Abstract
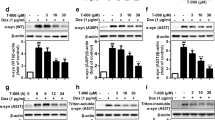
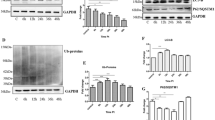
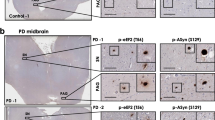
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is characterized, in part, by intracellular neurofibrillary tangles composed of hyperphosphorylated filamentous aggregates of the microtubule-associated protein,Tau. Such hyperphosphorylatedTau is also found in Lewy bodies (LBs), and cytoplasmic inclusion bodies in certain forms of Parkinson’s disease (PD). Further, LBs also contain aggregates of α-synuclein (α-Syn), also a microtubule-associated protein, which has been linked to the genesis of PD. To investigate a specific correlation betweenTau phosphorylation and α-Syn, we generated a SH-SY5Y cell line that stably expresses human wild type α-Syn. Protein expression levels in the stably transfected cell line (SHα-Syn) were within the physiological range of α-Syn expression found inSubstantia nigra. We show here, in the MPP+ (1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium ion) cell model of parkinsonism, a time- and dose-dependent increase in the hyperphosphorylation ofTau at pSer396/404 (PHF-1-reactiveTau, p-Tau), concomitant with increased accumulation of α-Syn, upon treatment of cells with the neurotoxin. This increase in p-Tau was strictly dependent on the presence of α-Syn, since in transfected cells not expressing any α-Syn, MPP+ failed to induce an increase in PHF-1-reactiveTau. The production ofp- Tau caused increased cytotoxicity as indexed by reduced cell viability. Moreover, in the absence of α-Syn, the cells were more resistant to MPP+-induced cell death. The increased levels of both p-Tau and α-Syn led to diminished levels of these proteins associated with the cytoskeleton, which was accompanied by enhanced presence of the proteins in the cytoskeletal-free fractions. These data indicate that α-Syn and p-Tau modulate the pathogenicity of one another, suggesting a novel convergent mechanism of neurodegeneration.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- DAT:
-
dopamine transporter
- FTDP-17:
-
frontotemporal dementia with parkinsonism linked to chromosome 17
- hDAT:
-
human DAT
- LBs:
-
Lewy bodies
- MAP:
-
microtubules-associated protein
- MPP+ :
-
1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium ion
- MPTP:
-
1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine
- MTT:
-
3[4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide
- PD:
-
Parkinson’s disease
- PHF:
-
paired helical filaments
References
Ancolio K, C Alves da Costa, K Ueda and F Checler (2000) alpha-Synuclein and the Parkinson’s disease-related mutant Ala53Thralpha-synuclein do not undergo proteasomal degradation in HEK293 and neuronal cells.Neurosci. lett. 285, 79–82.
Bennett MC, JF Bishop, Y Leng, PB Chock, TN Chase and MM Mouradian (1999) Degradation of alpha-synuclein by proteasome.J. Biol. Chem. 274, 33855–33858.
Cho JH and GV Johnson (2003) Glycogen synthase kinase 3beta phosphorylates tau at both primed and unprimed sites. Differential impact on microtubule binding.J. Biol. Chem. 278, 187–193.
Chun J, T Kwon, EJ Lee, CH Kim, YS Han, SK Hong, S Hyun and SS Kang (2004) 14-3-3 Protein mediates phosphorylation of microtubule-associated protein tau by serum- and glucocorticoidinduced protein kinase 1.Mol. Cells 18, 360–368.
Cuervo AM, L Stefanis, R Fredenburg, PT Lansbury and D Sulzer (2004) Impaired degradation of mutant alpha-synuclein by chap erone-mediated autophagy.Science 305, 1292–1295.
Dauer W and S Przedborski (2003) Parkinson’s disease: mechanisms and models.Neuron 39, 889–909.
