Abstract
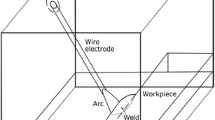
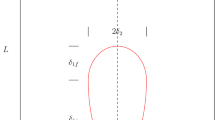
This paper summarizes progress in the development of methods, models, and software for analyzing or simulating the flow of heat in welds as realistically and accurately as possible. First the fundamental equations for heat transfer are presented and then a formulation for a nonlinear transient finite element analysis (FEA) to solve them is described. Next the magnetohydrodynamics of the arc and the fluid mechanics of the weld pool are approximated by a flux or power density distribution selected to predict the temperature field as accurately as possible. To assess the accuracy of a model, the computed and experimentally determined fusion zone boundaries are compared. For arc welds, accurate results are obtained with a power density distribution in which surfaces of constant power density are ellipsoids and on radial lines the power density obeys a Gaussian distribution. Three dimensional, in-plane and cross-sectional kinematic models for heat flow are defined. Guidelines for spatial and time discretization are discussed. The FEA computed and experimentally measured temperature field,T(x, y, z, t), for several welding situations is used to demonstrate the effect of temperature dependent thermal properties, radiation, convection, and the distribution of energy in the arc.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. R. Rykalin:Welding in the World, 1974, vol. 12, No. 9/10, pp. 227–48 (Houdrement Lecture, International Institute of Welding, London, 1974, pp. 1–23).
The Physics of Welding, J. F. Lancaster, ed., Pergamon Press, 1984, pp. 1–293.
A. H. Dilawari, J. Szekely, and T. W. Eagar:Metall. Trans. B, 1978, vol. 9B,pp. 371–81.
A. H. Dilawari, T. W. Eagar, and J. Szekely:Welding Journal, January 1978, pp. 24–30.
S. Lawson and H. Kerr:Welding Research International, 1976, vol. 6, No. 5, 6.
D. Rosenthal:Trans. ASME, 1946, vol. 68, pp. 849–65.
P. S. Myers, O. A. Uyehara, and G. L. Borman:Welding Research Council Bulletin, New York, NY, 1967, No. 123.
O. Westby: Report, Department of Metallurgy and Metals Working, The Technical University, Trondheim, Norway, 1968.
Z. Paley and P.D. Hibbert:Welding Journal Research Supplement, 1975, vol. 54, pp. 385s-92s.
V. Pavelic, R. Tanbakuchi, O. A. Uyehara, and P. S. Myers:Welding Journal Research Supplement, 1969, vol. 48, pp. 295s-305s.
S. Kou:Metall. Trans. A, 1982, vol. 13A, pp. 363–71.
J. H. Argyris, J. Szimmat, and K.J. Willan:Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 1982, vol. 33, pp. 635–66.
J.A. Goldak, A. Chakravarti, and M.J. Bibby:Trans. AIME, June 1984, vol. 15B, pp. 299–305.
N. Christensen, L. de.V. Davies, and K. Gjermundsen:British Welding Journal, 1965, vol. 12, pp. 54–75.
M.J. Bibby, G.Y. Shing, and J.A. Goldak:CIM Metallurgical Quarterly, Jan. 1985, in press.
A. P. Chakravarti, J. Goldak, and A. S. Rao:Thermal Analysis of Welds, International Conference on Numerical Methods in Thermal Problems, Swansea, U.K., Nov. 1985.
J.F. Key, H.B. Smartt, J.W. Chan, and M.E. McIlwain:Welding Technology for Energy Applications, Proceedings International Conference, Gatlinburg, TN, 16–19 May, 1982, compiled by S. A. David and G. M. Slaughter, pp. 179–99.
E. Friedman:Journal Pressure Vessel Technology, Trans. ASME, 1975, vol. 97, pp. 206–13.
B.A.B. Andersson:Journal of Engineering Materials and Technology, Trans. ASME, 1978, vol. 100, pp. 356–62.
D. R. Chapman:AIAA Journal, December 1969, vol. 17, No. 12, pp. 1293–1313.
B. M. Irons and S. Ahmad:Techniques for Finite Elements, Ellis Horwood, West Sussex, U.K., 1980.
A. Kela, H. Voelcker, and J. A. Goldak: International Conference on Accuracy Estimates and Adaptive Refinements in Finite Element Computations (ARFEC), Sponsored by the International Association of Computational Mechanics, Lisbon, Portugal, June 19–20, 1984.
M. S. Sheperd and K. H. Law: International Conference on Accuracy Estimates and Adaptive Refinements in Finite Element Computations (ARFEC), Sponsored by the International Association of Computational Mechanics, Lisbon, Portugal, June 19–20, 1984.
O. C. Zienkiewicz:The Finite Element Method, McGraw-Hill Book Company, New York, NY, 3rd ed., 1977.
T.J. R. Hughes:Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 1977, vol. 10, pp. 135–39.
J. Donea:International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 1974, vol. 8, pp. 103–10.
Z. Pammer:International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 1983, vol. 15, pp. 495–505.
W. M. Rohsenow and J. P. Hartnet:Handbook of Heat Transfer, McGraw-Hill, New York, NY, 1973.
Y. S. Touloukian, Powell, Ho, and Klemens:Thermal Conductivity: Metallic Elements of Alloys, Plenum Publishing Co., New York, NY, 1970.
Physical Constants of Some Commercial Steels at Elevated Temperatures, The British Iron and Steel Research Association, London, Butterworths Scientific Publications, 1953.
N. Yurioka, S. Ohsita, and H. Tamehiro: The Specialist Symposium on Pipeline Welding in the 80’s, Melbourne, Australia, March 18/81.
K. Farnia and J. V. Beck:Journal of Heat Transfer, Trans. ASME, vol. 99, pp. 471–78.
G. Comini, S. del Guidice, R.L. Lewis, and O.C. Zienkiewicz:IJNME, 1974, vol. 8, pp. 613–24.
W. D. Relphe, III and K. J. Bathe:IJNME, 1982, vol. 18, pp. 119–34.
D. Blanchard and M. Fremont:IJNME, 1984, vol. 20, pp. 757–71.
S. Al-Araji and J. V. Beck:Journal of Heat Transfer, Trans. ASME, 1975, pp. 148–49.
M.F. Ashby and K. E. Easterling:Acta Metall., 1982, vol. 30, pp. 1969–78.
J. C. Ion and K. E. Easterling: The Third Scandinavian Symposium in Materials Science, 20–21 June, 1983, The University of Oulu, Finland, Metal Abstracts 8407-72-0526.
V. A. Vinokurov:Welding Stresses and Distortions, The British Library, Lending Division, Translated from Russian into English by J.E. Baker, 1977, pp. 118–19.
B. Patel: Ph.D. Thesis, Carleton University, Ottawa, ON, Canada, Jan., 1985.
T.K. Hellen:IJNME, 1983, vol. 19, pp. 1713–37.
T.K. Hellen:IJNME, 1975, vol. 9, pp. 187–97.
I. Kalev:Computers and Structures, 1981, vol. 13, pp. 709–16.
B. Patel, J. A. Goldak, and M. J. Bibby: Carleton University, Ottawa, ON, Canada, unpublished research, 1985.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goldak, J., Bibby, M., Moore, J. et al. Computer modeling of heat flow in welds. Metall Trans B 17, 587–600 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02670226
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02670226