Abstract
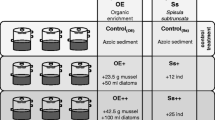
Thein vitro effect ofNereis diversicolor on denitrification has been studied in PVC tubes filled with a coastal marine sediment defaunated by sieving. The first aim of the experiment was to determine the effect of sediment defaunation on denitrification (denitrifying population and Denitrifying Enzyme Assays). Sieving induced a loss of 70% of the initial DEA. The number of denitrifying bacteria was 10 times lower than inin situ sediment. In the top two centimetres, the DEA rose by 75% of its initial value, after 82 days. Polychaetes were only added after a return to near pre-disturbance levels to ensure that our data on the effects of their addition would not be disturbed by changes in the sediment.
Introduction of Polychaetes increased the denitrifying population and DEA in the first layer (0–2 cm) of the sediment after 15 days. After 45 days, the surface of the polychaete burrows in sediment was 1.3 to 1.5 times higher than after 15 days, resulting in an increase in solute exchange between seawater and the top layer of sediment. An inhibitory effect of oxygen on denitrification was detected in the uppermost layer only.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aller, R. C. & J. Y. Yingst, 1985. Effects of the marine depositfeedersHeteromastus filiformis (Polychaeta),Macoma balthica (Bivalvia), andTellina texana (Bivalvia) on averaged sedimentary solute transport, reaction rates, and microbial distributions. J. mar. Res. 43: 615–645.
Andersen, F. Ø. & E. Kristensen, 1988. The influence of macrofauna on estuarine benthic community metabolism: a microcosm study. Mar. Biol. 99: 591–603.
Bauer, J. E., R. P. Kerr, M. K. Bautista, C. J. Decker & D. G. Capone, 1988. Stimulation of microbial activities and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degradation in marine sediments inhabited byCapitella capitata. Mar. envir. Res. 25: 63–84.
Binnerup, S. J., K. Jensen, N. P. Revsbech, M. H. Jensen & J. Sørensen, 1992. Denitrification, dissimilatory reduction of nitrate to ammonium, and nitrification in a bioturbated estuarine sediment as measured with 15N and microsensor techniques. Appl. envir. Microbiol. 58: 303–313.
Bonin, P., M. Gilewicz & J.-C. Bertrand, 1989. Effect of oxygen concentration on each step of denitrification. Can. J. Microbiol. 35: 1061–1064.
Bonin, P. & N. Raymond, 1990. Effects of oxygen on denitrification in marine sediments. Hydrobiologia 207: 115–122.
Chan, Y. K. & R. Knowles, 1979. Measurement of denitrification in two freshwater sediments by anin situ acetylene inhibition method. Appl. envir. Microbiol. 37: 1067–1072.
Chatarpaul, L., J. B. Robinson & N. K. Kaushik, 1980. Effects of tubificids worms on denitrification and nitrification in stream sediment. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 37: 656–663.
Findlay, R. H., M. B. Trexler, J. B. Guckert & D. C. White, 1990. Laboratory study of disturbance in marine sediments: response of a microbial community. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 62: 121–133.
Firestone, M. K., R. B. Firestone & J. M. Tiedje, 1980. Nitrous oxyde from soil denitrification: factors controlling its biological production. Science 208: 749–751.
Gerino, M., 1990. The effects of bioturbation on particle redistribution in Mediterranean coastal sediment. Preliminary results. Hydrobiologia 207: 251–258.
Gerino, M. & G. Stora, 1991. Analyse quantitativein vitro de la bioturbation induite par la PolychèteNereis diversicolor. C. r. Acad. Sci. 313: 489–494.
Henriksen, K., M. B. Rasmussen & A. Jensen, 1983. Effect of bioturbation on microbial nitrogen transport in the sediment and fluxes of ammonium and nitrate to the overlying water. In R. Hallberg (ed.), Environmental biogeochemistry. Ecol. Bull. 35: 193–205.
Hines, M. E. & G. E. Jones, 1985. Microbiological biogeochemistry and bioturbation in the sediments of Great Bay, New Hampshire. Estuar. coast. Shelf Sci. 20: 729–742.
