Summary
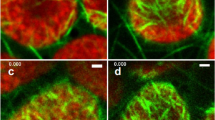
Examination of unfixed immature somatic embryos of white spruce (Picea glauca) with fluorescent rhodamine-labeled phalloidin revealed an extensive network of fine actin microfilaments (MFs) in the embryonal region which were not detected in specimens fixed with formaldehyde. Transition cells linking the embryonal region and suspensor cells contained fine MFs as well as bundles of MFs. The large, highly vacuolated suspensor cells were characterized by actin MF cables only. Treatment of embryos with cytochalasin B (CB) removed the fine MFs from the embryonal region and transition cells, but many MF cables in suspensor cells were resistant. Full recovery from CB treatment was observed in most somatic embryos. Embryogenic protoplasts capable of regenerating to somatic embryos in culture were released from only the embryonal region of somatic embryos. Both uninucleate and multinucleate embryogenic protoplasts retained the extensive network of fine actin MFs. In contrast, protoplasts derived from vacuolated suspensor cells and vacuolated free-floating cells contained thick MF bundles and were not embryogenic. Distinct MF cages enclosed nuclei in multinucleate protoplasts and may be responsible for preventing nuclear fusion. Microspectrophotometric analyses showed that the DNA contents of embryonal cells in the embryo and embryogenic protoplasts were similar and characteristic of rapidly dividing cell populations. However, transition and suspensor cells which released nonembryogenic protoplasts appeared to be arrested in G1, and suspensor cells showed signs of DNA degradation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe, S.; You, W.; Davies, E. Protein bodies in corn endosperm are enclosed by and enmeshed in F-actin. Protoplasma 165:139–149; 1991.
Attree, S. M.; Bekkaoui, F.; Dunstan, D. I., et al. Regeneration of somatic embryos from protoplasts isolated from an embryogenic suspension culture of white spruce (Picea glauca). Plant Cell Rep. 6:480–483; 1987.
Attree, S. M.; Dunstan, D. I.; Fowke, L. C. Initiation of embryogenic callus and suspension cultures, and improved embryo regeneration from protoplasts, of white spruce (Picea glauca). Can. J. Bot. 67:1790–1795; 1989.
Cho, S. O.; Wick, S. M. Actin in the developing stomatal complex of winter rye: a comparison of actin antibodies and Rh-Phalloidin labelling of control and CB-treated tissues. Cell Motil. Cytoskeleton 19:25–36; 1991.
Cutler, A. J.; Saleem, M.; Wang, H. Cereal protoplast recalcitrance. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 27P:104–111; 1991.
De Jong, A. J.; Schmidt, E. D. L.; De Vries, S. C. Early events in higherplant embryogenesis. Plant Mol. Biol. 22:367–377; 1993.
Dijak, M.; Simmonds, D. H. Microtubule organization during early embryogenesis from mesophyll protoplasts ofMedicago sativa L. Plant Sci. 58:183–191; 1988.
Dolezel, J. Improvement of accuracy of scanning absorption measurement of nuclear DNA content in plants. Acta Histochem. 86:123–127; 1989.
Fowke, L. C. Ultrastructural studies of plant protoplast fusion. In: Bajaj, Y. P. S., ed. Biotechnology in agriculture and forestry. Vol. 8. Plant protoplasts and genetic engineering I. Berlin: Springer Verlag; 1988:289–303.
Fowke, L. C.; Attree, S. M.; Wang, H., et al. Microtubule organization and cell division in embryogenic protoplast cultures of white spruce (Picea glauca). Protoplasma 158:86–94; 1990.
Gorst, J.; Wernicke, W.; Gunning, B. E. S. Is the preprophase band of microtubules a marker of organization in suspension cultures? Protoplasma 134:130–140; 1986.
Gunning, B. E. S. The cytokinetic apparatus: its development and spatial regulation. In: Lloyd, C. W., ed. The cytoskeleton in plant growth and development. New York: Academic Press; 1982:229–292.
Hakman, I.; Fowke, L. C. An embryogenic cell suspension culture ofPicea glauca (white spruce). Plant Cell Rep. 6:20–22; 1987.
