Abstract
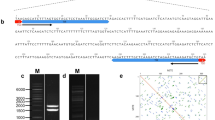
EcoRI restriction of theB. nigra rDNA recombinants, isolated from a lambda genomic library, showed that the 3.9-kb fragment corresponded to the Intergenic Spacer (IGS), which was sequenced and found to be 3,928 by in size. Sequence and dot-matrix analyses showed that the organization of theB. nigra rDNA IGS was typical of most rDNA spacers, consisting of a central repetitive region and flanking unique sequences on either side. The repetitive region was composed of two repeat families—RF ‘A’ and RF ‘B.’ TheB. nigra RF ‘A’ consisted of a tandem array of three full-length copies of a 106-bp sequence element. RF ‘B’ was composed of 66 tandemly repeated elements. Each ‘B’ element was only 21-bp in size and this is the smallest repeat unit identified in plant rDNA to date. The putative transcription initiation site (TIS) was identified as nucleotide position 3,110. Based on the sequence analysis it was suggested that the present organization of the repeat families was generated by successive cycles of deletions and amplifications and was being maintained by homogenization processes such as gene conversion and crossing-over.
A detailed comparison of the rDNA IGS sequences of the three diploidBrassica species—namely,B. nigra, B. campestris, andB. oleracea—was carried out. First, comparisons revealed thatB. campestris andB. oleracea were close to each other as the repeat families in both showed high sequence homology between each other. Second, the repeat elements in both the species were organized in an interspersed manner. Third, a 52-bp sequence, present just downstream of the repeats inB. campestris, was found to be identical to theB. oleracea repeats, thereby suggesting a common progenitor. On the other hand, inB. nigra no interspersion pattern of organization of repeats was observed. Further, theB. nigra RF ‘A’ was identified as distinct from the repeat families ofB. campestris andB. oleracea. Based on this analysis, it was suggested that during speciationB. campestris andB. oleracea evolved in one lineage whereasB. nigra diverged into a separate lineage. The comparative analysis of the IGS helped in identifying not only conserved ancestral sequence motifs of possible functional significance such as promoters and enhancers, but also sequences which showed variation between the three diploid species and were therefore identified as species-specific sequences.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appels R, Moran LB, Gustafson JP (1986) The structure of DNA from the rye (Secale cereale) NOR R1 locus and its behaviour in wheat backgrounds. Can J Genet Cytol 28:673–685
Barker RF, Harberd NP, Jarvis MG, Flavell RB (1988) Structure and evolution of the intergenic region of a ribosomal DNA repeat unit of wheat. J Mol Biol 201:1–17
Bennett RJ, Smith AG (1991) The complete nucleotide sequence of the intergenic spacer regions of an rDNA operon fromBrassica oleracea and its comparison with other crucifers. Plant Mol Biol 16: 1095–1098
Borisjuk N, Hemleben V (1993) Nucleotide sequence of the potato rDNA intergenic spacer. Plant Mol Biol 21:381–384
Chisholm D (1989) A convenient moderate-scale procedure for obtaining DNA from bacteriophage lambda. Biotechniques 7:21–23
Cordesse F, Cooke R, Tremousaygue D, Grellet F, Delseny M (1993) Fine structure and evolution of the rDNA intergenic spacer in rice and other cereals. J Mol Evol 36:369–379
Da Rocha PSCF, Bertrand H (1995) Structure and comparative analysis of the rDNA intergenic spacer ofBrassica rapa: implications for the function and evolution of theCruciferae spacer. Eur J Biochem 229:550–557
