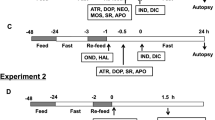
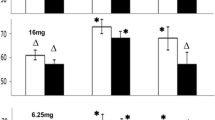
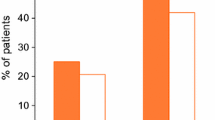
Abstract
The present study investigated both the healing rate (after four weeks) and the relapse rate (during six months) following treatment with the dopamine-like drugs bromocriptine (2.5 mg twice daily), amantadine (100 mg nocte), or with the H2 blockers cimetidine (800 mg nocte), and famotidine (40 mg nocte) in 124 patients with endoscopically proven duodenal ulcer (DU). The ulcer was completely healed in 27 (amantadine), 26 (bromocriptine), 23 (cimetidine), and in 24 (famotidine) patients. Relapse was noted in 34.7% (cimetidine) and 25% (famotidine) versus 11.7% (amantadine) and 7.7% (bromocriptine) DU patients. No significant difference was found in initial healing rates. However, the relapse rate in the cimetidine-treated group was significantly higher than in all the other test groups. Additional comparisons between all the treatment categories showed a significantly lower relapse rate with the dopamine-like agents. These important new results indicate that dopamine-like compounds are equally effective as H2 blockers in inducing DU healing and may offer a promising advantage over H2 blockers concerning their efficacy in preventing ulcer relapse in DU patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Szabo S, Neumeyer JL: Dopamine agonists and antagonists in duodenal ulcer disease.In ACS Symposium Series. C Kaiser, W Kebabian (eds). Washington, American Chemical Society, 1983, pp 175–196
Ho KY, Thorner MO: Therapeutic application of bromocriptine in endocrine and neurological diseases. Drugs 36:67–82, 1988
Roehrich H, Dackis CA, Gold MS: Bromocriptine. Med Res Rev 7:243–269, 1987
Sikiric P, Rotkvic I, Mise S, Krizanac S, Gjuris V, Jagic V, Suchanek E, Petek M, Udovicic I, Geber J, Tucan-Foretic M, Cvitanovic B, Ivanovic D, Marovic A: The influence of dopamine receptor agonists and an antagonist on acute pancreatitis in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 147:321–326, 1988
Hernandez DE, Orlando RC, Adcock JW, Patrick KS, Nemeroff CB, Prange AJ: Prevention of stress induced gastric ulcers by dopamine agonists in the rat. Life Sci 35:2453–2458, 1984
Parmar NS, Tariq M, Ageel AM: Effect of bromocriptine a dopamine receptor agonist on experimentally induced gastric ulcers in albino rats. Life Sci 35:2035–2039, 1984
Sikiric P, Rotkvic I, Mise S, Krizanac S, Gjuris V, Jukic J, Suchanek E, Petek M, Udovicic I, Kalogjera L, Geber J, Tucan-Foretic M, Duvnjak M, Philipp M, Balen I, Anic T: The influence of dopamine agonists and antagonists on indomethacin lesions in stomach and small intestine in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 158:61–67, 1988
Sikiric P, Geber J, Suchanek E, Ivanovic D, Gjuris V, Aleksic J, Reic P, Marovic A: The role of dopamine in the formation of gastric ulcers in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 112:127–128, 1985
Sikiric P, Geber J, Ivanovic D, Suchanek E, Gjuris V, Tucan-Foretic M, Mise S, Cvitanovic B, Rotkvic I: Dopamine antagonists induce gastric lesions in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 131:105–109, 1986
Sikiric P, Seiwerth S, Grabarevic Z, Rotkvic I, Jagic V, Mise S, Duvnjak M, Artukovic B, Brkic, H, Vukovic S, Banic M, Brkic T, Djermanovic Z, Dodig M, Bacic M, Marovic A, Uglesic M: The comparison between the effects of dopamine drugs on gastric and liver lesions as well as on duodenal liver lesions induced in two suitable experimental rats models. Dig Dis Sci 35:1567, 1990
Piper DW: Drugs for the prevention of peptic ulcer recurrence. Drugs 26:439–453, 1983
McLean AJ, Harcourt DM, McNeil JJ: Relapse rate as a major determinant of drug selection in peptic ulcer therapy. Drugs 35:329–333, 1988
Sikiric P, Mise S, Rotkvic I, Suchanek E, Geber J, Gjuris V, Tucan-Foretic M, Ivanovic D, Cvitanovic B, Marovic A: Bromocriptine in duodenal ulcer patients—a preliminary report.In Xth International Congress of Pharmacology. Sydney, August 23–27, 1987. Abstracts, p 1527
Sikiric P, Rotkvic I, Mise S, Petek M, Rucman R, Siewerth S: Dopamine agonists and H2 receptors antagonists in duodenal ulcer treatment—a comparative blind study. Dig Dis Sci 34:1320, 1989
Rotkvic I, Sikiric P, Mise S, Petek M, Rucman R, Seiwerth S, Zjacic-Rotkvic V, Lang N, Grabarevic Z, Jagic V, Brkic T, Banic M, Anic T, Anic B, Brkic H, Bacic M: Dopamine agonists and H2 receptor antagonists in duodenal ulcer treatment—follow-up. Dig Dis Sci 35:1567, 1990
Somerville KW, Langman MSJ: Newer anti-secretory agents for peptic ulcer. Drugs 25:315–330, 1983
Dobrilla G, Vallaperta P, Amplatz S: Influence of ulcer healing agents on ulcer relapse after discontinuation of acute treatment: A pooled estimate of controlled clinical trials. Gut 29:181–187, 1988
