Abstract
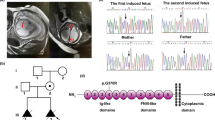
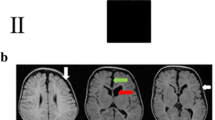
X-linked hydrocephalus (XLH) is a genetic disorder leading to a syndrome characterized by mental retardation, bilateral adducted thumbs, and spasticity of upper and lower limbs. In most cases, X-linked mutation leads to a defective activity of the neuronal cell adhesion molecule L1CAM (L1 cell adhesion molecule, OMIM 308840). Depending on mutations of L1CAM, four X-linked neurological syndromes have been described. These syndromes are very different albeit each one possesses marked variability. In the present study, we describe a novel L1CAM mutation in a 33-year-old woman reporting two voluntary terminations of pregnancy due to fetal hydrocephalus. The genetic analysis identified the potential splicing variant c.1267+5delG. When analyzed in vitro, this mutation produces the skipping of exon 10. The same mutation was confirmed in analyzing DNA from amniocytes from the second pregnancy, and ultrasound scan and autopsy confirmed the occurrence of a severe L1 syndrome. These data describe a novel L1 mutation which improves our understanding on genotype–phenotype correlation while confirming the importance of prenatal screening for L1CAM mutations.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basel-Vanagaite L, Straussberg R, Friez MJ, Inbar D, Korenreich L, Shohat M, Schwartz CE (2006) Expanding the phenotypic spectrum of L1CAM-associated disease. Clin Genet 69(5):414–419
Bateman A, Jouet M, MacFarlane J, Du JS, Kenwrick S, Chothia C (1996) Outline structure of the human L1 cell adhesion molecule and the sites where mutations cause neurological disorders. EMBO J 15(22):6050–6059
Claes S, Aguirre T, Simosa V, Bustos T, Lander R, Piras M, Legius E, Cassiman JJ, Raeymaekers P (1998) Hydrocephalus and spastic paraplegia result from a donor splice site mutation (2872 + 1G to a) in the L1CAM gene in a Venezuelan pedigree. Hum Mutat Suppl 1:S240–S241
Coucke P, Vits L, Van Camp G, Serville F, Lyonnet S, Kenwrick S, Rosenthal A, Wehnert M, Munnich A, Willems PJ (1994) Identification of a 5′ splice site mutation in intron 4 of the L1CAM gene in an X-linked hydrocephalus family. Hum Mol Genet 3(4):671–673
De Angelis E, Watkins A, Schäfer M, Brümmendorf T, Kenwrick S (2002) Disease-associated mutations in L1 CAM interfere with ligand interactions and cell-surface expression. Hum Mol Genet 11(1):1–12
Dobson CB, Villagra F, Clowry GJ, Smith M, Kenwrick S, Donnai D, Miller S, Eyre JA (2001) Abnormal corticospinal function but normal axonal guidance in human L1CAM mutations. Brain 124(Pt 12):2393–2406
Du YZ, Dickerson C, Aylsworth AS, Schwartz CE (1998) A silent mutation, C924T (G308G), in the L1CAM gene results in X linked hydrocephalus (HSAS). J Med Genet 35(6):456–462
Fernández RM, Núñez-Torres R, García-Díaz L, de Agustín JC, Antiñolo G, Borrego S (2012) Association of X-linked hydrocephalus and Hirschsprung disease: report of a new patient with a mutation in theL1CAM gene. Am J Med Genet A 158A(4):816–820
Finckh U, Schröder J, Ressler B, Veske A, Gal A (2000) Spectrum and detection rate of L1CAM mutations in isolated and familial cases with clinically suspected L1-disease. Am J Med Genet 92(1):40–46
Fransen E, Van Camp G, Vits L, Willems PJ (1997) L1-associated diseases: clinical geneticists divide, molecular geneticists unite. Hum Mol Genet 6(10):1625–1632
Fransen E, Van Camp G, D’Hooge R, Vits L, Willems PJ (1998) Genotype-phenotype correlation in L1 associated diseases. J Med Genet 35:399e404
Hübner CA, Utermann B, Tinschert S, Krüger G, Ressler B, Steglich C, Schinzel A, Gal A (2004) Intronic mutations in the L1CAM gene may cause X-linked hydrocephalus by aberrant splicing. Hum Mutat 23(5):526
Itoh K, Fushiki S (2015) The role of L1cam in murine corticogenesis, and the pathogenesis of hydrocephalus. Pathol Int 65(2):58–66
