Abstract
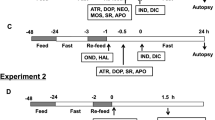
The ulcerogenic potential of dopamine antagonists and l-NAME in rats provides unresolved issues of anti-emetic neuroleptic application in both patients and experimental studies. Therefore, in a 1-week study, we examined the pressures within the lower oesophageal and the pyloric sphincters in rats [assessed manometrically (cm H2O)] after dopamine neuroleptics/prokinetics, l-NAME, l-arginine and stable gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157 were administered alone and/or in combination. Medication (/kg) was given once daily intraperitoneally throughout the 7 days, with the last dose at 24 h before pressure assessment. Given as individual agents to healthy rats, all dopamine antagonists (central [haloperidol (6.25 mg, 16 mg, 25 mg), fluphenazine (5 mg), levomepromazine (50 mg), chlorpromazine (10 mg), quetiapine (10 mg), olanzapine (5 mg), clozapine (100 mg), sulpiride (160 mg), metoclopramide (25 mg)) and peripheral(domperidone (10 mg)], l-NAME (5 mg) and l-arginine (100 mg) decreased the pressure within both sphincters. As a common effect, this decreased pressure was rescued, dose-dependently, by BPC 157 (10 µg, 10 ng) (also note that l-arginine and l-NAME given together antagonized each other’s responses). With haloperidol, l-NAME worsened both the lower oesophageal and the pyloric sphincter pressure, while l-arginine ameliorated lower oesophageal sphincter but not pyloric sphincter pressure, and antagonized l-NAME effect. With domperidone, l-arginine originally had no effect, while l-NAME worsened pyloric sphincter pressure. This effect was opposed by l-arginine. All these effects were further reversed towards a stronger beneficial effect, close to normal pressure values, by the addition of BPC 157. In addition, NO level was determined in plasma, sphincters and brain tissue. Thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) were also assessed. Haloperidol increased NO levels (in both sphincters, the plasma and brain), consistently producing increased TBARS levels in the plasma, sphincters and brain tissues. These effects were all counteracted by BPC 157 administration. In conclusion, we revealed that BPC 157 counteracts the anti-emetic neuroleptic class side effect of decreased pressure in sphincters and the dopamine/NO-system/BPC 157 relationship.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abi-Dargham A (2014) Schizophrenia: overview and dopamine dysfunction. J Clin Psychiatry 75:e31
Acosta A, Camilleri M (2015) Prokinetics in gastroparesis. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 44:97–111
Aziz Q, Thompson DG (1998) Brain-gut axis in health and disease. Gastroenterology 114:559–578
Balenovic D, Bencic ML, Udovicic M et al (2009) Inhibition of methyldigoxin-induced arrhythmias by pentadecapeptide BPC 157: a relation with NO-system. Regul Pept 156:83–89
Balenovic D, Barisic I, Prkacin I et al (2012) Mortal furosemide-hypokalemia-disturbances in rats NO-system related. Shorten survival by l-NAME. Therapy benefit with BPC 157 more than with l-arginine. J Clin Exp Cardiolog 3:201
Barisic I, Balenovic D, Klicek R et al (2013) Mortal hyperkalemia disturbances in rats are NO-system related. The life saving effect of pentadecapeptide BPC 157. Regul Pept 181:50–66
Bedekovic V, Mise S, Anic T et al (2003) Different effect of antiulcer agents on rat cysteamine-induced duodenal ulcer after sialoadenectomy, but not gastrectomy. Eur J Pharmacol 477:73–80
Bilic I, Zoricic I, Anic T et al (2001) Haloperidol-stomach lesions attenuation by pentadecapeptide BPC 157, omeprazole, bromocriptine, but not atropine, lansoprazole, pantoprazole, ranitidine, cimetidine and misoprostol in mice. Life Sci 68(16):1905–1912
Boban-Blagaic A, Blagaic V, Romic Z et al (2006) The influence of gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157 on acute and chronic ethanol administration in mice. The effect of N(G)-nitro-l-arginine methyl ester and l-arginine. Med Sci Monit 12(1):36–45
Braverman AS, Vegesna AK, Miller LS et al (2011) Pharmacologic specificity of nicotinic receptor-mediated relaxation of muscarinic receptor precontracted human gastric clasp and sling muscle fibers within the gastroesophageal junction. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 338:37–46
