Abstract
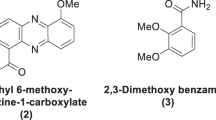
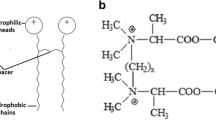
Antipseudomonadal activity of homologous series of six quaternary bisammonium salts (QBAS) (4,7-dioxo-3,8-dioxadekan-1,1-[bis(alkyldimethyldiammonium dibromide)] as well as the effect of their subinhibitory concentrations (sub-MICs) onPseudomonas aeruginosa virulence factors was studied. Antibacterial activity of QBAS increased up to a certain length of the chain and then decreased with further elongation. All the tested sub-MICs of QBAS caused a significant suppression of phospholipase C activity (to 0–41%). Elastase and proteinase activity were less efficiently reduced. A more effective decrease of these activities was only found after treatment with one-fourth of the MICs of the tested substances. QBAS caused only an erratic decrease of alginate production.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bitter T., Muir H.M.: A modified uronic acid carbazole reaction.Analyt. Biochem. 4, 330–334 (1962).
Botzenhart K., Ruden H.: Hospital infections caused byPseudomonas aeruginosa, pp. 1–15 inBasic Research and Clinical Aspects of Pseudomonas aeruginosa (G. Doring, I.A. Holder, K. Botzenhart, Eds). Karger, Basel-Munich-Paris-London-New York-New Delhi-Singapore-Tokyo-Sydney 1987.
Devínsky F., Lacko I., Mlynarčík D., Račanský V., Krasnec L.: Relationship between critical micelle concentrations and minimum inhibitory concentrations for some non-aromatic quaternary ammonium salts and amine oxides.Tenside Detergents 22, 10–15 (1985).
Devínsky F., Kopecká-Leitmanová A., Šeršeň F., Balgavý P.: Cut-off effect in antimicrobial activity and in membrane perturbation efficiency of the homologous series of N,N-dimethylalkylamine oxides.J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 42, 790–794 (1990).
Grimwood K., To M., Rabin H.R., Woods E.D.: Inhibition ofPseudomonas aeruginosa exoenzyme expression by subinhibitory antibiotic concentrations.Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 33, 41–47 (1989).
Hirakata Y., Kaku M., Mizukane R. et al.: Potential effects of erythromycin on host defense systems and virulence ofPseudomonas aeruginosa.Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 36, 1912–1927 (1992).
Hoštacká A., Majtán V.: Alterations inPseudomonas aeruginosa exoproducts by sub-MICs of some antibiotics.Folia Microbiol. 38, 349–352 (1993).
Hoštacká A., Majtán V.: Enzymic and permeability activity ofPseudomonas aeruginosa after treatment with sub-MICs of organic ammonium salts.Folia Microbiol. 39, 197–202 (1994).
Knutson C.A., Jeanes A.: A new modification of the carbazole analysis: Application to heteropolysaccharides.Analyt. Biochem. 24, 470–481 (1968).
Majtán V., Drobnica L'.: Dynamics of growth of atypical mycobacteria in different liquid cultivation media.Folia Microbiol. 25, 347–353 (1980).
Majtán V., Hoštacká A., Mlynarčík D., Devínsky F.: Suppression of virulence factors ofPseudomonas aeruginosa by subinhibitory concentrations (sub-MICs) of quaternary ammonium salts.Arzneimit. Forsch. Drug Res. 45, 327–330 (1995a).
Majtán V., Majtánová L'., Mlynarčík D.: Efficacy of new ammonium salts onPseudomonas aeruginosa andSalmonella typhimurium.Arzneimit. Forsch. Drug. Res. 45, 198–199 (1995b).
Morris G., Brown M.R.W.: Novel modes of action of aminoglycoside antibiotics againstPseudomonas aeruginosa.Lancet 18, 1359–1360 (1988).
Pollack M.:Pseudomonas aeruginosa, pp. 1673–1691 inPrinciples and Practise of Infectious Diseases (G.L. Mandell, R.G. Douglas Jr., J.E. Bennett, Eds), 3rd ed. Churchill Livingstone, New York 1990.
Ryden A.C., Lindbergh M., Philipson L.: Isolation and characterization of two-protease-producing mutants fromStaphylococcus aureus.J. Bacteriol. 116, 25–32 (1973).
Stinson M.W., Hayden C.: Secretion of phospholipase C byPseudomonas aeruginosa.Infect. Immun. 25, 558–564 (1979).
Sýkora P. Čeplíková V., Foltýnová Z., Horniak L., Ebringer L.: Elimination of plasmids pKM 101 and F'lac fromSalmonella typhimurium andEscherichia coli by bisammonium salt.Folia Microbiol. 36, 240–245 (1991).
Vasil M.L.:Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Biology, mechanisms of virulence, epidemiology.J. Pediatr. 108, 800–805 (1986).
Warren R.L., Baker N.R., Johnson J., Stapleton M.J.: Selective inhibitory of the accumulation of extracellular proteases ofPseudomonas aeruginosa by gentamicin and tobramycin.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 27, 468–472 (1985).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoštacká, A., Majtán, V. & Hybenová, D. Antimicrobial efficacy of quaternary bisammonium salts and the effect of their sub-MICs onPseudomonas aeruginosa virulence factors. Folia Microbiol 40, 283–287 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02814209
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02814209