Summary
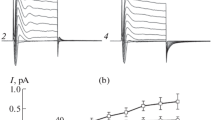
The apical membrane of epithelial cells from the A6 cell line grown on impermeable substrata was studied using the patch-clamp technique. We defined the apical membrane as that membrane in contact with the growth medium. In about 50% of the patches, channels with single-unit conductances of 360±45 pS in symmetrical 105mm NaCl solutions, and characteristic voltage-dependent inactivation were observed. Using excised membrane patches and varying the ionic composition of the bathing medium, we determined that the channels were anion selective, with a permeability ratio for Cl− over Na+ of about 9∶1, calculated from the reversal potential using the constantfield equation. The channel was most active at membrane potentials between ±20 mV and inactivated, usually within a few seconds, at higher potentials of either polarity. Reactivation from this inactivation was slow, sometimes requiring minutes. In addition to its fully open state, the channel could also enter a flickering state, which appeared to involve rapid transitions to one or more submaximal conductance levels. The channel was inhibited by the disulfonic stilbene SITS in a manner characteristic of reversible open-channel blockers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blatz, A.L., Magleby, K.L. 1983. Single voltage-dependent chloride-selective channels of large conductance in cultured rat muscle.Biophys. J. 43:237–241
Cabantchik, Z.I., Rothstein, A. 1972. The nature of the membrane sites controlling anion permeability of human red blood cells as determined by studies with disulfonic stilbene derivatives.J. Membrane Biol. 10:311–330
Colombini, M. 1979. A candidate for the permeability pathway of the outer mitochondrial membrane.Nature (London) 279:643–645
Erlij, D. 1976. Solute transport across isolated epithelia.Kidney Int. 9:76–87
Frizzell, R.A., Field, M., Schultz, S.G. 1979. Sodium-coupled chloride transport by epithelial tissues.Am. J. Physiol. 236:F1-F8
Grantham, J. 1970. Vasopressin: Effect on deformability of urinary surface of collecting duct cells.Science 168:1093–1095
Hamill, O.P., Marty, A., Neher, E., Sakmann, B., Sigworth, F.J. 1981. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches.Pfluegers Arch. 391:85–100
Handler, J.S., Perkins, F.M., Johnson, J.P. 1980. Studies of renal cell function using cell culture techniques.Am. J. Physiol. 238:F1-F9
Handler, J.S., Preston, A.S., Perkins, F.M., Matsumura, M., Johnson, J.P., Watlington, C.O. 1981. The effect of adrenal steroid hormones on epithelia formed in culture by A6 cells.Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 372:442–454
Higgins, J.T., Jr., Gebler, B., Frömter, E. 1977. Electrical properties of amphibian urinary bladder epithelia. II. The cell potential profile inNecturus maculosus.Pfluegers Arch. 371:87–97
Klyce, S.D., Wong, R.K.S. 1977. Site and mode of adrenaline action on chloride transport across the rabbit corneal epithelium.J. Physiol. (London) 266:777–799
Knauf, P.A., Rothstein, A. 1971. Chemical modification of membranes. I. Effects of sulfhydryl and amino reactive reagnets on anion and cation permeability of the human red blood cell.J. Gen. Physiol. 58:190–210
Kristensen, P. 1981. Is chloride transfer in frog skin localized to a special cell type?Acta Physiol. Scand. 113:123–124
Kristensen, P. 1983. Exchange diffusion, electrodiffusion and rectification in the chloride transport pathway of frog skin.J. Membrane Biol. 72:141–151
Larsen, E.H., Kristensen, P. 1978. Properties of a conductive cellular chloride pathway in the skin of the toad (Bufo bufo).Acta Physiol. Scand. 102:1–21
