Summary
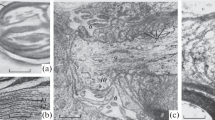
The relationship between the degree of nodal narrowing and the changes in the structure of the axonal cytoskeleton was studied in 53 fibres of mouse sciatic nerve. Nodal narrowing increased with increasing fibre calibre to reach about 20% of the internodal area in the thicker fibres. The narrowing corresponded quantitatively to a decreased number of nodal neurofilaments. Nodal microtubule numbers varied greatly, and a majority of fibres had considerably (approximately 55%) more microtubules in their nodal profile than in the internode. Nodal profiles of different calibre showed an increase in the number of filaments and of microtubules with nodal calibre, although at rates different from those in the internode. The degree of observed axon non-circularities had no discernible effect on the restructuring of the axonal cytoskeleton at the node. A transnodal transport of the axonal cytoskeleton can occur with: (1) accelerated transnodal transport of filaments, (2) stationary internodal fraction of filaments, (3) depolymerization of filaments proximal to the node and repolymerization distally, or (4) different nodal and internodal polymerization equilibria.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arbuthnott, E. R., Boyd, I. A. &Kalu, K. U. (1980) Ultrastructural dimensions of myelinated peripheral nerve fibres in the cat and their relation to conduction velocity.Journal of Physiology 308, 125–57.
Armstrong, R., Toews, A. D. &Morell, P. (1987) Axonal transport through nodes of Ranvier.Brain Research 412, 196–9.
Bamburg, J. R. (1988) The axonal cytoskeleton: stationary or moving matrix?Trends in Neurosciences 11, 248–9.
Berthold, C.-H. (1968) Ultrastructure of the nodeparanode region of mature feline ventral lumbar spinal-root fibres.Acta Societatis Medicorum Upsaliensis 123 (Suppl 9), 37–70.
Berthold, C.-H. (1978) Morphology of normal peripheral axons. InPhysiology and Pathobiology of Axons (edited byWaxman, S. G.) pp. 3–63. New York: Raven Press.
Berthold, C.-H., Corneliuson, O. &Rydmark, M. (1982) Changes in shape and size of cat spinal root myelinated nerve fibers during fixation and Vestopal-W embedding for electron microscopy.Journal of Ultrastructure Research 80, 23–41.
Berthold, C.-H., Corneliuson, O. &Mellström, A. (1986) Peroxidase activity at nodes of Ranvier in lumbosacral ventral spinal roots and in the PNS-CNS transitional region after intramuscular administration of horseradish peroxidase.Journal of Neurocytology 15, 253–60.
Berthold, C.-H., Mellström, A. (1982) Distribution of peroxidase activity at nodes of Ranvier after intramuscular administration of horseradish peroxidase in the cat.Neuroscience 7, 45–54.
Berthold, C.-H., Mellström, A. (1986) Peroxidase activity at consecutive nodes of Ranvier in the nerve to the medial gastrocnemius muscle after intramuscular administration of horseradish peroxidase.Neuroscience 19, 1349–62.
Black, M. M. &Laser, R. J. (1980) Slow components of axonal transport: two cytoskeletal networks.Journal of Cell Biology 86, 616–23.
Bray, D. &Bunge, M. B. (1981) Serial analysis of microtubules in cultured rat sensory axons.Journal of Neurocytology 10, 589–605.
Donoso, J. A. (1986) Microtubule stability along mammalian peripheral nerves.Journal of Neurobiology 17, 383–403.
Friede, R. L. (1971) Changes in microtubules and neurofilaments in constricted, hypoplastic nerve fibers.Acta Neuropathologica Supplement V, 216–25.
Friede, R. L. (1986) Computer editing of morphometric data on nerve fibers. An improved computer program.Acta Neuropathologica 72, 74–81.
Friede, R. L., Bardosi, A. &Wegener, G. (1985) Effects of cold adaptation and starvation on sciatic nerve fibers in the frog.Experimental Neurology 90, 434–43.
Friede, R. L. &Beuche, W. (1985) A new approach toward analyzing peripheral nerve fiber population. I. Variance in sheath thickness corresponds to different geometric proportions of the internodes.Journal of Neuropathology and Experimental Neurology 44, 60–72.
Friede, R. L. &Bischhausen, R. (1980) The fine structure of stumps of transected nerve fibers in subserial sections.Journal of the Neurological Sciences 44, 181–203.