Dauer W, N Kholodilov, M Vila, AC Trillat, R Goodchild, KA Larsen, R Staal, K Tieu, Y Schnitz, CA Yuan, V Jackson-Lewis, S Hersch, D Sulzer, S Przedborski, R Burke and R Hen (2002) Resistance of alpha-synuclein null mice to the parkinsonian neurotoxin MPTP.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 14524–14529.
Drolet RE, B Behrouz, KJ Lookingland and JL Goudreau (2004) Mice lacking alpha-synuclein have an attenuated loss of striatal dopamine following prolonged chronic MPTP administration.Neurotoxicology 25, 761–769.
Forman MS, MI Schmidt, S Kasturi, DP Perl, VM Lee and JQ Trojanowski (2002)Tau and alpha-synuclein pathology in amygdala of Parkinsonism-dementia complex patients of Guam.Am. J. Pathol. 160, 1725–1731.
Fornai F, OM Schluter, P Lenzi, M Gesi, R Ruffoli, M Ferrucci, G Lazzeri, CL Busceti, F Pontarelli, G Battaglia, A Pellegrini, F Nicoletti, S Ruggieri, A Paparelli and TC Sudhof (2005) Parkinson-like syndrome induced by continuous MPTP infusion: convergent roles of the ubiquitin-proteasome system and alphasynuclein.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 3413–3418.
Frasier M and B Wolozin (2004) Following the leader: fibrillization of alpha-synuclein and tau.exp. Neurol. 187, 235–239.
Frasier M, M Walzer, L McCarthy, D Magnuson, JM Lee, C Haas, P Kahle and B Wolozin (2005)Tau phosphorylation increases in symptomatic mice overexpressing A3 0P α-synuclein.Exp. Neurol. 192, 274–287.
Giasson BI, MS Forman, M Higuchi, LI Golbe, CL Graves, PT Kotzbauer, JQ Trojanowski and VM Lee (2003) Initiation and synergistic fibrillization of tau and alpha-synuclein.Science 300, 636–640.
Gomez-Santos C, I Ferrer, J Reiriz, F Vinals, M Barrachina and S Ammbrosio (2002) MPP+ increases alpha-synuclein expression and ERK/MAP-kinase phosphorylation in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells.Brain Res. 935, 32–39.
Hamilton RL (2000) Lewy bodies in Alzheimer’s disease: a neuropathological review of 145 cases using alpha-synuclein immunohistochemistry.Brain Pathol. 10, 378–384.
Hoglinger GU, G Carrard, PP Michel, F Medja, A Lombes, M Ruberg, B Friguet and EC Hirsch (2003) Dysfunction of mitochondrial complex I and the proteasome: interactions between two biochemical deficits in a cellular model of Parkinson’s disease.J. Neurochem. 86, 1297–1307.
Iqbal K and I Grundke-Iqbal (2005) Metabolic/signal transduction hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease and other tauopathies.Acta Neuropathol. (Berl.) 109, 25–31.
Jensen PH, H Hager, MS Nielsen, P Hojrup, J Gliemann and R Jakes (1999) alpha-Synuclein binds toTau and stimulates the protein kinase A-catalyzed tau phosphorylation of serine residues 262 and 356.J. Biol. Chem. 274, 25481–25489.
Judkins AR, MS Forman, K Uryu, DA Hinkle, AK Asbury, VM Lee and JQ Trojanowski (2002) Co-occurrence of Parkinson’s disease with progressive supranuclear palsy.Acta Neuropathol. 103, 526–530.
Junn E and MM Mouradian (2002) Human alpha-synuclein overexpression increases intracellular reactive oxygen species levels and susceptibility to dopamine.Neurosci. lett. 320, 146–150.
Klionsky DJ and SD Emr (2000) Autophagy as a regulated pathway of cellular degradation.Science 290, 1717–1721.
