Summary
Jejunal absorption of glucose, water, sodium and potassium was investigated under the influence of intravenously injected glucagon. This was done in 1) metabolically healthy adults, 2) patients with growth onset diabetes and reduced insulin secretion after glucagon, 3) patients with juvenile onset diabetes who do not secrete insulin after glucagon injection. A triple lumen perfusion technique was used.
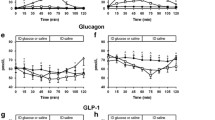
Results: There is an initial short lasting increase of glucose absorption after glucagon administration in all three groups investigated. This was more pronounced in the diabetics than in the metabolically healthy adults. In a second phase, which was most marked 30–45 minutes after glucagon administration, a significant decrease of glucose absorption was seen. Sodium and water uptake were reduced after glucagon administration and potassium was found to be secreted into the lumen.
Zusammenfassung
Der Einfluß von Glucagon auf die Resorption von Glucose, Wasser, Natrium und Kalium wurde mittels der segmentalen Dünndarmperfusion mit einer dreilumigen Sonde im oberen Jejunum bei 1) stoffwechselgesunden Probanden, 2) Altersdiabetikern mit verminderter Insulinsekretion nach Glucagongabe, 3) insulinbedürftigen Diabetikern vom Typ des juvenilen Diabetes mellitus untersucht.
Nach Messung der Resorption über zwei 30 min-Perioden wurde den Probanden 1 mg Glucagon intravenös injiziert und danach die Resorption über vier 15 min-Perioden ermittelt.
Ergebnisse: Nach der Glucagongabe trat in allen drei Gruppen zunächst ein kurzdauernder Anstieg der Glucoseresorption auf. Dieser war bei den Diabetikern stärker als bei den stoffwechselgesunden Probanden. Anschließend kam es zu einer signifikanten Resorptionsminderung für Glucose. Die Wasser- und Natriumresorption wurden durch Glucagon gehemmt, Kalium wurde ins Darmlumen sezerniert.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Barbezat, G. O., Grossman, M. J.: Glucagon stimulates intestinal secretion. Lancet1971 I, 918
Barbezat, G. O., Grossman, M. J.: Cholera-like diarrhoea induced by glucagon plus gastrin. Lancet1971 I, 1025–1026
Barbezat, G. O., Bank, S., Marks, J. N.: Diarrhoea induced in humans by glucagon plus gastrin. Lancet1972 I, 904–905
Beyreiss, K., Müller, F.: Die quantitative Bestimmung der Resorption von Monosacchariden im Gesamtorganismus. In: Rommel, K., Clodi, P. H., Biochemische und klinische Aspekte der Zuckerabsorption, S. 35–50. Stuttgart-New York: F. K. Schattauer Verlag 1970
Bloch, R., Menge, H., Lorenz-Meyer, H., Riecken, E. O.: Automatisierte segmentale Dünndarmperfusion. Eine Methode zur Messung der intestinalen Resorption. Klin. Wschr.49, 1218–1222 (1971)
Cooper, H., Levitan, R., Fordtran, J. S., Ingelfinger, F. J.: A method for studying absorption of water and solute from the human small intestine. Gastroenterology50, 1–7 (1966)
Dotevall, G., Kock, N. G.: The effect of glucagon on intestinal motility in man. Gastroenterology45, 364–367 (1963)
Ewe, K., Laubental, G., Hoditz, U.: Die Wirkung von Pentagastrin und Glucagon auf die Wasser-, Elektrolyt-und Glucoseresorption im menschlichen Jejunum. Vortrag 79. Tagung der Dtsch. Ges. Inn. Med., Wiesbaden 1973
Gleeson, M. H., Bloom, S. R., Polak, J. M., Henry, K. Dowling, R. H.: Endocrine tumour in kidney affecting small bowel structure, motility, and absorptive function. Gut12, 773–782 (1971)
Gottesbüren, H., Schmitt, E., Menge, H., Bloch, R., Lorenz-Meyer, H., Riecken, E. O.: Untersuchungen zum Einfluß des Insulins auf die intestinale Resorption beim Menschen. I. Vergleich der Glucose-, Wasser- und Elektrolytresorption bei Diabetikern und bei stoffwechselgesunden Probanden. Res. exp. Med.160, 326–330 (1973)
Gottesbüren, H., Schmitt, E., Menge, H., Bloch, R., Lorenz-Meyer, H., Riecken, E. O.: Untersuchungen zum Einfluß des Insulins auf die intestinale Resorption beim Menschen. II. Der Einfluß endogenen und intravenös injizierten Insulins auf die Resorption. Res. exp. Med.161, 262–271 (1973)
Heding, G. L., Rasmussen, S. M.: Determination of pancreatic and gut glucagon-like immunoreactivity in normal and diabetic subjects. Diabetologia8, 408–411 (1972)
Hubel, K. A.: Effects of secretin and glucagon on intestinal transport of ions and water in the rat. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. (N.Y.)139, 656–658 (1972)
Hydén, S.: A turbidometric method for the determination of higher polyethylene glycols in biological materials. K. Lantbr. Högsk. Annlr.22, 139–145 (1955)
Kock, N. G., Darle, N., Dotevall, G.: Inhibition of intestinal motility in man by glucagon given intraportally. Gastroenterology53, 88–92 (1967)
Kock, N. G., Tibblin, S., Schenk, W. G.: Haemodynamic responses to glucagon: an experimental study of central, visceral and peripheral effects. Ann. Surg.171, 373–379 (1970)
Lawrence, A. M., Forland, M.: Glucagon provocative test for pheochromocytoma. J. Lab. clin. Med.64, 875 (1964)
Mekhjian, H., King, D., Sanzenbacher, L., Zollinger, R.: Glucagon and secretin inhibit water and electrolyte transport in the human jejunum. Gastroenterology62, 782 (1972) (Abstract)
Nagler, R., Forrest, W. J., Shapiro, H. N.: Effect of glucagon on transfer of glucose utilising everted sacs of small intestine. Amer. J. Physiol.198, 1323–1325 (1960)
Necheles, H., Sporn, J.: Effect of glucagon on gastrointestinal motility. Amer. J. Gastroent.45, 34–40 (1966)
Paul, F.: Wirkung von Pankreas-Glucagon und Sekretin auf die Motilität des proximalen und distalen Magen-Darmtraktes des Menschen. Vortrag 79. Tagung der Dtsch. Ges. Inn. Med., Wiesbaden 1973
Ponz, F., Lluch, M., Planas, J.: Efectos del glucagón sobre la absorción intestinal de glucosa. Rev. esp. Fisiol.13, 25–33 (1957)
Varro, V., Csernay, L.: The effect of intra-arterial insulin and glucagon on the glucose metabolism of the small intestine in the dog. Scand. J. Gastroent.1, 232–237 (1966)
Verner, J. V., Morrison, A. B.: Islet cell tumor and a syndrome of refractory watery diarrhea and hypokalemia. Amer. J. Med.25, 374–380 (1958)
Whalen, G. E., Harris, J. A., Geenen, J. E., Soergel, K. H.: Sodium and water absorption from the human small intestine. The accuracy of the perfusion method. Gastroenterology51, 975–984 (1966)
Wide, L., Porath, J.: Radioimmunoassay of proteins with the use of Sephadex-coupled antibodies. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.)130, 257–260 (1966)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Mit Unterstützung durch die Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft Ri. 136/9.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gottesbüren, H., Leising, H., Menge, H. et al. Einfluß von Glucagon auf die Glucose-, Wasser-und Elektrolytresorption des menschlichen Jejunums. Klin Wochenschr 52, 926–929 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01468939
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01468939