Friede, R. L. &Samorajski, T. (1970) Axon caliber related to neurofilaments and microtubules in sciatic nerve fibers of rats and mice.Anatomical Record 167, 379–88.
Heidemann, S. R., Landers, J. M. &Hamborg, M. A. (1981) Polarity orientation of axonal microtubules.Journal of Cell Biology 91, 661–5.
Heriot, K., Gambetti, P. &Lasek, R. J. (1985) Proteins transported in slow components a and b of axonal transport are distributed differently in the transverse plane of the axon.Journal of Cell Biology 100, 1167–72.
Hirokawa, N. (1982) Cross-linker system between neuro-filaments, microtubules, and membranous organelles in frog axons revealed by the quick-freeze, deep-etching method.Journal of Cell Biology 94, 129–42.
Hirokawa, N., Bloom, G. S. &Vallee, R. B. (1985) Cytoskeletal architecture and immunocytochemical localization of microtubule-associated proteins in regions of axons associated with rapid axonal transport: the ß,ß′-iminodipropionitrile-intoxicated axon as a model system.Journal of Cell Biology 101, 227–39.
Hirokawa, N. &Yorifuji, H. (1986) Cytoskeletal architecture of reactivated crayfish axons, with special reference to crossbridges among microtubules and between microtubules and membrane organelles.Cell Motility and the Cytoskeleton 6, 458–68.
Hoffman, P. N., Cleveland, D. W., Griffin, J. W., Landes, P. W., Cowan, N. J. &Price, D. L. (1987) Neurofilament gene expression: a major determinant of axonal caliber.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 84, 3472–6.
Hoffman, P. N., Griffin, J. W., Koo, E. H., Muma, N. A. &Price, D. L. (1988b) Neurofilaments, axonal caliber, and perikaryalsize. InAging and the Brain (edited byTerry, R. D.) pp. 205–17. New York: Raven Press.
Hoffman, P. N., Koo, E. H., Muma, N. A., Griffin, J. W. &Price, D. L. (1988a) Role of neurofilaments in the control of axonal caliber in myelinated nerve fibers. InIntrinsic Determinants of Neuronal Form and Function, pp. 389–402. New York: Alan R. Liss.
Hoffman, P. N. &Lasek, R. J. (1980) Axonal transport of the cytoskeleton in regenerating motor neurons: constancy and change.Brain Research 202, 317–33.
Hoffman, P. N., Thompson, G. W., Griffin, J. W. &Price, D. L. (1985) Changes in neurofilament transport coincide temporally with alterations in the caliber of axons in regenerating motor fibers.Journal of Cell Biology 101, 1332–40.
Lasek, R. J., Garner, J. A. &Brady, S. T. (1984) Axonal transport of the cytoplasmic matrix.Journal of Cell Biology 99, 212s-21s.
Lasek, R. J., Oblinger, M. M. &Drake, P. F. (1983) Molecular biology of neuronal geometry: expression of neurofilament genes influences axonal diameter.Cold Spring Harbor Symposia on Quantitative Biology 48, 731–44.
Letourneau, P. C. (1982) Analysis of microtubule number and length in cytoskeletons of cultured chick sensory neurons.Journal of Neuroscience 2, 806–14.
Malbouisson, A. M. B., Ghabriel, M. N. &Allt, G. (1985) Axonal microtubules: a computer-linked quantitative analysis.Anatomy and Embryology 171, 339–44.
Matsumoto, G., Tsukita, S. &Arai, T. (1989) Organization of the axonal cytoskeleton: differentiation of the microtubule and actin filament arrays. InCell Movement, Vol. 2,Kinesin, Dynein, and Microtubule Dynamics, pp. 335–56. New York: Alan R. Liss.
Meller, K. (1985) Ultrastructural aspects of cryofixed nerves.Cell and Tissue Research 242, 289–300.
Minwegen, P. &Friede, R. L. (1984) Conduction velocity varies with osmotically induced changes in the area of the axon's profile.Brain Research 297, 105–13.
Morris, J. R. &Lasek, R. J. (1984) Monomer-polymer equilibria in the axon: direct measurement of tubulin and actin as polymer and monomer in axoplasm.Journal of Cell Biology 98, 2064–76.
Nadelhaft, I. (1974) Microtubule densities and total numbers in selected axons of the crayfish abdominal nerve cord.Journal of Neurocytology 3, 73–86.