Martin DF, May, SJ, Tweedle DEF, Hollanders D, Ravenscroft MM, Miller JP: Difference in relapse rates of duodenal ulcer after healing with cimetidine or tripotassium dicitrato bismuthate. Lancet 1:7–10, 1981
Kang JK, Piper DW: Cimetidine and colloidal bismuth in treatment of chronic duodenal ulcer. Comparison of initial healing and recurrences after healing. Digestion 23:73–79,1982
Shreeve DR, Klass HJ, Jones PE: Comparison of cimetidine and tripotassium dicitrato bismuthate in healing and relapse of duodenal ulcer. Digestion 28:96–101, 1983
Lee FI, Samlof IM, Hardman M: Comparison of tripotassium dicitrate bismuthate tablets and ranitidine in healing and relapse of duodenal ulcers. Lancet 1:1299–1301, 1985
Hamilton I, O'Connor HJ, Wood NC, Bradbury I, Axon ATR: Healing and recurrence of duodenal ulcer after treatment with tripotassium dicitrato bismuthate (TDB) tablets of cimetidine. Gut 27:106–110, 1986
Hansky J, Korman MG, Schmidt GT, Stern AI, Shaw RG: Relapse rate of duodenal ulcer after healing with cimetidine or Mylanta II. Gastroenterology 78:1179, 1980
Vezzadini P, Sternini C, Bonora G, Botti CP, Lugli C, Labo G: Relapse rates of duodenal ulcer after healing with pirenzepine or cimetidine: A double-blind study. Scand J Gastroenterol 17(S78):100, 1982
Dzieniszewski J, Pokora J, Knapik Z: Duodenal ulcer relapse rate in treatment with pirenzipine and ranitidine. Dig Dis Sci 31:210, 1986
Hentschel EK, Schutze K, Dufek W: Relapse rate of duodenal ulcer after treatment with sucralfate or cimetidine. Wien Klin Wochenschr 96:153–156, 1984
Caldara R, Grimaldi D, Ferrari C: Bromocriptine, gastric acid output and gastrin secretion. Lancet 1:902–903, 1977
Cowan GO: Bromocriptine and gastric acid output. Lancet 1:425, 1977
Parkes D: Amantadine. Adv Drug Res 8:1–81, 1974
Parkes D: Bromocriptine. Adv Drug Res 12:247–344, 1977
Wormsley KG: Aetiology of duodenal ulcer.In Peptic Ulcer Disease: Basic and Clinical Aspects. GF Nelis, J Boeve, JJ Misiewicz (eds). Dordrecht, Martinus Nijhoff Publishers, 1985, pp 53–57
Willems JL, Buylaert WA, Lefebvre RA, Bogaert MG: Neuronal dopamine receptors on autonomic ganglia and sympathetic nerves and dopamine receptors in the gastrointestinal system. Pharmacol Rev 37:165–216, 1985
Valenzuela JE, Defilippi C, Diaz G, Navia E, Merino J: Effect of dopamine on human gastric and pancreatic secretion. Gastroenterology 76:323–326, 1979
Maeda-Hagiwara M, Watanabe K: Bromocriptine inhibits 2-deoxy-d-glucose-stimulated gastric acid secretion in rat. Eur J Pharmacol 90:11–17, 1983
Maeda-Hagiwara M, Watanabe K: Influence of dopamine receptor agonists on gastric acid secretion induced by thyrotropin-releasing hormone in the perfused stomach of anesthetized rats. Br J Pharmacol 79:297–303, 1983
Hovendal CP, Bech K: Effect of dopamine on bethanecholstimulated gastric mucosal blood flow and gastric acid secretion in dogs with gastric fistula. Scand J Gastroenterol 17:637–651, 1982
Caldara R, Ferrari C, Romussi M, Paracchi A: Effect of bromocriptine administration on gastric acid and gastrin secretion in man. J Endocrinol Invest 2:45–49, 1979
Hirst BH, Lund PK, Reed JD, Sanders DJ: Bromocriptine, gastric acid output and gastrin secretion. Lancet 1:902, 1977
Robert A: Cytoprotection by prostaglandins. Gastroenterology 77:761–767, 1979
Orloff LA, Orloff MS, Bunnet NW, Walsh JH: Dopamine and norepinephrine in the alimentary tract changes after chemical sympathectomy and surgical vagotomy. Life Sci 36:1625–1631, 1985
Kullmann R, Breull WR, Reinsberg J, Wassermann K, Konopatzki A: Dopamine produces vasodilation in specific regions and layers of the rabbit gastrointestinal tract. Life Sci 32:2115–2122, 1983
Hernandez DE, Walker CH, Valenzuela JE, Mason GA: Increased dopamine receptor binding in duodenal mucosa of duodenal ulcer patients. Dig Dis Sci 34:543–547, 1989
Hernandez DE, Mason GA: Involvement of dopamine receptors in stress gastric ulceration.In Ulcer Disease: New Aspects of Pathogenesis and Pharmacology. S Szabo, CJ Pfeiffer (eds) CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, 1988, pp 207–215
Pinder RM, Brodgen RN, Sawyer PR, Speight TM, Spencer R, Avery GS: Metoclopramide: A review of its pharmacological properties and clinical use and therapeutic efficacy in peptic ulcer disease. Drugs 12:81–113, 1976
Harrington RA, Hamilton CW, Brodgen RN, Linkewich JA, Romankievicz JA, Heel RC: Metoclopramide: An updated review of its pharmacological properties and clinical use. Drugs 25:451–494, 1983
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sikiric, P., Rotkvic, I., Mise, S. et al. Dopamine agonists prevent duodenal ulcer relapse. Digest Dis Sci 36, 905–910 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01297139
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01297139