Cesarec V, Becejac T, Misic M et al (2013) Pentadecapeptide BPC 157 and the esophagocutaneous fistula healing therapy. Eur J Pharmacol 701(1–3):203–212
Chang CH, Tsai WC, Lin MS, Hsu YH, Pang JH (2011) The promoting effect of pentadecapeptide BPC 157 on tendon healing involves tendon outgrowth, cell survival, and cell migration. J Appl Physiol 110(3):774–780
Chang CH, Tsai WC, Hsu YH, Pang JH (2014) Pentadecapeptide BPC 157 enhances the growth hormone receptor expression in tendon fibroblasts. Molecules 19(11):19066–19077
Costa MA, Elesgaray R, Loria A, Balaszczuk AM, Arranz C (2006) Vascular and renal effects of dopamine during extracellular volume expansion: role of nitric oxide pathway. Life Sci 78(14):1543–1549
Del Bel EA, Guimarães FS, Bermúdez-Echeverry M et al (2005) Role of nitric oxide on motor behavior. Cell Mol Neurobiol 25(2):371–392
Dobric I, Drvis P, Petrovic I et al (2007) Prolonged esophagitis after primary dysfunction of the pyloric sphincter in the rat and therapeutic potential of the gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157. J Pharmacol Sci 104:7–18
Gallagher G, Brown A, Szabo S (1987) Effect of dopamine-related drugs on duodenal ulcer induced by cysteamine or propionitrile: prevention and aggravation may not be mediated by gastrointestinal secretory changes in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 240(3):883–889
Glare P, Miller J, Nikolova T, Tickoo R (2011) Treating nausea and vomiting in palliative care: a review. Clin Interv Aging 6:243–259
Grabarevic Z, Tisljar M, Artukovic B et al (1997) The influence of BPC 157 on nitric oxide agonist and antagonist induced lesions in broiler chicks. J Physiol Paris 91(3–5):139–149
Grande L, Lacima G, Ros E et al (1992) Lack of effect of metoclopramide and domperidone on esophageal peristalsis and esophageal acid clearance in reflux esophagitis. Digest Dis Sci 37(4):583–588
Hsieh MJ, Liu HT, Wang CN et al (2017) Therapeutic potential of pro-angiogenic BPC157 is associated with VEGFR2 activation and up-regulation. J Mol Med (Berl) 95(3):323–333
Huang T, Zhang K, Sun L et al (2015) Body protective compound-157 enhances alkali-burn wound healing in vivo and promotes proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis in vitro. Drug Des Devel Ther 9:2485–2499
Ilic S, Drmic D, Zarkovic K et al (2010) High hepatotoxic dose of paracetamol produces generalized convulsions and brain damage in rats. A counteraction with the stable gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157 (PL 14736). J Physiol Pharmacol 61:241–250
Jandric I, Vrcic H, Jandric Balen M et al (2013) Salutary effect of gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157 in two different stress urinary incontinence models in female rats. Med Sci Monit Basic Res 19:93–102
Jelovac N, Sikiric P, Rucman R et al (1998) A novel pentadecapeptide, BPC 157, blocks the stereotypy produced acutely by amphetamine and the development of haloperidol-induced supersensitivity to amphetamine. Biol Psychiatry 43:511–519
Jelovac N, Sikiric P, Rucman R et al (1999) Pentadecapeptide BPC 157 attenuates disturbances induced by neuroleptics: the effect on catalepsy and gastric ulcers in mice and rats. Eur J Pharmacol 379:19–31
Klicek R, Sever M, Radic B et al (2008) Pentadecapeptide BPC 157, in clinical trials as a therapy for inflammatory bowel disease (PL14736), is effective in the healing of colocutaneous fistulas in rats: role of the nitric oxide-system. J Pharmacol Sci 108:7–17
Klicek R, Kolenc D, Suran J et al (2013) Stable gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157 heals cysteamine-colitis and colon–colon-anastomosis and counteracts cuprizone brain injuries and motor disability. J Physiol Pharmacol 64:597–612
Kokot A, Zlatar M, Stupnisek M et al (2016) NO system dependence of atropine-induced mydriasis and l-NAME- and l-arginine-induced miosis: reversal by the pentadecapeptide BPC 157 in rats and guinea pigs. Eur J Pharmacol 771:211–219
Luetic K, Sucic M, Vlainic J et al (2017) Cyclophosphamide induced stomach and duodenal lesions as a NO-system disturbance in rats: l-NAME, l-arginine, stable gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157. Inflammopharmacology 25:255–264