Jouet M, Kenwrick S (1995) Gene analysis of L1 neural cell adhesion molecule in prenatal diagnosis of hydrocephalus. Lancet 345(8943):161–162
Kenwrick S, Watkins A, De Angelis E (2000) Neural cell recognition molecule L1: relating biological complexity to human disease mutations. Hum Mol Genet 9(6):879–886
Liebau MC, Gal A, Superti-Furga A, Omran H, Pohl M (2007) L1CAM mutation in a boy with hydrocephalus and duplex kidneys. Pediatr Nephrol 22(7):1058–1061
Luksys G, Fastenrath M, Coynel D, Freytag V, Gschwind L, Heckb A, Jessen F, Maierd W, Milnik A, Riedel-Hellerg SG, Schererh M, Spaleka K, Vogler C, Wagner M, Wolfsgruber S, Papassotiropoulos A, de Quervain DJF (2015) Computational dissection of human episodic memory reveals mental process-specific genetic profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112(35):E4939–E4948
Lyonnet S, Pelet A, Royer G, Delrieu O, Serville F, Le Marec B, Gruensteudel A, Pfeiffer RA, Briard ML, Dubay C, Hors-Cayla NC, le Merrer M, Munnich A (1992) The gene for X linked hydrocephalus maps to Xq28, distal to DXS52. Genomic. 14:508–510
Moos M, Tacke R, Scherer H, Teplow D, Früh K, Schachner M (1988) Neural adhesion molecule L1 as a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily with binding domains similar to fibronectin. Nature 334(6184):701–703
Okamoto N, Wada Y, Goto M (2004) Hydrocephalus and Hirschsprung’s disease with a mutation of L1CAM. J Hum Genet 49(6):334–337
Raveh S, Gavert N, Ben-Ze’ev A (2009) L1 cell adhesion molecule (L1CAM) in invasive tumors. Cancer Lett 282(2):137–145
Rolf B, Kutsche M, Bartsch U (2001) Severe hydrocephalus in L1-deficient mice. Brain Res 891(1–2):247–252
Saugier-Veber P, Martin C, Le Meur N, Lyonnet S, Munnich A, David A, Hénocq A, Héron D, Jonveaux P, Odent S, Manouvrier S, Moncla A, Morichon N, Philip N, Satge D, Tosi M, Frébourg T (1998) Identification of novel L1CAM mutations using fluorescence-assisted mismatch analysis. Hum Mutat 12(4):259–266
Schrander-Stumpel C, Legins E, Fryns JP, Cassiman JJ (1990) MASA syndrome: new clinical features and linkage analysis using DNA probes. J Med Genet 27:688–692
Tonosaki M, Itoh K, Umekage M, Kishimoto T, Yaoi T, Lemmon VP, Fushiki S (2014) L1cam is crucial for cell locomotion and terminal translocation of the Soma in radial migration during murine corticogenesis. PLoS ONE 9(1):e86186
Tryns JP, Schrander-Stumpel C (1998) Congenital hydrocephalus: nosology and guidelines for clinical approach and genetic counseling. Eur J Pediatr 157:355–362
Van Camp G, Vits L, Coucke P, Lyonnet S, Schrander-Stumpel C, Darby J, Holden J, Munnich A, Willems PJ (1993) A duplication in the L1CAM gene associated with X-linked hydrocephalus. Nat Genet 4(4):421–425
Van Camp G, Fransen E, Vits L, Raes G, Willems PJ (1996) A locus-specific mutation database for the neural cell adhesion molecule L1CAM (Xq28). Hum Mutat 8(4):391
Vos YJ, de Walle HEK, Bos KK, Stegeman JA, ten Berge AM, Bruining M, van Maarle MC, Elting MW, den Hollander NS, Hamel B, Ana Maria Fortuna AM, Sunde LEM, Stolte-Dijkstra I, Schrander-Stumpel CTRM, Hofstra RMW (2010) Genotype-phenotype correlations in L1 syndrome: a guide for genetic counselling and mutation analysis. J Med Genet 47(3):169–175
Yamasaki M, Thompson P, Lemmon V (1997) CRASH syndrome: mutations in L1CAM correlate with severity of the disease. Neuropediatrics 28:175e8
Zahl SM, Egge A, Helseth E and Wester K (2011) Benign external hydrocephalus: a review, with emphasis on management. Neurosurg Rev. 34(4):417–432
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the patients enrolled in this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no financial or other conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferese, R., Zampatti, S., Griguoli, A.M.P. et al. A New Splicing Mutation in the L1CAM Gene Responsible for X-Linked Hydrocephalus (HSAS). J Mol Neurosci 59, 376–381 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-016-0754-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-016-0754-3