Abstract
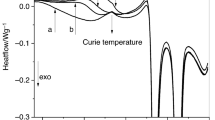
An accurate four-line ac electrical resistance measurement (ERM) apparatus was developed. By using the ERM the crystallization kinetics of amorphous Ni80P20, FeZr2, Fe86B14 alloys were investigated. The experimental results show that the ERM can identify the early stage of crystallization in amorphous alloys. The ERM detects a crystallization temperature range obviously wider than the DSC does, indicating that the ERM is more sensitive to the structure evolution in crystallization. For the eutectic or polymorphic crystallization, three distinct processes can be identified from the measured resistance variation: (i) crystal nucleation, (ii) subsequent growth of crystal nuclei, and (iii) coarsening of the crystallites. In the early stage of the primary crystallization, the ERM results reflect the nucleation information as well.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Luborsky, F. E., Amorphous Metallic Alloys, London-Frome: Butterworth & Co (Publishers) Ltd., 1983: 144–168.
Cahn, R. W., Haasen, P., Physical Metallurgy, Amsterdam: North-Holland Physics Publ., 1983: 1825.
Ranganathan, S., Vonheimendahl, M., The three activation energies with isothermal transformations: application to metallic glasses, J. Mater. Sci., 1981, 16: 2401.
Vonheimendalh, M., Kuglstatter, G., The activation energies of crystallization in the amorphous alloy metglass 2826A, J. Mater. Sci., 1981, 16: 2405.
Christian, J. W., Transformation in Metals and Alloys, Oxford: Pergamon, 1975.
Yinnon, H., Uhlmann, D. H., Applications of thermoanalytical techniques to the study of crystallization kinetics in glassforming liquids, part I: theory., J. Non-Crys. Solids, 1983, 54: 253.
Lu, K., Lück, R., Predel, B., The temperature vs time transformation (T-T-T) diagram for a transition from the amorphous to the nanocrystalline state, Acta Metall. Mater., 1994, 42: 2303.
Kelton, K. F., Spaepen, F., A study of the devitrification of Pd82Si18 over a wide temperature range, Acta Metall., 1985, 3: 455.
Altounian, Z., Volkert, C. A., Strom-Olsen, J. O., Crystallization characteristics of Fe-Zr metallic glasses from Fe43Zr57 to Fe20Zr80, J. Appl. Phys., 1985, 57: 1777.
Kwong, V., Koo, Y. C., Thorpe, S. J. et al., Crystallization behavior of Al85Y10Ni5 by isochronal and isothermal annealing, Acta Metall. Mater., 1991, 39: 1563.
Jáskiewicz, P., Method to study crystallization kinetics by electrical resistivity, Mater. Sci. Forum, 1998, 269-272: 743.
Hofstetter, W., Sassik, H., Grossinger, R. et al., Determination of the onset of crystallization of amorphous materials using defferent methods, Mater. Sci. Eng., 1997, A226–228: 213.
Schulz, R., Samwer, K., Johnson, W. L., Kinetics of phase separation in Cu50Zr50 metallic glasses, J. Non-Crys. Solids, 1984, 61&62: 997.
Smits, F. M., Measurement of sheet resistivities with the four-point probe, Bell System Technical Journal 1958, 37: 711.
Cohen, R. L., West, K. W., Characterization of metals and alloys by electrical resistivity measurements, Material Evaluation, 1983, 41: 1074.
Kelton, K. F., Holzer, J. C., Apparatus forin-situ measurements of changes in the electrical resistivity accompanying phase changes in metastable metallic alloys, Rew. Sci. Instru., 1988, 59: 347.
Muir, W. B., Strom-Olsen, J. O., A sensitive ac difference method for electron transport measurements, J. Phys. E: Sci. Instru., 1976, 9: 163.
Lu, K., Wang, J. T., Relationship between crystallization temperature and pre-existing nuclei in amorphous Ni-P alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng., 1988, 97: 399.
Kissinger, H. E., Reaction kinetics in differential thermal analysis, Anal. Chem., 1957, 29: 1702.
Wang, J. T., Di L. M., Li, S. L. Z., Phys. Chem., 1987, 2: 383.
Lu, K., Wang, J. T., Crystallization kinetics of Ni-P glass activation energies for nucleation and growth of nuclei, J. Mater. Sci., 1988, 23: 3001.
Hamlyn-Harris, J. H., Stjohn, D. H., Sood, D. K., The thermal stability of Ni-11 wt% P metallic glass, J. Mater. Sci., 1990, 25: 3008.
Lu, K., Wei, W. D., Wang, J. T., Grain growth kinetics and interfacial energies in nanocrystalline Ni-P alloys, J. Appl. Phys., 1991, 69: 7345.
Blank-Bewersdorf, W., Koester, U., Mater. Sci. Eng., 1988, 9: 313.
Lu, K., Zhang, X. H., Electrical resistance measurements for identification of crystal nucleation and growth in amorphous solids: a case study, to be published in Phil. Mag. Letters, 2000.
Lu, K., Grain growth processes in nanocrystalline materials studied by differential scanning calorimetry, Scripta Metall. Mater., 1991, 25: 2047.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Lu, K. Accurate electrical resistance measurement of the crystallization kinetics of amorphous alloys. Sci. China Ser. E-Technol. Sci. 44, 33–41 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02916723
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02916723