Delcasso-Tremousaygue D, Grellet F, Panabieres F, Ananiev ED, Delseny M (1988) Structural and transcriptional characterization of the external spacer of a ribosomal RNA nuclear gene from a higher plant. Eur J Biochem 172:767–776
Dellaporta SL, Wood J, Hicks JB (1984) Maize DNA mini-prep. In: Molecular biology of plants: a laboratory course manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY, pp 36–37
Delseny M, McGrath JM, This P, Chevre AM, Quiros CF (1990) Ribosomal RNA genes in diploid and amphidiploidBrassica and related species: organization, polymorphism and evolution. Genome 33:733–744
Dover G (1982) Molecular drive: a cohesive mode of species evolution. Nature 299:111–117
Doelling JH, Pikaard CS (1995) The minimal ribosomal RNA gene promoter ofArabidopsis thaliana includes a critical element at the transcription initiation site. Plant J 8:683–692
Doelling JH, Gaudino RJ, Pikaard CS (1993) Functional analysis ofArabidopsis thaliana rRNA gene and spacer promotersin vivo and by transient expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:7528–7532
Doyle JJ, Beachy RN (1985) Ribosomal RNA gene variation in soybean (Glycine) and its relatives. Theor Appl Genet 70:369–376
Echeverria M, Delcasso-Tremousaygue D, Delseny M (1992) A nuclear protein fraction binding to dA/dT-rich sequences upstream from the radish DNA promoter. Plant J 2:211–219
Echeverria M, Penon P, Delseny M (1994) Plant ribosomal DNA external spacer binding factors: a novel protein binds specifically to a sequence close to the primary pre-rRNA processing site. Mol Gen Genet 243:442–452
Ganal M, Hemleben V (1986) Comparison of the ribosomal RNA genes in four closely relatedCucurbitaceae. Plant Syst Evol 154: 63–77
Gerlach WL, Bedbrook JR (1979) Cloning and characterization of ribosomal RNA genes from wheat barley. Nucleic Acids Res 7: 1869–1885
Gerstner J, Schiebel K, Von Waldburg G, Hemleben V (1988) Complex organization of the length heterogenous 5′ external spacer of mung bean (Vigna radiata) ribosomal DNA. Genome 30:723–733
Grellet F, Delcasso-Tremousaygue D, Delseny M (1989) Isolation and characterization of an unusual repeated sequence from the ribosomal intergenic spacer of the cruciferSisymbrium irio. Plant Mol Biol 12:695–706
Gruendler P, Unfried I, Poinmer R, Schweizer C (1989) Nucleotide sequence of the 25S-18S ribosomal gene spacer fromArabidopsis thaliana. Nucleic Acids Res 17:6395–6396
Gruendler P, Untried I, Pascher K, Schweizer D (1991) The rDNA intergenic region fromArabidopsis thaliana: structural analysis, intraspecific variation and functional implications. J Mol Biol 221: 1209–1222
Harbinder S, Lakshmikumaran M (1990) A repetitive sequence fromDiplotaxis erucoides is highly homologous to that ofBrassica campestris andB. oleracea. Plant Mol Biol 15:155–156
Jackson SD, Flavell RB (1992) Protein-binding to reiterated motifs within the wheat rRNA gene promoter and upstream repeats. Plant Mol Biol 20:911–919
Katayama S, Hirano Y, Tsukaya H, Naito S, Komeda Y (1992) Analysis of intergenic spacer regions in the nuclear rDNA ofPharbitis nil. Genome 35:92–97
Lakshmikumaran M, Negi MS (1994) Structural analysis of two length variants of the rDNA intergenic spacer fromEruca sativa. Plant Mol Biol 24:915–927
Lakshmikumaran M, Ranade SA (1990) Isolation and characterization of a highly repetitive DNA ofBrassica campestris. Plant Mol Biol 14:447–448
Long EO, Dawid IB (1980) Repeated genes in eukaryotes. Anon Rev Biochem 49:727–764
Maggini F, Carmona MJ (1981) Sequence heterogeneity of the ribosomal DNA inAllium cepa (Liliaceae). Protoplasma 108:163–171
Malmberg R, Messing J, Sussex I (1985) Molecular biology of plants: a laboratory course manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