Mauri MC, Paletta S, Maffini M et al (2014) Clinical pharmacology of atypical antipsychotics: an update. EXCLI J 13:1163–1191
Meng LN, Chen S, Chen JD, Jin HF, Lu B (2016) Effects of Transcutaneous Electrical Acustimulation on Refractory Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Evid Based Complement Altern Med 2016:8246171
Moncada S, Palmer RMJ, Higgs EA (1991) Nitric oxide: physiology and pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev 43:109–142
Murray-Brown F, Dorman S (2015) Haloperidol for the treatment of nausea and vomiting in palliative care patients. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 11:CD006271
Niedringhaus M, Jackson PG, Evans SR, Verbalis JG, Gillis RA, Sahibzada N (2008) Dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus: a site for evoking simultaneous changes in crural diaphragm activity, lower esophageal sphincter pressure, and fundus tone. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 294:R121–R131
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358
Oldham KM, Bowen PE (1998) Oxidative stress in critical care: is antioxidant supplementation beneficial? J Am Diet Assoc 98:1001–1008
Palheta MS, Graça JR, Santos AA et al (2014) The participation of the nitrergic pathway in increased rate of transitory relaxation of lower esophageal sphincter induced by rectal distension in dogs. Arq Gastroenterol 51:102–106
Paré WP, Glavin GB (1986) Restraint stress in biomedical research: a review. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 10:339–370
Perkins P, Dorman S (2009) Haloperidol for the treatment of nausea and vomiting in palliative care patients. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2:CD006271
Petrovic I, Dobric I, Drvis P et al (2006) An experimental model of prolonged esophagitis with sphincter failure in the rat and the therapeutic potential of gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157. J Pharmacol Sci 102:269–277
Petrovic I, Dobric I, Drmic D et al (2011) BPC 157 therapy to detriment sphincters failure-esophagitis-pancreatitis in rat and acute pancreatitis patients low sphincters pressure. J Physiol Pharmacol 62:527–534
Ramkumar D, Schulze KS (2005) The pylorus. Neurogastroenterol Motil 17(Suppl 1):22–30
Seiwerth S, Brcic L, Batelja Vuletic L et al (2014) BPC 157 and blood vessels. Curr Pharm Des 20:1121–1125
Sikiric P, Geber J, Suchanek E et al (1985) The role of dopamine in the formation of gastric ulcers in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 112:127–128
Sikiric P, Geber J, Ivanovic D et al (1986) Dopamine antagonists induce gastric lesions in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 131:105–109
Sikiric P, Rotkvic I, Mise S et al (1987) The influence of dopamine agonists and antagonists on gastric lesions in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 144:237–239
Sikiric P, Rotkvic I, Mise S et al (1991) Dopamine agonists prevent duodenal ulcer relapse. A comparative study with famotidine and cimetidine. Dig Dis Sci 36:905–910
Sikiric P, Seiwerth S, Grabarevic Z et al (1993) Hepatoprotective effect of BPC 157, a 15-amino acid peptide, on liver lesions induced by either restraint stress or bile duct and hepatic artery ligation or CCl4 administration. A comparative study with dopamine agonists and somatostatin. Life Sci 53:PL291–PL296
Sikiric P, Seiwerth S, Grabarevic Z et al (1997) The influence of a novel pentadecapeptide, BPC 157, on N(G)-nitro-l-arginine methylester and l-arginine effects on stomach mucosa integrity and blood pressure. Eur J Pharmacol 332:23–33
Sikiric P, Marovic A, Matoz W et al (1999) A behavioural study of the effect of pentadecapeptide BPC 157 in Parkinson’s disease models in mice and gastric lesions induced by 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydrophyridine. J Physiol Paris 93:505–512
Sikiric P, Separovic J, Buljat G et al (2000) Gastric mucosal lesions induced by complete dopamine system failure in rats. The effects of dopamine agents, ranitidine, atropine, omeprazole and pentadecapeptide BPC 157. J Physiol Paris 94:105–110
