Abstract
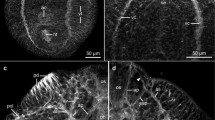
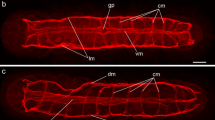
The organization of the nervous system ofDendrocoelum lacteum (Tricladida, Paludicola, Dendrocelidae) andPolycelis tenuis (Tricladida, Paludicola, Planariidae) was studied by immunocytochemical double staining, using neuropeptide RFamide and serotonin (5-HT) antisera on cryosections. The study confirmed the status of the main nerve cords (MCs) as the most important and stable of the longitudinal cords and supported the hypothesis of a common phylogenetic origin of the MCs in flatworms. The ganglion-like structures along the MCs at the beginning of transverse commissures and laterla branches showed a close contact with ventral fibres of the submuscular nerve plexus indicating an origin from crossing points of insunken ring commissures. The distributional pattern and morphology of the RFamide-IR cell bodies inD. lacteum corresponded to that of neurosecretory cells. Most RFamide-IR cells were unipolar and rounded while 5-HT-IR cells were uni- bi- and multipolar. The neutropile consisted of a dense RFamide-IR and a loose 5-HT-IR network. RFamide dominated in all parts of the genital plexus.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baguña J, Ballester R (1978) The nervous system in planarians: peripheral and gastrodermal plexuses, pharynx innervation, and the relationship between central nervous system and the acoelomate organization. J Morphol 155:237–252
Bullock TH, Horridge GA (1965) Structure and function in the nervous systems of invertebrates, vol I. WH Freeman, San Francisco
Coons AH, Leduc EH, Conolly JM (1955) Studies on antibody production. I. A method for the histochemical demonstration of specific antibody and its application to a study of the hyperimmune rabbit. J Exp Med 102:49–60
Ehlers U (1985) Das Phylogenetische System des Plathelminthes. Gustav Fischer, Stuttgart New York
Falkmer S, Gustafsson MKS, Sundler F (1985) Phylogenetic aspects on the neuroendocrine system. A minireview with particular reference to cells storing neurohormonal peptides in some primitive protostomian invertebrates (flatworms, annelids). Nord Psykiatr Tidsskr 39 (suppl 11):21–30
Fujita T, Kobayashi S, Yui R, Iwanaga T (1980) Evolution of neurons and paraneurons. In: Ishi S, Hirano T, Wada M (eds) Hormones, adaption and evolution. Springer, Berlin, pp 35–43
Fujita T, Kanno T, Kobayashi S (1988) The Paraneuron. Springer, Tokyo Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 367
Gelei J (1912) Tanulmányok ADendrocoelum lacteum Oerstd. Szövettanárol (in Hungarian). Mag Tud Akad Kiadása 289 pp
Golding DW (1988) Control systems. In: Barnes RSK, Calow P, Olive PJW (eds) The invertebrates. A new synthesis. Blackwell Scientific Publications. Oxford, pp 491–548
Grimelikhuijzen CJP (1985) Antisera to the sequence Arg-Pheamide visualize neuronal centralization in hydroid polyps. Cell Tissue Res 241:171–182
Gustafsson MKS (1992) The neuroanatomy of parasitic flatworms. Adv Neuroimmunol 2:267–286
Gustafsson MKS, Halton DW, Maule AG, Reuter M, Shaw S (1994) The gull tapeworm,Diphyllobothrium dendriticum and neuropeptide F: an immunocytochemical study. Parasitology 109:599–609
Gustafsson MKS, Fagerholm H-P, Halton DW, Hanzelova, Maule AG, Reuter M, Shaw C (1995) Neuropeptides and serotonin in the cestode,Proteocephalus exiguus: an immunocytochemical study. Int J Parasitol 25:673–682
Hyman LH (1951) The Invertebrates. II. Platyhelminthes and Rhynchocoela. The acoelomate Bilateria. McGraw-Hill, New York
Joffe BI, Reuter M (1993) The nervous system ofBothriomolus balticus (Proseriata)—a contribution to the knowledge of the orthogon in the Plathelminthes. Zoomorphology 113:113–127
Kabotyanski KA, Nezlin LP, Sakharov DA (1990) Serotonin neurones in the planarian pharynx. In: Sakharov DA, Winlow W (eds) Simpler nervous systems. Studies in neurosciences 13. Manchester University Press, Manchester, pp 138–152
Koopowitz H (1989) Polyclad neurobiology and evolution of central nervous system. In: Anderson PAV (ed) Evolution of the first nervous systems. Ser A, Life Sciences. Plenum Press, New York, 188:315–328
Krieger DT (1983) Brain peptide: what, where, and why? Science 222:975–985
Reisinger E (1970) Zur Problematik der Evolution der Coelomaten. Z Zool Syst Evolutionsforsch 8:81–109
Reisinger E (1972) Die Evolution des Orthogon der Spiralier und das Archicöelomatenproblem. Z Zool Syst Evolutionsforsch 10:1–43
Reuter M, Gustafsson MKS (1995) The flatwormnervous system—pattern and phylogeny. In: Breidbach O, Kutsch W (eds) The nervous systems of invertebrates: an evolutionary and comparative approach. Advances in life sciences, Birkhäuser Company, Basel, pp 25–59
Reuter M, Lehtonen M, Wikgren M (1988) Immunocytochemical evidence of neuroactive substances in flatworms of different taxa—a comparison. Acta Zool (Stockholm) 69:29–37
Reuter M, Maule AG, Halton DW, Gustafsson MKS, Shaw C (1995a) The organization of the nervous system in Plathelminthes. The neuropeptide F(NPF)-immunoreactivity pattern in Catenulida, Macrostomida and Proseriata. Zoomorphology 115:83–97
Reuter M, Gustafsson MKS, Sahlgren C, Halton DW, Maule AG, Shaw C (1995b) The nervous system of Tricladida. I. Neuroanatomy ofProcerodes littoralis (Maricola, Procerodidae): an immunocytochemical study. Invertebrate Neurosci 1:113–122
Reuter M, Gustafsson MKS, Sheiman IM, Terenina N, Halton DW, Maule AG, Shaw C (1995c) The nervous system of Tricladida. II. Neuroanatomy ofDugesia tigrina (Paludicola, Dugesiidae): an immunocytochemical study. Invertebrate Neurosci 1:133–143
Rieger RM, Tyler S, Smith III JPS, Rieger G (1991) Platyhelminthes: Turbellaria. In: Harrison FW, Bogitsh BJ (eds) Microscopic anatomy and invertebrates. 3: Platyhelminthes and Nemertinea. Wiley-Liss, New York London, pp 7–140
Ude J (1964) Untersuchungen zur Neurosekretion beiDendrocoelum lacteum (Plathelminthes-Turbellaria). Z Wiss Zool 170:223–255
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reuter, M., Gustafsson, M.K.S., Mäntylä, K. et al. The nervous system of Tricladida. III. Neuroanatomy ofDendrocoelum lacteum andPolycelis tenuis (Plathelminthes, Paludicola): an immunocytochemical study. Zoomorphology 116, 111–122 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02526943
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02526943