Nixon, R. A. &Logvinenko, K. B. (1986) Multiple fates of newly synthesized neurofilament proteins: evidence for a stationary neurofilament network distributed nonuniformly along axons of retinal ganglion cell neurons.Journal of Cell Biology 102, 647–59.
Ochs, S., Jersild, R. A. Jr., Li, J.-M. (1989) Slow transport of freely movable cytoskeletal components shown by beading partition of nerve fibers in the cat.Neuroscience 33, 421–30.
Price, R. L., Laser, R. J. &Katz, M. J. (1988a) Neurofilaments pack differently in different parts of the same axon. InProceedings of the 46th Annual Meeting of the Electron Microscopy Society of America (edited byBailey, G. W.) pp. 270–1. San Francisco, CA: San Francisco Press.
Price, R. L., Paggi, P., Lasek, R. J. &Katz, M. J. (1988b) Neurofilaments are spaced randomly in the radial dimension of axons.Journal of Neurocytology 17, 55–62.
Raine, C. S. (1982) Differences between the nodes of Ranvier of large and small diameter fibres in the P.N.S.Journal of Neurocytology 11, 935–47.
Raine, C. S., Röytta, M. &Dolich, M. (1987) Microtubulemitochondrial associations in regenerating axons after taxol intoxication.Journal of Neurocytology 16, 461–8.
Rydmark, M. (1981) Nodal axon diameter correlates linearly with internodal axon diameter in spinal roots of the cat.Neuroscience Letters 24, 247–50.
Rydmark, M. &Berthold, C-H. (1983) Electron microscopic serial section analysis of nodes of Ranvier in lumbar spinal roots of the cat: a morphometric study of nodal compartments of fibres of different sizes.Journal of Neurocytology 12, 537–65.
Sahenk, Z. &Brady, S. T. (1987) Axonal tubulin and microtubules: morphologic evidence for stable regions on axonal microtubules.Cell Motility and the Cytoskeleton 8, 155–64.
Sasaki, S., Stevens, J. K. &Bodick, N. (1983) Serial reconstruction of microtubular arrays within dendrites of the cat retinal ganglion cell: the cytoskeleton of a vertebrate dendrite.Brain Research 259, 193–206.
Schnapp, B. J. Reese, T. S. (1982) Cytoplasmic structure in rapid-frozen axons.Journal of Cell Biology 94, 667–79.
Tashiro, T. &Komiya, Y. (1989) Stable and dynamic forms of cytoskeletal proteins in slow axonal transport.Journal of Neuroscience 9, 760–8.
Tsukita, S. &Ishikawa, H. (1976) Three-dimensional distribution of smooth endoplasmic reticulum in myelinated axons.Journal of Electron Microscopy 25, 141–9.
Tsukita, S. &Ishikawa, H. (1981) The cytoskeleton in myelinated axons: serial section study.Biomedical Research 2, 424–37.
Tsukita, S., Usukura, J., Tsukita, S. &Ishikawa, H. (1982) The cytoskeleton in myelinated axons: a freezeetch replica study.Neuroscience 7, 2135–47.
Watson, D. F., Hoffman, P. N., Fittro, K. P. &Griffin, J. W. (1989) Neurofilament and tubulin transport slows along the course of mature motor axons.Brain Research 477, 225–32.
Weiss, P. A. &Mayr, R. (1971) Neuronal organelles in neuroplasmic (‘axonal’) flow. II. Neurotubules.Acta Neuropathologica Supplement V, 198–206.
Williams, P. L. &Hall, S. M. (1971) Prolongedin vivo observations of normal peripheral nerve fibres and their acute reactions to crush and deliberate trauma.Journal of Anatomy 108, 397–408.
Wujek, J. R., Lasek, R. J. &Gambetti, P. (1986) The amount of slow axonal transport is proportional to the radial dimensions of the axon.Journal of Neurocytology 15, 75–83.
Zenker, W. &Hohberg, E. (1973) A-α-nerve-fibre: number of neurotubules in the stem fibre and in the terminal branches.Journal of Neurocytology 2, 143–8.
Zimmermann, H. &Vogt, M. (1989) Membrane proteins of synaptic vesicles and cytoskeletal specializations at the node of Ranvier in electric ray and rat.Cell and Tissue Research 258, 617–29.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reles, A., Friede, R.L. Axonal cytoskeleton at the nodes of Ranvier. J Neurocytol 20, 450–458 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01252273
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01252273