identifying and classifying Musa germplasm. Genome 37:328–332
IRRI (International Rice Research Institute) (1980) Descriptors for rice Oryza sativa L. IBPGR-IRRI rice advisory committee. Manila, Philippines
Kazan K, Manners JM, Cameron DF (1993) Genetic variation in agronomically important species of Stylosanthes determined using random amplified polymorphic DNA markers. Theor Appl Genet 85:882–888
Mantel N (1967) The detection of disease clustering and a generalized regression approach. Cancer Res 27:209–220
MINITAB (1994) MINITAB User's guide. Release 10 for windows. State college. Philadelphia, Pen.
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.
SAS (1990) SAS/STAT User's guide. Version 6, 4th edn, vol 1. SAS Institute, Cary, N.C.
Virk PS, Ford-Lloyd BV, Jackson MT, Newbury HJ (1995) Use of RAPD for the study of diversity within plant germplasm collections. Heredity 74:170–179
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by J. W. Snape
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Virk, P.S., Newbury, H.J., Jackson, M.T. et al. The identification of duplicate accessions within a rice germplasm collection using RAPD analysis. Theoret. Appl. Genetics 90, 1049–1055 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00222920
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00222920