Abstract
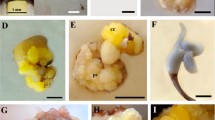
Somatic embryogenesis and further plant regeneration were observed using zygotic embryos, young inflorescences and young leaves ofEuterpe edulis (Palmae) as explants. Both for the cultures of zygotic embryos and inflorescences, activated charcoal in the medium was essential for the establishment of viable cultures. Embryogenesis was induced by using a gelled basal medium with MS or Euwens salts supplemented by high 2, 4-D levels (50–100 mg L−1). The embryogenic process was direct without a callus stage. For further development, cultures with globular or post-globular embryos were transferred to the basal medium with 2-iP (2.5 mg L−1) and NAA (0.1 mg L−1). To convert embryos to plantlets, cultures were transferred to a third medium in which sucrose and salts were reduced to the half-strenght of the basal medium, without growth regulators. In the case of liquid medium, with either 2, 4-D or NAA (10–20 mg L−1). The developmental stage of each explant was critical for the induction of embryogenesis. The histological study of embryogenic cultures revealed that in the case of zygotic embryos, somatic embryos arise directly from the surface of the cotyledonar node, or from subepidermal tissues. In the inflorescences, a pro-embryogenic tissue is formed at the floral primordium region; in the leaves, the first morphogenic event is cell proliferation in the vascular parenchyma.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahée, J., Artuis, P., Cas, G., Duval, Y., Guénin, G., Hanower, J., Hanower, P., Lievoux, D., Liret, C., Malaurie, B., Pannettier, C., Raillot, D., Varechon, C. andZuckerman, L. 1981. La multiplication végétativein vitro du palmier á huile par embryogénese somatique. Oleagineux36: 113–115.
Blake, J. andHornung, R. 1995. Somatic embryogenesis in coconut (Cocos nucifera L.).In S.M. Jain, P.K. Gupta and R.J. Newton, eds., Somatic Embryogenessis in Woody Plants. vol. 2. Angiosperms. Kluwer Academics, Dordrecht, pp. 327–340.
Blake, J. 1983. Tissue culture propagation of coconut palm tissues with a view to vegetative propagation.In J.H. Dodds, ed., Tissue Culture of Trees. AVI Publ. Company, Westport, pp. 29–50.
Buffard-Morel, J., Verdeil, J.L. andPannetier, C. (1992 Embryogenèse somatique du cocotier (Cocos nucifera L.) a partir d'explants foliares: etudes histologiques. Can. J. Bot.70: 735–741.
Canhoto, J.M. andCruz, G.S. 1996. Histodifferentiation of somatic embryos in cotyledons of pineapple guava (Feijoa sellowiana Berg). Protoplasma191: 34–35.
Euwens, C.J. 1976. Mineral requirements for growth and callus initiation of tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant.15: 473–497.
Evans, D.A., Sharp, W.R. andFlick, C.E. 1981. Growth and behavior of cell cultures.In T.A. Thorpe, ed., Plant Tissue Culture: Methods and Applications in Agriculture. Academic Press, New York, pp. 45–112.
Fantini, A.C., Reis, A.M.S. andGuerra, M.P. 1992. Sustained yield management in tropical forest: a proposal based on the autoecology of the species. Sellowia42–44: 25–33.
George, E.F. 1996. Plant Propagation by Tissue Culture. Part 2. Exegetics Ltd, Edington.
Guerra, M.P. andHandro, W. 1988. Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in embryo culture ofEuterpe edulis Mart. (Palmae). Plant Cell Reports7: 550–552.
Guerra, M.P. andHandro, W. 1991. Somatic embryogenesis in tissue cultures ofEuterpe edulis Mart. (Palmae).In R.M. Ahuja, ed., Wood Plant Biotechnology, Plenum Press, New York, pp. 189–196.
Haccius, B. 1978. Question of unicellular origin of nonzygotic embryos in callus cultures. Phytomorphology28: 74–81.
Ho, W.J. andVasil, I.K. 1983. Somatic embryogenesis in sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum L.) I. The morphology and physiology of callus formation and the ontogeny of somatic embryos. Protoplasma118: 169–180.
Hu, C.Y. andSussex, I.M. 1971.In vitro development of embryoids on cotyledons ofllex aquifolium. Phytomorphology21: 103–107.
Maheswaran, G. andWilliams, E.E. 1986. Direct secondary somatic embryogenesis from immature sexual embryos ofTrifolium repens culturedin vitro. Ann. Bot.57: 109–117.
Maheswaran, G. andWilliams, E.G. 1985. Origin and development of somatic embryos formed directly on immature embryos ofTrifolium repens in vitro. Ann. Bot.56: 619–630.
Morel, C.G., andWetmore, R.H. 1951. Fern callus tissue culture. Amer. J. Bot.38: 141–143.
Murashige, T. andSkoog, F. 1962. A revised medium for rapid growth and biossays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant.15: 473–497.
Rabechault, G. andMartin, J.P. 1976. Multiplication végétative du palmier a huile (Elaeis guineensis Jacq.) à l'aide de culture de tissus foliares. C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris283: 1735–1737.
Sass, J.E. 1951. Botanical Microtechnique. The Iowa State College Press, Iowa.
Schwendiman, J., Pannetier, C. andMichaux-Ferriere, N. 1988. Histology of somatic embryogenesis from leaf explants of the oil palmElaeis guineensis. Ann. Bot.62: 43–52.
Teixeira, J.B., Söndhal, M.R. andKirby, E.G. 1994. Somatic embryogenesis from immature inflorescences of oil palm. Plant Cell Reports13: 247–250.
Teixeira, J.B., Söndhal, M.R., Nakamura, T. andKirby, E.G. 1995. Establishment of oil palm cell suspensions and plant regeneration. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture40: 105–111.
Tisserat, B. 1981. Production of free-living date palms through tissue culture. Date Palm Journal1: 43–54.
Tisserat, B. 1984a. Date palm.In W.R. Sharp, D.A. Evans, P.V. Ammirato and Y. Yamada, eds., Handbook of Plant Cell Culture, vol. 2, McMillan, New York, pp. 505–545.
Tisserat, B. 1984b. Clonal propagation:, palms.In I.K. Vasil, ed., Cell Culture and Somatic Cell Genetics of Plants, vol. 1, Academic Press, Orlando, pp. 74–81.
Tisserat, B. 1987. Palms.In J.M. Bonga and D.J. Durzan, eds., Cell and Tissue Culture in Forestry. Martinus Nijhoff, Dordrecht, pp. 339–356.
Vasil, I.K. 1982. Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in cereals and grasses.In A. Fujiwara, ed., Plant Tissue Culture 1982, Maruzen, Tokyo, pp. 101–103.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guerra, M.P., Handro, W. Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in different organs ofEuterpe edulis mart. (Palmae): Control and structural features. J. Plant Res. 111, 65–71 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02507151
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02507151