Abstract
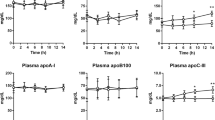
A protein-free microemulsion (LDE) with a lipid composition resembling that of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) was used in metabolic studies in rats to compare LDE with the native lipoprotein. LDE labeled with radioactive lipids was injected into the bloodstream of male Wistar rats, and plasma kinetics of the labeled lipids were followed on plasma samples collected at regular intervals for 12 h after injection. The 24-h LDE uptake by different tissues was also measured in tissue samples excised after the animals had been sacrificed. We found that LDE plasma kinetics were similar to those described for native LDL [fractional clearance rate (FCR) of cholesteryl ester, 0.42±0.11 h−1]. The major site for LDE uptake was the liver, and the tissue distribution of the LDE injected radioactivity was as one would expect for LDL. To test whether LDE was taken up by the specific LDL receptors, the LDE emulsion was injected into rats treated with 17α-ethinylestradiol, which is known to increase the activity of these receptors; as expected, removal of LDE from the bloodstream increased (FCR=0.90±0.35 h−1). On the other hand, saturation of the receptors that remove remnants by prior infusion of massive amounts of lymph chylomicrons did not change LDE plasma kinetics. These results indicate that LDE is cleared from plasma by B,E receptors and not by the E receptors that remove remnants. Incorporation of free cholesterol into LDE increased LDE plasma clearance. Incubation studies also showed that LDE incorporates a variety of apolipoproteins, including apo E, a ligand for recognition of lipoproteins by specific receptors. Our data suggest that LDE can be a useful tool to test LDL metabolism and B,E receptor function.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AML:
-
acute myeloid leukemia
- LDE:
-
microemulsion resembling low-density lipoprotein
- LDL:
-
low-density lipoprotein
- TLC:
-
thin-layer chromatography
- VLDL:
-
very low density lipoprotein
References
Brown, M.S., and Goldstein, J.L. (1986)Science 232, 34–47.
Redgrave, T.G., and Maranhão, R.C. (1985)Biochim. Biophys. Acta 835, 104–112.
Maranhão, R.C., Tercyak, A.M., and Redgrave, T.G. (1986)Biochim. Biophys. Acta 875, 247–255.
Redgrave, T.G., Maranhão, R.C., Tercyak, A.M., Lincoln, E.C., and Brunengraber, H. (1988)Lipids 23, 101–105.
Ginsburg, G.S., Small, D.M., and Atkinson, D. (1982)J. Biol. Chem. 257, 8216–8227.
Tilley, Q.L., Sawyer, W.H., Looney, F., and Curtain, C.C. (1990)Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1042, 42–50.
Reisinger, R.E., and Atkinson, D. (1990)J. Lipid Res. 31, 849–858.
Bartlett, G.R. (1959)J. Biol. Chem. 234, 466–468.
Zlatkis, A., and Zak, B. (1969)Anal. Biochem. 29, 143–148.
Soloni, F.G. (1971)Clin. Chem. 17, 529–533.
Chao, Y., Windler, E.E., Chen, G.C., and Havel, R.J. (1979)J. Biol. Chem. 254, 11360–11366.
Dory, L., and Roheim, P.S. (1981)J. Lipid Res. 22, 287–296.
Folch, J., Lees, M., and Sloane-Stanley, G.H.S. (1957)J. Biol. Chem. 226, 497–509.
Kobayashi, Y., and Mausdley, D.V. (1974)Biological Applications of Liquid Scintillation Counting, p. 51, Academic Press, New York.
Redgrave, T.G., and Snibson, D.A. (1977)Metabolism 26, 493–503.
Oliveira, H.C.F., Hirata, M.H., Redgrave, T.G., and Maranhao, R.C. (1988)Biochem. Biophys. Acta 958, 211–217.
Redgrave, T.G., Roberts, D.C.K., and West, C.E. (1975)Anal. Biochem. 65, 42–49.
Lowry, D.H., Rosebrough, N.J., Farr, A.L., and Randall, R.J. (1951)J. Biol. Chem. 193, 265–275.
Nichols, A.V., Kraus, R.M., and Musliner, T.A. (1986)Methods Enzymol. 128 (part A), 417–431.
Osborne, Jr., J.C. (1986)Methods Enzymol. (part A), 213–217.
Godfrey, K. (1983)Compartmental Models and Their Application, Academic Press, New York.
Bevington, P.R. (1969)Data Reduction and Error Analysis for the Physical Sciences, McGraw Hill, New York.
Draper, N.R., and Smith, H. (1966) inApplied Regression Analysis, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York.
Matthews, C.M.E. (1857)Phys. Med. Biol. 2, 36–53.
Maranhão, R.C., Roland, I.A., and Hirata, M.H. (1990)Lipids 25, 701–705.
Stein, Y., Halperin, G., and Stein, O. (1981)Biochim. Biophys. Acta 663, 569–574.
Windler, E.E., Kovanen, P.T., Chao, Y., Brown, M.S., Havel, R.J., and Goldstein, J.L. (1980)J. Biol. Chem. 255, 10464–10471.
Cooper, A.D., Nutik, R., and Chen, J. (1987)J. Lipid Res. 28, 59–68.
Chao, Y., Windler, E.E., Chen, C.C., and Havel, R.J. (1979)J. Biol. Chem. 254, 11360–11366.
Kovanen, P.T., Brown, M.S., and Goldstein, J.L. (1979)J. Biol. Chem. 254, 11367–11373.
Bhattacharya, S., Balasubramaniam, S., and Simons, L.A. (1984)Biochem. J. 220, 333–336.
Bhattacharya, S., Balasubramaniam, S., and Simons, L.A. (1986)Biochem. J. 234, 493–496.
Maranhão, R.C., Zerbinatti, C.V., Quintao, E.C., and Pileggi, F.C. (1986)Arteriosclerosis 6, 569.
Redgrave, T.G., Vassiliou, G.G., and Callow, M.J. (1987)Biochim. Biophys. Acta 921, 154–157.
Eisenberg, S., Yitzchak, O., and Zimmerman, J. (1984)J. Lipid Res. 25, 121–128.
Goldstein, J.L., and Brown, M.S. (1984)J. Lipid. Res. 25, 1450–1461.
Roland, I., Ramires, J., Vinagre, C., and Maranhão, R.C. (1991)Arteriosclerosis 5, 1490–1491.
Maranhão, R.C., Garicochea, B., Silya, E.L., Llacer, P.D., Pileggi, F.J.C., and Chamone, D.A.F. (1992)Brazilian J. Med. Biol. Res. 25, 1003–1007.
Ho, Y.K., Smith, R.G., Brown, M.S., and Goldstein, J.L. (1978)Blood 52, 1099–1114.
Vitols, S., Angelin, B., Ericsson, S., Gahrton, G., Juliusson, G., Masquelier, M., Peterson, C., Rudling, K., Soderberg-Reid, K., and Tidefelt, U. (1990)Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87, 2598–2602.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Maranhão, R.C., Cesar, T.B., Pedroso-Mariani, S.R. et al. Metabolic behavior in rats of a nonprotein microemulsion resembling low-density lipoprotein. Lipids 28, 691–696 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02535988
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02535988