Jørgensen, B. B. & N. P. Revsbech, 1985. Diffusion boundary layers and the oxygen uptake of sediments and detritus. Limnol. Oceanogr. 30: 111–122.
Kapralek, F., E. Jechova & M. Otavova, 1982. Two sites of oxygen control in induced synthetis of respiratory nitrate reductase byEscherichia coli. J. Bact. 149: 1142–1145.
Kikuchi, E., 1986. Contribution of the polychaete,Neanthes japonica (Izuka), to the oxygen uptake and carbon dioxide production of an intertidal mud-flat of the Nanakita estuary, Japan. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 97: 81–93.
Koerting-Walker, C. & J. D. Buck, 1989. The effect of bacteria and bioturbation byClymenella torquata on oil removal from sediment. Water Air Soil Pollut. 43: 413–424.
Koike, I., 1990. Measurement of sediment denitrification using 15-N tracer method. In N. P. Revsbech & J. Sørensen (eds), Denitrification in soil and sediment. Plenum Press, New-York: 291–300.
Kristensen, E., 1985. Oxygen and inorganic nitrogen exchange in aNereis virens (Polychaeta) bioturbated sediment-water system. J. coast Res. 1: 109–116.
Kristensen, E. & T. H. Blackburn, 1987. The fate of organic carbon and nitrogen in experimental marine sediment systems: influence of bioturbation and anoxia. J. mar. Res. 45: 231–257.
Kristensen, E., 1988. Benthic fauna and biogeochemical processes in marine sediment: microbial activities and fluxes. In T. H. Blackburn & J. Sørensen (eds), Nitrogen cycling in coastal marine environments. John Wiley and Sons Press, New-York: 275–298.
Kristensen, E., M. H. Jensen & R. C. Aller, 1991. Direct measurement of dissolved inorganic nitrogen exchange and denitrification in individual polychaete (Nereis virens) burrows. J. mar. Res. 49: 355–377.
Mac Aulife, L., 1971. GC determination of solutes by multiple phase equilibration. Chem. Technol. 1: 46–51.
Mahaut, M. L. & G. Graf, 1987. A luminophore tracer technique for bioturbation studies. Oceanol. Acta 10: 323–328.
Oremland, R. S. & D. G. Capone, 1987. Use of specific inhibitors in microbial ecology and biogeochemical studies. In K. C. Marshall (ed.), Advances in microbial ecology. Plenum Press, New York 10: 285–383.
Payne, W. J., 1976. Reduction of nitrogenous oxides by microorganisms. Bact. Rev. 37: 409–452.
Raymond, N., P. Bonin & J. C. Bertrand. 1992. Comparison of methods for measuring denitrifying activity in marine sediments from the Western mediterranean coast. Oceanol. Acta 15: 137–143.
Reichardt, W., 1988. Impact of bioturbation byArenicola marina on microbiological parameters in intertidial sediments. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 44: 149–158.
Robertson, L. A. & J. G. Kuenen, 1984. Aerobic denitrification, old wine in new bottles. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 50: 351–354.
Sayama, M. & Y. Kurihara, 1983. Relationship between burrowing activity of the polychaetous annelid,Neanthes japonica (Isuka) and nitrification-denitrification processes in the sediments. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 72: 233–241.
Tiedje, J. M., 1988. Ecology of denitrification and dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium. In A. J. B. Zehnder (ed.), Biology of anaerobic microorganisms. Wiley & Sons, New-York: 179–244.
Tiedje, J. M., S. Sinkins & P. M. Groffman, 1989. Perspectives on measurement of denitrification in the fields including recommended protocols for acetylene based methods. Plant Soil 115: 261–284.
Treguer, P. & P. Le Corre, 1975. Manuel d'analyse des sels nutritifs dans l'eau de mer. Laboratoire d'Océanologie chimique, Université de Bretagne Occidentale, Brest, France, 110 pp.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gilbert, F., Bonin, P. & Stora, G. Effect of bioturbation on denitrification in a marine sediment from the West Mediterranean littoral. Hydrobiologia 304, 49–58 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02530703
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02530703