McMullen MD, Hunter B, Philips RL, Rubenstein I (1986) The structure of the maize ribosomal DNA spacer region. Nucleic Acids Res 14:4953–4969
Olmedilla A, Delcasso D, Delseny M, Cawet-Mart A-M (1985) Variability in giant fennel (Ferula communis, Umbelliferae): ribosomal RNA nuclear genes. Plant Syst Evol 150:263–274
Piller KJ, Baerson S, Polaris NO, Kaufman LS (1990) Structural analysis of the short length ribosomal DNA variant fromPisum sativum L cv alaska. Nucleic Acids Res 18:3135–3145
Prakash S, Hinata K (1980) Taxonomy, cytogenetics and origin of cropBrassica (a review). Opera Bot 55:1–57
Rathgeber J, Capesius I (1990) Nucleotide sequence of the intergenic spacer and the 18S ribosomal RNA gene from mustard (Sinapis alba). Nucleic Acids Res 18:1288
Saghai-Maroof MA, Soliman KM, Jorgenson RA, Allard RW (1984) Ribosomal DNA spacer-length polymorphisms in barley: Mendelian inheritance, chromosomal location and population dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:8014–8018
Sanger F, Nicklen S, Coulson AR (1977) DNA sequencing with chain terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:5463–5467
Sano Y, Sano T (1990) Variation in the intergenic spacer region of ribosomal DNA in cultivated and wild rice species. Genome 33: 209–218
Schmidt-Puchta W, Guenther I, Saenger HL (1989) Nucleotide sequence of the intergenic spacer (IGS) of the tomato ribosoma DNA. Plant Mol Biol 13:251–253
Schmitz ML, Maier UG, Brown JWS, Feix G (1989) Specific binding of nuclear proteins to the promoter region of a maize nuclear rRNA gene unit. J Biochem 264:1467–1472
Song KM, Obsorn TC, Williams PH (1988)Brassica taxonomy based on nuclear restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLPs). 1 Genome evolution of diploid and amphidiploid species. Theor App Genet 75:784–794
Song KM, Obsorn TC, Williams PH (1990)Brassica taxonomy based on nuclear restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLPs). 3. Genome relationship inBrassica and related genera and the origin ofB. oleracea andB. rapa (syn. campestris). Theor Appl Gene 79:497–506
Taira T, Kato A, Tanifuji S (1988) Difference between two major size classes of carrot rDNA repeating units is due to reiteration of sequences of about 460 by in the large spacer. Mol Gen Genet 213: 170–174
Toloczyki Ch, Feix G (1986) Occurrence of nine homologous repeat units in the external spacer region of a nuclear maize rRNA gene unit. Nucleic Acids Res 14:4969–4986
Tremousaygue D, Laudie M, Grellet F, Delseny M (1992) TheBrassica oleracea rDNA spacer revisited. Plant Mol Biol 18:1013–1018
Warwick SI, Black LD (1991) Molecular systematics ofBrassica and allied genera (subtribeBrassicinae, Brassiceae)—Choroplast genome and cytodeme congruence. Theor Appl Genet 82:81–92
Yakura K, Kato A, Tanifuji S (1984) Length heterogeneity in the large spacer ofVicia faba rDNA is due to the differing number of a 325 bp repetitive sequence element. Mol Gen Genet 193:400–405
Yanagino T, Takahata Y, Hinata K (1987) Chloroplast DNA variations among diploid species inBrassica and allied genera. Jpn J Gene 62:119–125
Zentgraf U, Ganal M, Hemleben V (1990) Length heterogeneity of the rRNA precursor in cucumber (Cucumis sativus). Plant Mol Biol 15:465–474
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Correspondence to: M. Lakshmikumaran
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhatia, S., Negi, M.S. & Lakshmikumaran, M. Structural analysis of the rDNA intergenic spacer ofBrassica nigra: Evolutionary divergence of the spacers of the three diploidBrassica species. J Mol Evol 43, 460–468 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02337518
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02337518