Kotzbauer PT, BI Giasson, AV Kravitz, LI Golbe, MH Mark, JQ Trojanowski and VM Lee (2004) Fibrillization of alpha-synuclein and tau in familial Parkinson’s disease caused by the A53T alpha-synuclein mutation.exp. Neurol. 187, 279–288.
Lindersson E, R Beedholm, P Hojrup, T Moos, W Gai, KB Hendil and PH Jensen (2004) Proteasomal inhibition by alpha-synuclein filaments and oligomers.J. Biol. Chem. 279, 12924–12934.
Lippa CF, H Fujiwara, DM Mann, B Giasson, M Baba, ML Schmidt, LE Nee, B O’Connell, DA Pollen, P St George-Hyslop, B Ghetti, D Nochlin, TD Bird, NJ Cairns, VM Lee, T Iwatsubo and JQ Trojanowski (1998) Lewy bodies contain altered alphasynuclein in brains of many familial Alzheimer’s disease patients with mutations in presenilin and amyloid precursor protein genes.Am. J. Pathol. 151, 1365–1370.
Lippa CF, MI Schmidt, VM-Y Lee and JQ Trojanowski (1999) Antibodies to alpha-synuclein detect Lewy bodies in many Down’s syndrome brains with Alzheimer’s disease.Ann. Neurol. 45, 353–357.
Loo DT and JR Rillema (1998) Measurement of cell death.Methods Cell. Biol. 57, 251–264.
Machida Y, T Chiba, A Takayanagi, Y Tanaka, M Asanuma, N Ogawa, A Koyama, T Iwatsubo, S Ito, PH Jansen, N Shimizu, K Tanaka, Y Mizuno and N Hattori (2005) Common anti-apoptotic roles of parkin and alpha-synuclein in human dopaminergic cells.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 332(1), 233–240.
McNaught KS, LM Bjorklund, R Belizaire, O Isacson, P Jenner and CW Olanow (2002) Proteasome inhibition causes nigral degeneration with inclusion bodies in rats.Neuroreport 13, 1437–1441.
Meredith GE, S Totterdell, E Petroske, K Santa Cruz, RC Callison Jr and YS Lau (2002) Lysosomal malfunction accompanies alpha-synuclein aggregation in a progressive mouse model of Parkinson’s disease.Brain Res. 956, 156–165.
Mori H, M Oda, T Komori, N Arai, M Takanashi, T Mizutani, S Hirai and Y Mizuno (2002) Lewy bodies in progressive supranuclear palsy.Acta Neuropathol. 104, 273–278.
Osterova N, L Petrucelli, M Farrer, N Mehta, P Choi, J Hardy and B Wolozin (1999) alpha-Synuclein shares physical and functional homology with 14-3-3 proteins.J. Neurosci. 19, 5782–5791.
Paxinou E, Q Chen, M Weisse, BI Giasson, EH Norris, SM Rueter, JQ Trojanowski, VM Lee and H Ischiropoulos (2001) Induction of alpha-synuclein aggregation by intracellular nitrative insult.J. Neurosci. 21, 8053–8061.
Purisai MG, AL McCormack, WJ Langston, LC Johnston and DA DiMonte (2005) alpha-Synuclein expression in the substantia nigra of MPTP-lesioned non-human primates.Neurobiol. Dis. 20, 898–906.
Rideout HJ, KE Larsen, D Sulzer and L Stefanis (2001) Proteasomal inhibition leads to formation of ubiquitin/alpha-synuclein-immunoreactive inclusions in PC12 cells.J. Neurochem. 78, 899–908.
Robertson DC, O Schmidt, N Ninkina, PA Jones, J Sharkey and VL Buchman (2004) Developmental loss and resistance to MPTP toxicity of dopaminergic neurones in substantia nigra pars compacta of gamma-synuclein, alpha-synuclein and double alpha/ gamma-synuclein null mutant mice.J. Neurochem. 89, 1126–1136.
