Abstract
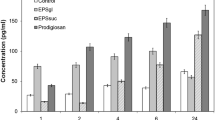
The immunomodulatory activities of monophosphoryl lipid A (MLA) and diphosphoryl lipid A analogues obtained from the sensitive strain ofE. coli and from the resistant strains adapted to a quaternary ammonium salt and an amine oxide were compared. All analogues considerably stimulated the activity of human leukocytes although the analogue from the sensitive strain at a higher concentration significantly suppressed phagocytosis. The MLA analogue exhibited a suppressive effect on the microbicidal activity of human leukocytes againstE. coli and the peroxidase activity. Adaptation of bacteria to amphiphilic antimicrobial compounds, which is accompanied by chemical changes in their lipid A, only slightly reduced their immunomodulatory activity when compared with the analogue from the sensitive strain. On the other hand, the diphosphoryl analogues were less active than MLA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boyum A.: Isolation of leukocytes from human blood — further observations. Methylcellulose dextran, and ficoll as erythrocyte aggregating agents.Scand.J.Clin.Lab.Invest. 97 Suppl., 31–50 (1968).
Bukovsky M., Mlynarčik D., Nagy A., Bella J.: Outer membrane alterations inEscherichia coli cells adapted to amine oxides.Acta Fac.Pharm. 46, 153–167 (1991).
Bukovsky M., Mlynarčík D., Koščová H.: Change of immunomodulating properties ofEscherichia coli caused by artificial resistance to amine oxides. (In Slovak)Farm.Obzor 57, 59–68 (1998).
Čupková V., Vinter V., Devinsky F., Lacko I., Mlynarčik D.: Inhibitory effect of 1-methyldodecyldimethylamine oxide andN,N-bis(dodecylidmethyl)-1,2-ethanediammonium dibromide on the spores ofBacillus cereus.Folia Microbiol. 33, 433–439 (1988).
Dubois-Brissonnet F., Malgrange C., Guerin-Mechin L., Heyd B., Leveau J.-Y.: Changes in fatty acid composition ofPseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 15442 induced by growth conditions: consequences of resistance to quaternary ammonium compounds.Microbios 106, 97–110 (2001).
Elliot G.T.: Monophosphoryl lipid A induces delayed preconditioning against cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury.J.Mol.Cell.Cardiol. 30, 3–17 (1998).
Fekenčík M., Lacko I., Devínsky F.: Immunomodulatory activity of some amphiphilic compounds.Pharmazie 45, 695–696 (1990).
Frecer V., Ho B., Ding L.J.: Molecular dynamics study on lipid A fromEscherichia coli: insights into its mechanism of biological action.Biochim.Biophys.Acta 1466, 87–104 (2000).
Hagen S.R., Thomson J.D., Snyder S.D., Myers K.R.: Analysis of monophosphoryl lipid A immunostimulant preparation fromSalmonella minnesota RP 595 by high-performance liquid chromatography.J.Chromatogr.A 767, 53–61 (1997).
Hoštacká A., Majtán V.: Enzymic and permeability activity ofPseudomonas aeruginosa after treatment with sub-MICs of organic ammonium salts.Folia Microbiol. 39, 197–202 (1994).
Hoštacka A., Majtán V., Hybenová D.: Antimicrobial efficacy of quaternary bisammonium salts and the effect of their sub-MICs onPseudomonas aeruginosa virulence factors.Folia Microbiol. 40, 283–287 (1995).
Ikeda S., Nishumira C., Matsuura M., Homma J.Y., Kiso M., Hasegawa A.: Effect of acyl substituents of synthetic lipid A-subunit analogues on their immunomodulating antiviral activity.Antiviral.Res. 13, 327–333 (1990).
Ismaili J., Rennesson J., Aksoy E., Vekemans J., Vincart B., Amraoui Z., Van Laethem F., Goldman M., Dubois P.M.: Monophosphoryl lipid A activates both human dendritic cells and T cells.J.Immunol. 168, 926–932 (2002).
Kuželová M., Bukovský M., Solčanova M., Košćova H., Švec P.: The immunomodulatory properties of modificated lipid A-endotoxin A in ischemic/reperfusion injury conditions. (In Slovak)Českosl.Fyziol. 48, 153 (1999).
Lentschat A., El-Samalouti V.T., Schletter J., Kusumoto S., Brade L., Rietchel E.T., Gerdes J., Ernst M., Flad H.-D., Ulmer J.: The internalization time course of a given lipopolysaccharide chemotype does not correspond to its activation kinetics in monocytes.Infect.Immun. 67, 2515–2521 (1999).
Lüderitz O., Galanos C., Lehmann V., Meyer H., Rietschel E.T., Weckesser J.: Chemical structure and biological activities of lipid A’s from various bacterial families.Naturwissenschaften 65, 578–585 (1978).
Majtánová E., Majtán V., Hoštacká A.: Effects of amphiphilic compounds on metabolic and biological activities ofSalmonella typhimurium.Arzhem.Forsch./Drug Res. 46, 64–67 (1996).
Masihi K.N., Lange W., Johnson A.G., Ribi E.: Enhancement of chemiluminescence and phagocytic activities by non-toxic and toxic forms of lipid A.J.Biol.Resp.Mod. 5, 462–469 (1986).
Matsuura M., Kiso M., Hasegawa A.: Activity of monosaccharide lipid A analogues in human monocyte cells as agonist or antagonist of bacterial lipopolysaccharide.Infect.Immun. 67, 6286–6292 (1999).
Pospíšil S., Řezanka T.: Changes in fatty acid branching and unsaturation ofStreptomyces cinnamonensis as a response to NaCl concentration.Folia Microbiol. 39, 187–190 (1994).
Saha D.C., Barua R.S., Astiz M.E., Rackow E.C., Eales-Reynolds L.J.: Monophosphoryl lipid A stimulated up-regulation of reactive oxygen intermediates in human monocytesin vitro.J.Leukoc.Biol. 70, 381–385 (2001).
Salkowski C.A., Detore G., Franks A., Falk M.C., Vogel S.N.: Pulmonary and hepatic gene expression following cecal ligation and puncture: monophosphoryl lipid A prophylaxis attenues sepsis-induced cytokine and chemokine expression and neutrophil infiltration.Infect.Immun. 66, 3569–3578 (1998).
Van Alphen L., Lugtenberg B., Rietschel E.T., Mombers C.: Architecture of the outer membrane ofEscherichia coli K12. Phase transitions of the bacteriophage K3 receptor complex.Eur.J.Biochem. 101, 571–579 (1979).
Westphal O., Jann K.: Bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Extraction with phenol-water and further applications of the procedure, pp. 83–91 in R.L. Whistler, J.N. BeMiller, M. Wolfrom (Eds):Methods in Carbohydrate Chemistry, Vol. 5. Academic Press, New York-London 1965.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dubničková, M., Bukovský, M. & Mlynarčik, D. Activation of human leukocytes by lipid A fromE. coli strains adapted to quaternary ammonium salt and amine oxide. Folia Microbiol 48, 543–547 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02931338
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02931338