Summary
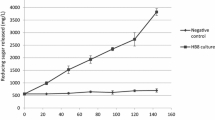
The production of extracellular amylase by the thermophilic fungusThermomyces lanuginosus was studied in shake flask cultures with different carbon sources in the growth medium. Maximum amylase production was obtained with dextran as carbon source. The greatest yield of amylolytic activity was found when low molecular weight dextrans were used as carbon source.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, P.R. (1981). Mycopathologia 76, 97–101.
Barnett, E.A. and Fergus, C.L. (1971). Mycopath. Mycol. Appl. 44, 131–141.
Basaveswara Rao, V., Maheshwari, R., Sastry, N.V.S. and Subba Rao, P.V. (1979). Current Science 48(3), 113–115.
Hudson, H.J. (1986). Fungal Biology, Edward Arnold, London.
Manning, G.B. and Campbell, L.L. (1961). J. Biol. Chem. 236, 2952–2957.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jensen, B., Olsen, J. & Allermann, K. Effect of media composition on the production of extracellular amylase from the thermophilic fungusThermomyces lanuginosus . Biotechnol Lett 9, 313–316 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01025795
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01025795