Summary
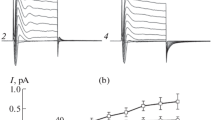
Addition of filipin (50 μm) to the inside bathing solution of the frog skin resulted in a transient increase in the active sodium transport [measured as short-circuit current (SCC)]. The filipin-induced increase in the SCC required the presence of calcium. The calcium ionophore A23187 (4 μm) also induced a transient increase in the SCC. After the activation of the SCC by A23187, the SCC could not be activated by filipin. This indicates that the polyene antibiotic filipin acts as a calcium ionophore. Higher concentrations (40 μm) of A23187 resulted in a shrinking of the cells in the transporting cell layer. A23187 also increased the potassium-42 exchange in the isolated epithelium. It is suggested that calcium inophores enhanced the intracellular calcium concentration; this increase in the calcium concentration resulted in an increase in the potassium permeability of the inward-facing membrane. The increase in the potassium permeability might explain the observed increase in the SCC.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreoli, T.E., Schafer, A.J. 1976. Mass transport across cell membranes: The effects of antidiuretic hormone on water and solute flows in epithelia.Annu. Rev. Physiol. 38:451
Berridge, M.J. 1975. The interaction of cyclic nucleotides and calcium in the control of cellular activity.In: Advances in Cyclic Nucleotide Research. Vol. 6, p. 1. P. Greengard and G.A. Robinson, editor. Raven Press, New York
Biber, T.U.L., Aceves, J., Mandel, L.J. 1972. Potassium uptake across serosal surface of isolated frog skin epithelium.Am. J. Physiol. 222:1366
Curran, P.F., Cereijido, M. 1965. K fluxes in frog skin.J. Gen. Physiol. 48:1011
Cuthbert, A.W., Shum, W.K. 1974. Binding of amiloride to sodium channels in frog skin. Mol. Pharmacol.10:880
Finn, A.L., Nellans, H. 1972. The kinetics and distribution of potassium in the toad bladder.J. Membrane Biol. 8:189
Gardos, G., Lassen, U.V., Pape, L. 1976. Effect of antihistamines and chlorpromazine on the calcium-induced hyperpolarization of theAmphiuma red cell membrane.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 448:599
Handler, J.S., Butcher, E.W., Orloff, J. 1965. The effect of vasopressin and of theophylline in the concentration of adenosine 3′, 5′-phosphate in the urinary bladder of the toad.J. Biol. Chem. 240:1024
Hodgkin, A. 1957. Ionic movements and electrical activity in giant nerve fibres.Proc. R. Soc. London B 148:1
Johnsen, A.H., Nielsen, R. 1978. Effects of the antidiuretic hormone, arginine vasotocin, theophylline, filipin and A23187 on cyclic AMP in isolated frog skin epithelium (Rana Temporaria). Acta Physiol. Scand. (in press.)
Koefoed-Johnsen, V., Ussing, H.H. 1958. The nature of the frog skin potential.Acta Physiol. Scand. 42:298
Lichenstein, N.S., Leaf, A. 1965. Effect of amphotericin B on the permeability of the toad bladder.J. Clin. Invest. 44:1328
Nielsen, R. 1971. Effect of amphotericin B on the frog skinin vitro. Evidence for outward active potassium transport across the epithelium.Acta Physiol. Scand. 83:106
Nielsen, R. 1977. Effect of the antibiotic filipin on the permeability of the inward-and the outward-facing membranes of the isolated frog skin (Rana temp.).Acta Physiol. Scand. 99:399
Nielsen, R., Tomlinson, R.W.S. 1970. The effect of amiloride on sodium transport in the normal and moulting frog skin.Acta Physiol. Scand. 79:238
Reed, P.W. 1976. Effects of the divalent cation ionophore A23187 on potassium permeability of rat erythrocytes.J. Biol. Chem. 251:3489
Salako, L.A., Smith, A.J. 1970. Changes in sodium pool and kinetics of sodium transport in frog skin produced by amiloride.Br. J. Pharmacol. 39:99
Sousa, R.C., de, Grosso, A. 1973. Effects of diphenylhydantoin on transport processes in frog skin (Rana ridibunda).Experientia 29:1097
Ussing, H.H., Zerahn, K. 1951. Active transport of sodium as the source of electric current in the short-circuited isolated frog skin.Acta Physiol. Scand. 23:110
Van Zutphen, H., Demel, R.N., Norman, A.W., Van Deenen, L.L.M. 1971. The action of polyene antibiotics on lipid bilayer membranes in the presence of several cations and anions.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 241:310
Voûte, C.L., Ussing, H.H. 1968. Some morphological aspects of active sodium transport.J. Cell Biol. 36:625
Zylber, E.A., Rotunno, C.A., Cereijido, M. 1975. Ionic fluxes in isolated epithelial cells of the abdominal skin of the frogLeptodactylus ocellatus.J. Membrane Biol. 22:265
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nielsen, R. Effect of the polyene antibiotic filipin and the calcium ionophore A23187 on sodium transport in isolated frog skin (Rana temporaria). J. Membrain Biol. 40 (Suppl 1), 331–345 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02026015
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02026015