Sawada H, R Kohno, T Kihara, Y Izumi, N Sakka, M Ibi, M Nakanishi, T Nakamizo, K Yamakawa, H Shibasaki, N Yamamoto, A Akaike, M Inden, Y Kitamura, T Taniguchi and S Shimohama (2004) Proteasome mediates dopaminergic neuronal degeneration, and its inhibition causes alpha-synuclein inclusions.J. Biol. Chem. 279, 10710–10719.
Schlüter OM, F Fornai, MG Alessandri, S Takamori, M Geppert, R Jahn and TC Sudhof (2003) Role of alpha-synuclein in 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-induced parkinsonism in mice.Neuroscience 118, 985–1002.
Sidhu A, C Wersinger, CE Moussa and P Vernier (2004) The role of alpha-synuclein in both neuroprotection and neurodegeneration.Ann. NyAcad. Sci. 1035, 250–270.
Skoulakis EM and RL Davis (1998) 14-3-3 Proteins in neuronal development and function.Mol. Neurobiol. 16, 269–284.
Snyder H, K Mensah, C Theisler, J Lee, A Matouschek and B Wolozin (2003) Aggregated and monomeric alpha-synuclein bind to the S6’ proteasomal protein and inhibit proteasomal function.J. Biol. Chem. 278, 11753–11759.
Song X and M Ehrich (1998) Alterations of cytoskeletal tau protein of SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells after exposure to MPTP.Neurotoxicology 19, 73–81.
Tofaris GK, R Layfield and MG Spillantini (2002) alpha-Synuclein metabolism and aggregation is linked to ubiquitin-independent degradation by the proteasome.FeBSlett. 509, 22–26.
Vila M, S Vukosavic, V Jackson-Lewis, M Neystat, M Jakowec and S Przedborski (2001) alpha-Synuclein up-regulation in substantia nigra dopaminergic neurons following administration of the parkinsonian toxin MPTP.J. Neurochem. 74, 721–729.
Webb JL, B Ravikumar, J Atkins, JN Skepper and DC Rubinsztein (2003) alpha-Synuclein is degraded by both autophagy and the proteasome.J. Biol. Chem. 278, 25009–25013.
Wersinger C and A Sidhu (2003) Attenuation of dopamine transporter activity by alpha-synuclein.Neurosci. lett. 340, 189–192.
Wersinger C and A Sidhu (2005) Disruption of the interaction of alpha-synuclein with microtubules enhances cell surface recruitment of the dopamine transporter.Biochemistry 44, 13612–13624.
Wersinger C, D Prou, P Vernier and A Sidhu (2003) Modulation of dopamine transporter function by alpha-synuclein is altered by impairment of cell adhesion and by induction of oxidative stress.FASeBJ. 17, 2151–2153.
Wersinger C, M Banta and A Sidhu (2004) Comparative analyses of alpha-synuclein expression levels in rat brain tissues and transfected cells.Neurosci lett. 358, 95–98.
Wilhelmsen KC, MS Forman, HJ Rosen, LI Alving, J Goldman, J Feiger, JV Lee, SK Segall, JH Kramer, C Lomen-Hoerth, KP Rankin, J Johnson, HS Feiler, MW Weiner, VM Lee, JQ Trojanowski and BL Miller (2004) 17q-Linked frontotemporal dementia-amyotrophic lateral sclerosis without tau mutations with tau and alpha-synuclein inclusions.Arch. Neurol. 61, 398–406.
Yuan Z, A Agarwal-Mawal and HK Paudel (2004) 14-3-3 Binds to and mediates phosphorylation of microtubule-associated tau protein by Ser9-phosphorylated glycogen synthase kinase 3beta in the brain.J. Biol. Chem. 279, 26105–26114.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duka, T., Sidhu, A. The neurotoxin, MPP+, induces hyperphosphorylation ofTau, in the presence of α-Synuclein, in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. neurotox res 10, 1–10 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03033329
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03033329