Larsen, E.H., Rasmussen, B.E. 1982. Chloride channels in toad skin.Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London B299:413–434
Macknight, A.D.C. 1977. Contribution of mucosal chloride to chloride in toad bladder epithelial cells.J. Membrane Biol. 36:55–63
Macknight, A.D.C., DiBona, D.R., Leaf, A. 1980. Sodium transport across toad urinary bladder: A “model” tight epithelium.Physiol. Rev. 60:615–715
Miller, C., White, M.M. 1980. A voltage-gated conductance fromTorpedo electroplax membrane.Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 341:534–551
Nagel, W., Garcia-Diaz, J.F., Armstrong, W. McD. 1981. Intracellular ionic activities in frog skin.J. Membrane Biol. 61:127–134
Narvarte, J., Finn, A.L. 1980. Anion-sensitive sodium conductance in the apical membrane of toad urinary bladder.J. Gen. Physiol. 76:69–81
Neher, E. 1983. The charge carried by single-channel currents of rat cultured muscle cells in the presence of local anaesthetics.J. Physiol. (London) 339:663–678
Neher, E., Steinbach, J.H. 1978. Local anaesthetics transiently block currents through single acetylcholine-receptor channels.J. Physiol. (London) 277:153–176
Perkins, F.M., Handler, J.S. 1981. Transport properties of toad kidney epithelia in culture.Am. J. Physiol. 241:C154-C159
Petersen, K.U., Reuss, L. 1983. Cyclic AMP-induced chloride permeability in the apical membrane ofNecturus gallbladder epithelium.J. Gen. Physiol. 81:705–729
Rafferty, K.A. 1969. Mass culture of amphibia cells: Methods and observations concerning stability of cell type.In: Biology of Amphibian Tumors. M. Mizell, editor. pp. 52–81. Springer-Verlag, New York
Rick, R., Dörge, A., Arnim, E. von, Thurau, K. 1978a. Electron microprobe analysis of frog skin epithelium: Evidence for a syncytial sodium transport compartment.J. Membrane Biol. 39:313–331
Rick, R., Dörge, A., Macknight, A.D.C., Leaf, A., Thurau, K. 1978b. Electron microprobe analysis of the different epithelial cells of toad urinary bladder: Electrolyte concentrations at different functional states of transepithelial sodium transport.J. Membrane Biol. 39:257–271
Rothstein, A., Cabantchik, Z.I., Knauf, P. 1976. Mechanism of anion transport in red blood cells: Role of membrane proteins.Fed. Proc. 35:3–10
Russell, J.M., Boron, W.F. 1976. Role of chloride transport in regulation of intracellular pH.Nature (London) 264:73–74
Sachs, F., Neil, J., Barkakati, N. 1982. The automated analysis of data from single ionic channels.Pfluegers Arch. 395:331–340
Sariban-Sohraby, S., Burg, M.B., Turner, R.J. 1983. Apical sodium uptake in the toad kidney epithelial cell line A6.Am. J. Physiol. 244:C167-C171
Schein, S.J., Colombini, M., Finkelstein, A. 1976. Reconstitution in planar lipid bilayers of a voltage-dependent anion-selective channel obtained fromParamecium mitochondria.J. Membrane Biol. 30:99–120
Ussing, H.H. 1960. The alkali metal ions in biology. I. The alkali metals in isolated systems and tissues.In: Handbuch der Experimentellen Pharmakologie. Erganzungswerk. 11–13. O. Eichler and A. Farah, editors. pp. 1–195. Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Voûte, C.L., Meier, W. 1978. The mitochondria-rich cell of frog skin as hormone-sensitive “shunt-path”.J. Membrane Biol. Special Issue:151–165
White, M.M., Miller, C. 1979. A voltage-gated anion channel from the electric organ ofTorpedo californica.J. Biol. Chem. 254:10161–10166
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nelson, D.J., Tang, J.M. & Palmer, L.G. Single-channel recordings of apical membrane chloride conductance in A6 epithelial cells. J. Membrain Biol. 80, 81–89 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01868692
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01868692