Hakman, I.; Rennie, P.; Fowke, L. C. A light and electron microscope study ofPicea glauca (white spruce) somatic embryos. Protoplasma 140:100–109; 1987.
Hush, J. M.; Overall, R. L. Re-orientation of cortical F-actin is not necessary for wound-induced microtubule re-orientation and cell polarity establishment. Protoplasma 169:97–106; 1992.
Jung, G.; Hahne, B.; Wernicke, W. Cell cycle in potentially dedifferentiating cereal mesophyll protoplasts cultured in vitro II. Behaviour of the cytoskeleton. J. Plant Physiol. 141:428–435; 1993.
Jung, G.; Wernicke, W. Patterns of actin filaments during cell shaping in developing mesophyll of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Eur. J. Cell Biol. 56:139–146; 1991.
Kengen, H. M. P.; Derksen, J. Organization of microtubules and microfilaments in protoplasts from suspension cells ofNicotiana plumbaginifolia: a quantitative analysis. Acta Bot. Neerl. 40:29–40; 1991.
La Claire, J. W.; Fulginiti, R. Dynamics of microtubule reassembly and reorganization in the coenocytic green algaErnodesmis verticillata (Kutzing) Boergesen. Planta 185:447–457; 1991.
Lehrer, S. S. Damage to actin filaments by glutaraldehyde: protection by tropomyosin. J. Cell Biol. 90:459–466; 1981.
Liu, B.; Palevitz, B. A. Organization of cortical microfilaments in dividing root cells. Cell Motil. Cytoskeleton 23:252–264; 1992.
Lloyd, C. W. Cytoskeletal elements of the phragmosome establish the division plane in vacuolated higher plant cells. In: Lloyd, C. W., ed. The cytoskeletal basis of plant growth and form. New York: Academic Press; 1991:245–257.
McLean, B. G.; Huang, S.; McKinney, E. C., et al. Plants contain highly divergent actin isovariants. Cell Motil. Cytoskeleton 17:276–290; 1990.
Meyer, U.; Buttner, G.; Jurgens, G. Apical-basal pattern formation in theArabidopsis embryo: studies on the role of the gnom gene. Development 117:149–162; 1993.
Nagl, W. Endopolyploidy and polyteny in differentiation and evolution. Elsevier/North-Holland Biomedical Press, Amsterdam; 1978.
Owens, J. N.; Blake, M. D. Forest tree seed production. Petawawa Nat. For. Inst. Inf. Rep. PI-X-53; 1985.
Sonobe, S.; Shibaoka, H. Cortical fine actin filaments in higher plant cells visualized by rhodamine-phalloidin after pretreatment with m-maleimidobenzoyl N-hydroxysuccinimide ester. Protoplasma 148:80–86; 1989.
Strome, S. Determination of cleavage planes. Cell 72:3–6; 1993.
Sun, H.-Q.; Kwiatkowska, K.; Yin, H. L. Actin monomer binding proteins. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 7:102–110; 1995.
Tang, X.; Lancelle, S. A.; Hepler, P. K. Fluorescence microscopic localization of actin in pollen tubes: comparison of actin antibody and phalloidin staining. Cell Motil. Cytoskeleton 12:216–224; 1989.
Von Aderkas, P. Embryogenesis from protoplasts of haploid European larch. Can. J. For. Res. 22:397–402; 1992.
Wang, H.; Cutler, A. J.; Fowke, L. C. High frequencies of preprophase bands in soybean protoplast cultures. J. Cell Sci. 92:575–580; 1989.
Webb, M. C.; Gunning, B. E. S. The microtubular cytoskeleton during development of the zygote, proembryo and free-nuclear endosperm inArabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh. Planta 184:187–195; 1991.
Wick, S. M. Spatial aspects of cytokinesis in plant cells. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 3:253–260; 1991.
Zalokar, M.; Erk, I. Division and migration of nuclei during early embryogenesis ofDrosophila melanogaster. J. Microsc. Biol. Cell 25:97–106; 1976.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Binarova, P., Cihalikova, C., Dolezel, J. et al. Actin distribution in somatic embryos and embryogenic protoplasts of white spruce (Picea glauca). In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Plant 32, 59–65 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02823132
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02823132