Abstract
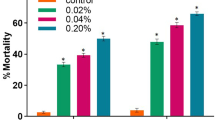
The acute toxicities of acidic and alkaline pH to nymphs of the stonefliesPteronarcys dorsata, P. proteus, andTallaperla maria were determined in 96-hr static bioassays. The acidic and alkaline 96-hr LC50 values were 2.8 to 3.3 and 12.1 to 10.3, respectively. Exposure to pH 3.0 for 72 hr or longer caused a significant loss of sodium from nymphs ofP. proteus. Morphological changes, including distension of cuticular disk and increased number of vesicles, were observed in gill tissue from nymphs ofP. dorsata exposed to pH 2.5 for 9 hr while minor changes were observed in nymphs exposed to pH 4.0 for 96 hr. Changes in gill tissue ultrastructure included an increase in number of vesicles and a decrease in number and size of mitochondria in nymphs exposed to alkaline pH of 11.75.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alabaster JS, Lloyd R (1980) Water Quality Criteria for Freshwater Fish. Butterworths, London-Boston, 300 pp
American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, Water Pollution Control Federation (1976) Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 14th edn. Washington DC, 1193 pp
Barr AJ, Goodnight JH, Sall JP, Blair WH, Chilko DM (1979) SAS User's Guide. SAS Institute Inc., Raleigh NC, 494 pp
Bell HL (1970) Effects of pH on the life cycle of the midgeTanytarsus dissimilis. Comp Ent 102:636–639
— (1971) Effects of low pH on the survival and emergence of aquatic insects. Water Res 5:313–319
Bell HL, Nebeker AV (1969) Preliminary studies on the tolerance of aquatic insects to low pH. J Kans Entomol Soc 12:230–236
Brown DJA (1981) The effects of various cations on the survival of brown trout,Salmo trutta at low pHs. J Fish Biol 18:31–40
Cairns J Jr, Dickson KL, Crossman JS (1972) The response of aquatic communities to spills of hazardous materials. In: Proceedings of the National Conference on Hazardous Materials Spills. Graphics Management Corp, Washington, DC, pp 179–197
Cherry DS, Guthrie RK, Larrick SR, Sherberger F (1979a) The influence of coal ash and thermal discharges upon the distribution and bioaccumulation of aquatic invertebrates. Hydrobiologia 62:257–267
Cherry DS, Guthrie RK, Larrick SR, Davis EM, Sherberger F (1979b) Recovery of invertebrate and vertebrate populations in a coal-ash stressed drainage system. J Fish Res Board Can 36:1089–1096
Chu TJ, Ruane RJ, Krenkel PA (1978) Characterization and reuse of ash pond effluents in coal-fired powerplants. J Water Pollut Control Fed 50:2494–2508
Daye P, Garside F (1980) Development, survival, and structural alterations of embryos and alevins of Atlantic salmonSalmo salar L. continuously exposed to alkaline levels of pH, from fertilization. Can J Zool 58:369–377
Dively J, Mudge J, Neff W, Anthony A (1977) Blood Po2, Pco2 and changes in brook trout (Salvelinus fontinalis) exposed to sublethal levels of acidity. Comp Biochem Physiol 57A:374–351
Evans DH (1975) Ionic exchange mechanisms in fish gills. Comp Biochem Physiol 51A:491–495
Fiance SB (1978) Effects of pH on the biology and distribution ofEphemerella fienerallis (Ephemeroptera). Oikos 31:332–339
Fromm M (1980) Review of some physiological and toxicological responses of freshwater fish to acid stress. Environ Biol Fish 5:79–93
Haines TA (1981) Acidic precipitation and its consequences for aquatic ecosystems: A review. Trans Am Fish Soc 110:669–707
Herricks EE, Cairns J Jr (1977) The recovery of stream macrobenthos from low pH stress. Rev Biol 10(1–4):1–11
Kapoor NN (1978) Effect of salinity on the osmoregulatory cells in the tracheal gills of the stonefly nymph,Paragnetina media (Plecoptera:Perlidae). Can J Zool 56:2608–2613
— (1980) Relationship between gill Na+-K+ activated ATPase activity and osmotic stress in the plecopterean nymph,Paragnetina media. J Exp Zool 213:213–218
Kapoor NN, Zachariah K (1973a) A study of specialized cells of the tracheal gills ofParagnetina media (Plecoptera). Can J Zool 51:983–986
— (1973b) Presence of specialized cellular complexes in the tracheal gills of the stonefly nymph,Paragnetina media (Walker). Experienta 29:848–851
Letterman RD, Mitsch WJ (1978) Impact of mine drainage on a mountain stream in Pennsylvania. Environ Pollut 17:53–73
McDonald D, Hobe H, Wood C (1980) The influence of calcium on the physiological responses of rainbow trout,Salmo gairdneri, to low environment pH. J Exp Biol 88:109–131
McWilliams P (1980) Effects of pH on sodium uptake in Norwegian brown trout (Salmo trutta) from an acid river. J Exp Biol 88:259–267
McWilliams P, Potts W (1978) The effects of pH and calcium concentrations on gill potentials in the brown trout,Salmo trutta. J Comp Physiol 126B:277–286
Moon TC, Lucostic CM (1979) Effects of acid mine drainage on a southwestern Pennsylvania stream. Water Air Soil Pollut 11:377–390
Oduleye S (1975) The effects of calcium on water balance of brown troutSalmo trutta. J Exp Biol 63:343–356
Parker R, Dunson W (1978) Effects of low environmental pH on blood pH and sodium balance of brook trout. Exp Zool 174:65–72
Shaw TL (1981) Acute toxicity of increased pH to the freshwater shrimpParatya curvirostris. N Z J Mar Freshwater Res 15(1):91–93
Stickney F (1922) The relationship of the nymphs of a dragon fly (Libellula pulchella Drury) to acid and temperature. Ecology 3:250–254
Strange K, Phillips JE, Quamme GA (1982) Active HCO3 secretion in the rectal salt gland of a mosquito larva inhabiting NaHCO3 lakes. J Exp Biol 101:171–186
Ultsch GR, Gros G (1979) Mucus as a diffusion barrier to oxygen: Possible role in O2 uptake at low pH in carp (Cyprinus carpio) gills. Comp Biochem Physiol 62A:685–689
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lechleitner, R.A., Cherry, D.S., Cairns, J. et al. Ionoregulatory and toxicological responses of stonefly nymphs (Plecoptera) to acidic and alkaline pH. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 14, 179–185 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01055609
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01055609