Abstract
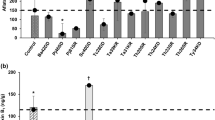
Applications of the fungicide Matador to winter wheat (Slejpner) inoculated at earing withFusarium culmorum resulted in a considerable decrease in the incidence ofFusarium headblight. In the study presented here, subsequent mycotoxin analyses by selected ion monitoring gas chromatography-mass spectrometry revealed higher levels of nivalenol (NIV) in samples singly treated with Matador at 1 L/ha. Amounts as high as 2432 μg NIV/kg and 860 μg NIV/kg, representing a 16- or six-fold increase as compared to controls, were found in wheat treated with the fungicide 3 h before or 24 h after inoculation of the grain withF. culmorum, respectively. In parallel, higher cytotoxic activities of these samples were obtained when testing crude sample extracts in the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT)-cell culture bioassay using swine kidney monolayers as target cells. It is concluded that treatment of grain with the fungicide Matador could result in a marked stimulation of the production of NIV byF. culmorum. As the incidence ofFusarium headblight did not correlate with the amount of mycotoxins found, the need for mycotoxin analyses combined with bioassays such as the MTT-cell culture assay is recommended for a meaningful assessment of the quality of grain treated in such a manner.
Zusammenfassung
Die Anwendung des Fungicids Matador bei Winterweizen der Sorte Slejpner, der zum Zeitpunkt der Blüte mitFusarium culmorum inoculiert wurde, resultierte in einem deutlichen Rückgang der durch die Inoculation hervorgerufenen Ährenfusariose („Partielle Taubährigkeit“). Bei den in der vorliegenden Studie durchgeführten Mykotoxinanalysen mittels Gaschromatography-Massenspektrometrie im Selected Ion Monitoring Modus wurden höhere Gehalte an Nivalenol (NIV) in den Weizenproben detektiert, die aus der einmaligen Behandlung mit Matador in einer Aufwandmenge von 1 L/ha entstammten. Dabei wurden Werte von 2432 μg NIV/kg und 860 μg NIV/kg (entsprechend einer 16- bzw. 6fachen Erhöhung im Vergleich zu unbehandelten Kontrollen) in den Weizenproben ermittelt, die 3 h vor bzw. 24 h nach der Inoculation mitF. culmorum mit dem Fungicid behandelt wurden. Parallel dazu wurden höhere cytotoxische Aktivitäten in Rohextrakten dieser Proben im MTT-Zellkulturtest mit Schweinenierenzellen festgestellt. Die Ergebnisse lassen den Schluß zu, daß der Einsatz des Fungicids Matador mit einer deutlichen Stimulation der Nivalenolproduktion durchF. culmorum verbunden sein kann. Da das Auftreten der partiellen Taubährigkeit nicht mit den Mykotoxingehalten korrelierte, erscheint es notwendig, Mykotoxinanalysen zusammen mit Bioassays wie dem MTT-Zellkulturtest einzusetzen, um eine aussagekräftige Beurteilung über die Qualität derartig behandelter Getreide zu erhalten.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Lepschy-v Gleissenthal J, Dietrich R, Märtlbauer E, Schuster M, Süss A, Terplan G (1989) Z Lebensm Unters Forsch 188:521
Müller H-M, Schwadorf K (1993) Myopathol 121:115
Gareis M (1992) CI-Massenspektrometrie und MTT-Zellkulturtest-Anwendungen in der Mykotoxinologie. Habilitationsschrift, Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München
Gareis M, Bauer J, Enders C, Gedek B (1989) In: Chelkowski J (ed) Fusarium — mycotoxins, taxonomy and pathogenicity. Elsevier, Amsterdam Oxford New York, Tokyo, pp 442–472
Gareis M, Reubel G, Amselgruber W (1987) Book of abstracts, XXIII World Vet Congr, 16.–21.8.1987, Montreal, Canada, p 446
Gareis M, Bauer J, Montgelas A von, Gedek B (1984) Appl Environ Microbiol 47:416
Jarvis B (1971) J Appl Bacteriol 34:199
Draughon FA, Ayres JC (1981) Appl Environ Microbiol 41:72
Produktliste Pflanzenschutzmittel (1993) Fa. Bayer, Leverkusen
Versuchsbericht (1990) des Pflanzenschutzdienstes des Landes Schleswig-Holstein, Ministerium für Ernährung, Landwirtschaft, Forsten und Fischerei, pp 44–46
Tanaka T, Hasegawa A, Matsuki Y, Ishii K, Ueno Y (1985) Food Add Contam 2:125
Enders C (1984) Diss vet med, Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München
Mosmann T (1983) J Immunol Methods 65:55
Reubel GH, Gareis M, Amselgruber WM (1989) Toxic Vitro 3:311
Reubel GH, Gareis M, Amselgruber WM (1987) Mycotoxin Res 3:85
Lauren DR, Sayer ST, Di Menna ME (1992) Mycopathol 120:167
Betina V (1989) Mycotoxins: chemical, biological and environmental aspects. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Moss MO, Frank JM (1985) Trans Br Mycol Soc 84:585
Ueda S, Yoshizawa T (1988) Ann Phytopath Soc Jap 54:476
Gabal MA (1987) Vet Hum Toxicol 29:217
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Frau Professor Dr. Brigitte Gedek zum 65. Geburtstag gewidmet
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gareis, M., Ceynowa, J. Einfluß des Fungicids Matador (Tebuconazole/Triadimenol) auf die Mykotoxinbildung durchFusarium culmorum . Z Lebensm Unters Forch 198, 244–248 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01192603
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01192603