Abstract
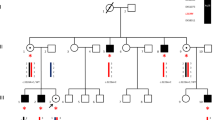
X-linked hydrocephalus (HSAS) is the most common form of inherited hydrocephalus characterized by hydrocephalus due to stenosis of the aqueduct of Sylvius, mental retardation, clasped thumbs, and spastic paraparesis. MASA syndrome (mental retardation, aphasia, shuffling gait and adducted thumbs) and SPG1 (X-linked complicated spastic paraplegia) are also X-linked disorders with overlapping clinical signs. Linkage analysis studies implicated the neural cell adhesion molecule L1 (LICAM) gene as a candidate gene for these X-linked disorders. This genetic study analyzes the LICAM gene in a Japanese family with members suffering from HSAS, and describes a deletion of five nucleotides in exon 8. Screening byBg1I digestion of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) products revealed that two siblings have the same mutation and a sister was identified as a heterozygous carrier. The 5 nucleotide deletion causes a shift of the reading frame and introduces a premature stop codon 72 nucleotides downstream, which might result in a truncated protein. The mutation identified herein is a novel L1 CAM mutation, which triggers hydrocephalus. We report a unique LlCAM mutation that causes HSAS: the first report of such a mutation in a Japanese family.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Coucke P, Vits L, Van Camp G, Serville F, Lyonnet S, Kenwrick S, Rosenthal A, Wehnert M, Munnich A, Willems PJ (1994) Identification of 5′ splice site mutation in intron 4 of the LICAM gene in an X-linked hydrocephalus family. Hum Mol Genet3:671–673
Djabali M, Mattei MG, Nguyen C, Roux D, Demengeot J, Denizot F, Moos M, Schachner M, Goridis C, Jordan BR (1990) The gene encoding L1, a neural adhesion molecule of the immunoglobulin family, is located on the X chromosome in mouse and human. Genomics 7:587–593
Fransen E, Schrander-Stumpel C, Vits L, Coucke P, Van Camp G, Willems PJ (1994) X-linked hydrocephalus and MASA syndrome present in one family are due to a single missense mutation in exon 28 of the LICAM gene. Hum Mol Genet 3:2255–2256
Gareis FS, Mason JD (1984) X-linked mental retardation associated with bilateral clasp thumb anomaly. Am J Med Genet 17 333–338
Jouet M, Rosenthal A, MacFarlance J, Kenwrick S, Dornani D (1993) A missense mutation confirms the Ll defect in X-linked hydrocephalus (HSAS). Nature Genet 4:331
Jouet M, Rosenthal A, Armstrong G, MacFarlane J, Stevenson R, Paterson J, Metzenberg A, Ionasescu V, Temple K, Kenwrick S (1994) X-linked spastic paraplegia (SPG1), MASA syndrome and X-linked hydrocephalus result from mutations in the L1 gene. Nature Genet 7:402–407
Kenwrick S, Ionasescu V, Ionasescu G, Searby C, King A, Dubowitz M, Davies KE (1986) Linkage studies of X-linked recessive spastic paraplegia using DNA probe. Hum Genet 73 264–266
Kobayashi M, Miura M, Asou H, Uyemura K (1991) Molecular cloning of cell adhesion molecule L1 from human nervous tissue: a comparison of the primary sequence of L1 molecules of different origin. Biochim Biophys Acta 1090:238–240
Macias VR, Day DW, King TE, Wilson GN (1992) Claspedthumb mental retardation (MASA) syndrome: conformation of linkage to Xg28. Am J Med Genet 43:408–414
McKusick VA (1992) Mendelian inheritance in man, 10th edn. Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore
Miura M, Kobayashi M, Asou H, Uyemura K (1991) Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding the rat neural cell adhesion molecule L1; two Ll isoforms in the cytoplasmic region are produced by differential splicing. FEBS Lett 289:91–95
Rosenthal A, Jouet M, Kenwrick S (1992) Aberrant splicing of neural cell adhesion molecule Ll mRNA in a family with Xlinked hydrocephalus. Nature Genet 2:107–112
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Van Camp G, Vits L, Coucke P, Lyonnet S, Schrander-Stumpel C, Darby J, Holden J, Munnich A, Willems PJ (1993) A duplication in the LICAM gene associated with X-linked hydrocephalus. Nature Genet 4:421–425
Vits L, Van Camp C, Coucke P, Fransen E, Boulle KD, Reyniers E, Korn B, Poustka A, Wilson G, Schrander-Stumpel C, Winter RM, Schwartz C, Willems PJ (1994) MASA syndrome is due to mutations in the neural cell adhesion gene LICAM. Nature Genet 7:408–413
Willems PJ, Brouwer OF, Dijkstra I, Wilmink J (1987) X-linked hydrocephalus Am J Med Genet27:921–928
Willems PJ, Dijkstra I, Van der Auwere BJ, Vits L, Coucke P, Raeymaekers P, Van Broeckhoven C, Consalez GG, Freeman SB, Warren ST, Brouwer OF, Brunner HG, Renier WO, Van Elsen AF, Dumon JE (1990) Assignment of X-linked hydrocephalus to Xg28 by linkage analysis. Genomics 8: 367–370
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takechi, T., Tohyama, J., Sakuragawa, N. et al. A deletion of five nucleotides in the LICAM gene in a Japanese family with X-linked hydrocephalus. Hum Genet 97, 353–356 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02185770
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02185770