Abstract.
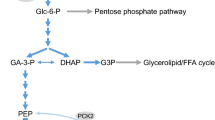
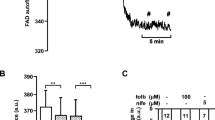
Mitochondrial metabolism is crucial for the coupling of glucose recognition to the exocytosis of the insulin granules. This is illustrated by in vitro and in vivo observations discussed in the present review. Mitochondria generate ATP, which is the main coupling messenger in insulin secretion. However, the subsequent Ca2+ signal in the cytosol is necessary but not sufficient for full development of sustained insulin secretion. Hence, mitochondria generate ATP and other coupling factors serving as fuel sensors for the control of the exocytotic process. Numerous studies have sought to identify the factors that mediate the amplifying pathway over the Ca2+ signal in glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. Predominantly, these factors are nucleotides (GTP, ATP, cAMP, NADPH), although metabolites have also been proposed, such as long-chain acyl-CoA derivatives and glutamate. Hence, the classical neurotransmitter glutamate receives a novel role, that of an intracellular messenger or co-factor in insulin secretion. This scenario further highlights the importance of glutamate dehydrogenase, a mitochondrial enzyme well recognized to play a key role in the control of insulin secretion. Therefore, additional putative messengers of mitochondrial origin are likely to participate in insulin secretion.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received 28 February 2002; received after revision 27 May 2002; accepted 29 May 2002
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maechler, P. Mitochondria as the conductor of metabolic signals for insulin exocytosis in pancreatic β-cells. CMLS, Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 59, 1803–1818 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00012507
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00012507