Abstract
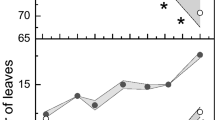
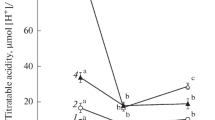
Growth analysis indicated that carbon gain in the alpine succulentSedum album tended to take place early during the growing season. Leaf water potential remained unchanged for a considerable length of time after the imposition of water stress in the field. Induction of crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM) by protracted water stress occurred before any signs of stress could be observed in the leaves, and appeared to be influenced by a complex interaction of environmental conditions including temperature and duration of sunshine. Increased levels of proline and betaine towards the end of the growing season appeared to reflect seasonal changes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackerson, R.C., Radin, J.W.: Abscisic acid accumulation in cotton leaves in response to dehydration at high pressure.—Plant Physiol.71: 432–433, 1983.
Arnon, D.I.: Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. Polyphenoloxidase inBeta vulgaris.—Plant Physiol.24: 1–15, 1949.
Chiariello, N.R., Mooney, H.A., Williams, K.: Growth, carbon allocation and cost of plant tissues.— In: Pearcey, R.W., Ehleringer, J., Mooney, H.A., Rundel, P.W. (ed.): Physiological Ecology. Pp. 327–365. Chapman & Hall, London 1989.
Earnshaw, M.J., Carver, K.A., Lee, J.A.: Changes in leaf water potential and CAM inSemprevivum montanum andSedum album in response to water availability in the field.—Oecologia67: 486–492, 1985.
Earnshaw, M.J., Carver, K.A., Charlton, W.A.: Leaf anatomy, water relations and crassulacean acid metabolism in the chlorenchyma and colourless internal water-storage tissue ofCarpobrotus edulis andSenecio mandraliscae.—Planta170: 421–432, 1987.
Groenhof, A.C., Bryant, J.A., Etherington, J.R.: Photosynthetic changes in the inducible CAM plantSedum telephium L. following the imposition of water stress. I. General characteristics.—Ann. Bot.57: 689–695, 1986.
Hartung, W., Davis, W.J.: Drought-induced changes in physiology and ABA.—In: Davis, W.J., Jones, H.G. (ed.): Abscisic Acid Physiology and Biochemistry. Pp. 63–79, Bios Scientific Publishers, Oxford 1991.
Kluge, M.: IsSedum acre a CAM plant?.—Oecologia29: 77–83, 1977.
Lee, H.S.J., Griffiths, H.: Induction and repression of CAM inSedum telephium L. in response to photoperiod and water stress.—J. exp. Bot.38: 834–84, 1989.
Raschke, K.: Involvement of abscisic acid in the regulation of gas exchange: evidence and inconsistancies.— In: Wareing, P.F. (ed.): Plant Growth Substances. Pp 851–859. Academic Press, London 1982.
Sayed, O.H., Hegazy, A.K.: Life table analysis and ecophysiology ofMesembryanthemum nodiflorum in its natural environment.—Acta oecol.12: 753–760, 1991.
Schuber, M., Kluge, M.:In situ studies of crassulacean acid metabolism inSedum mite Gil.— Oecologia50: 82–87, 1981.
Singh, T.N., Paleg, L.G., Aspinall, D.: Stress metabolism. I. Nitrogen metabolism and growth in the barley plant during water stress.—Aust. J. biol. Sci.26: 45–56, 1973.
Stewart, G.P.: Desiccation injury, anhydrobiosis and survival.—In: Hamlyn, G.J., Flowers, T.J., Jones, M.B. (ed.): Plants Under Stress. Pp. 115–127. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge 1989.
Storey, R., Wyn Jones, R.G.: Quaternary ammonium compounds in plants in relation to salt resistance.—Phytochemistry16: 447–543, 1977.
Winter, K.: Crassulacean acid metabolism.—In: Barber, J., Baker, N.R. (ed.): Photosynthetic Mechanisms and the Environment. Pp. 329–387. Elsevier, Amsterdam 1985.
Winter, K., Lüttge, U., Winter, E., Troughton, J.H.: Seasonal shift from C3 photosynthesis to crassulacean acid metabolism inMesembryanthemum crystallinum growing in its natural environment.—Oecologia34: 225–237, 1978.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sayed, O.H., Earnshaw, M.J. & Cooper, M. Growth, water relations, and CAM induction inSedum album in response to water stress. Biol Plant 36, 383–388 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02920936
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02920936