Sikiric P, Seiwerth S, Grabarevic Z et al (2001a) Cysteamine-colon and cysteamine-duodenum lesions in rats. Attenuation by gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157, cimetidine, ranitidine, atropine, omeprazole, sulphasalazine and methylprednisolone. J Physiol Paris 95:261–270
Sikiric P, Seiwerth S, Aralica G et al (2001b) Therapy effect of antiulcer agents on new chronic cysteamine colon lesion in rat. J Physiol Paris 95:283–288
Sikiric P, Jelovac N, Jelovac-Gjeldum A et al (2002) Pentadecapeptide BPC 157 attenuates chronic amphetamine-induced behavior disturbances. Acta Pharmacol Sin 23:412–422
Sikiric P, Seiwerth S, Brcic L et al (2010) Revised Robert’s cytoprotection and adaptive cytoprotection and stable gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157. Possible significance and implications for novel mediator. Curr Pharm Des 16:1224–1234
Sikiric P, Seiwerth S, Rucman R et al (2011) Stable gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157: novel therapy in gastrointestinal tract. Curr Pharm Des 17:1612–1632
Sikiric P, Seiwerth S, Rucman R et al (2014) Stable gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157-NO-system relation. Curr Pharm Des 20:1126–1135
Sikiric P, Seiwerth S, Rucman R et al (2016) Brain-gut axis and pentadecapeptide BPC 157. Theoretical and practical implications. Curr Neuropharmacol 14(8):857–865
Sikiric P, Seiwerth S, Rucman R et al (2017) Stress in gastrointestinal tract and stable gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157. Finally, do we have a solution? Curr Pharm Des. doi:10.2174/1381612823666170220163219
Sivarao DV, Mashimo H, Goyal RK (2008) Pyloric sphincter dysfunction in nNOS-/- and W/Wv mutant mice: animal models of gastroparesis and duodenogastric reflux. Gastroenterology 135:1258–1266
Skorjanec S, Kokot A, Drmic D et al (2015) Duodenocutaneous fistula in rats as a model for “wound healing-therapy” in ulcer healing: the effect of pentadecapeptide BPC 157, L-nitro-arginine methyl ester and l-arginine. J Physiol Pharmacol 66:581–590
Stupnisek M, Kokot A, Drmic D et al (2015) Pentadecapeptide BPC 157 reduces bleeding and thrombocytopenia after amputation in rats treated with heparin, warfarin l-NAME and l-arginine. PLoS ONE 10(4):e0123454
Szabo S, Neumeyer JL (1983) Dopamine agonists and antagonists in duodenal ulcer disease. In: Kaiser C, Kebabian JW (eds) Dopamine Receptors, ACS Symposium Series 224. Am Chem Soc Publ, Washington, pp 175–196
Szabo S, Horner HC, Maull H, Schnoor J, Chiueh CC, Palkovits M (1987) Biochemical changes in tissue catecholamines and serotonin in duodenal ulceration caused by cysteamine or propionitrile in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 240:871–878
Tkalcevic VI, Cuzic S, Brajsa K et al (2007) Enhancement by PL 14736 of granulation and collagen organization in healing wounds and the potential role of egr-1 expression. Eur J Pharmacol 570:212–221
Tohyama Y, Sikirić P, Diksic M (2004) Effects of pentadecapeptide BPC157 on regional serotonin synthesis in the rat brain: alpha-methyl-l-tryptophan autoradiographic measurements. Life Sci 76:345–357
Turkovic B, Sikiric P, Seiwerth S et al (2004) Stable gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157 studied for inflammatory bowel (PLD-116, PL14736, Pliva) induces nitric oxide synthesis. Gastroenterology 126:287
Whittle BJR, Boughton-Smith NK, Moncada S (1992) Biosynthesis and role of the endothelium-derived vasodilator, nitric oxide in gastric mucosa. Ann NY Acad Sci 664:126–139
Zemba M, Cilic AZ, Balenovic I et al (2015) BPC 157 antagonized the general anaesthetic potency of thiopental and reduced prolongation of anaesthesia induced by l-NAME/thiopental combination. Inflammopharmacology 23:329–336
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Ministry of Science, Education and Sports, Republic of Croatia (Grant Number 108-1083570-3635).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Belosic Halle, Z., Vlainic, J., Drmic, D. et al. Class side effects: decreased pressure in the lower oesophageal and the pyloric sphincters after the administration of dopamine antagonists, neuroleptics, anti-emetics, l-NAME, pentadecapeptide BPC 157 and l-arginine. Inflammopharmacol 25, 511–522 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-017-0358-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-017-0358-8