Abstract
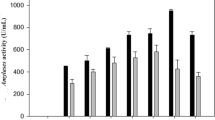
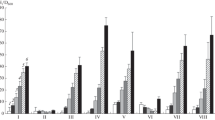
We studied the effects of different sources of carbon, nitrogen, and dietary elements on the biosynthesis of amylase inhibitor produced by two strains from the Russian National Collection of Industrial Microorganisms: Streptomyces violaceus (code: Ac-1734) and Streptomyces lucensis (Ac-1743). We found that the biosynthesis of amylase inhibitor can be regulated by limiting carbon and oxygen concentrations, maintaining constant a C: N ratio and a stable proportion of carbohydrates (dextrins, maltose and glucose) in the medium, and by adding an extra organic source of nitrogen to the medium. The inhibitors produced by the cultures are pseudo-polysaccharides.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AA:
-
amylolytic activity
- IU:
-
inhibitory unit
- CMC:
-
carboxymethylcellulolytic activity
- MW:
-
molecular weight
- DE:
-
dextrose equivalent
References
Chen, X., Zheng, Y., and Shen, Y., Voglibose (Basen, AO-128), one of the most important alpha-glucosidase inhibitors, Curr. Med. Chem., 2006, vol. 13, no. 1, pp. 109–116.
Wang, H., Ni, Y., Yang, S., Li, H., Li, X., and Feng, B., The effects of gliclazide, metformin, and acarbose on body composition in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitutus, Curr. Ther. Res. Clin. Exp., 2013, no. 75, pp. 88–92.
Scott, L.J. and Spencer, C.M., Miglitol: a review of its therapeutic potential in type 2 diabetes mellitus, Drugs, 2000, vol. 59, no. 3, pp. 521–549.
Frommer V., Pulse, V., and Schmidt, D., A method for producing amylase inhibitor, DE Patent no. 504502, 1976.
Sharova, N.Yu., Pozdnyakova, T.A., and Khodkevich, O.A., The actinomycete Streptomyces lucensis strain producing glycosidase inhibitor, RF Patent no. 2355755, 2009.
Sharova, N.Yu., Nikiforova, T.A., and Pozdnyakova, T.A., The actinomycete Streptomyces violaceus strain producing glycosidase inhibitor, RF Patent no. 2346042, 2009.
Sharova, N.Yu., Kamen’kova, N.V., and Khodkevich, O.A., New enzyme formulations for preparing destructured rye grain for fermentation to citric acid, Khranenie i pererab. sel’khozsyr’ya, 2012, no. 6, pp. 37–39.
Tregubov, N.N. and Kostenko, V.G., Tekhnokhimicheskii kontrol’ krakhmalopatochnogo proizvodstva (Technical and Chemical Control of Starch and Molasses Production), Moscow: Agropromizdat, 1991.
Sharova, N.Yu., Amylase inhibitors from Streptomyces lucensis VKPM Ac-1743 and Streptomyces violaceus VKPM Ac-1734, Appl. Biochem. Microbiol., 2015, vol. 51, no. 1, pp. 58–63.
Chukhchin, D.G. and Tupin, P.A., A method for quantitative determination of dehydrogenase activity of microorganisms, RF Patent no. 2476598, 2006.
Xiao, Z., Storms, R., and Tsang, A., A quantitative starch-iodine method for measuring alpha-amylase and glucoamylase activities, Anal. Biochem., 2006, vol. 351, no. 1, pp. 146–148.
Akulova, N.Yu. and Selezneva, A.A., Microbial inhibitors of α-glucosidases of a pseudosaccharide nature, Prikl. Biokhim. Mikrobiol., 1995, vol. 31, no. 4, pp. 371–380.
Kolodjaznaja, V.A. and Jakovleva, E.P., Stabilization of α-glucosidase inhibitor (an antidiabetic drug gipoglugine) producer inoculum, in Biotechnology and Industry, New York: Nova Science Publishers, 2004, pp. 371–380.
Yamagishi, T., Uchida, C., and Ogawa, S., Total synthesis of the trehalase inhibitor salbostatin, Chem. Eur. J., 2006, vol. 1, no. 9, pp. 634–636.
Vertesy, L., Oeding, V., and Bender, R., Tendamistat (HOE 467), a tight-binding α-amylase inhibitor from Streptomyces tendae 4158, Eur. J. Biochem., 2004, vol. 141, no. 3, pp. 505–512.
Kalakutskii, L.V. and Agre, N.S., Razvitie aktinomitsetov (Development of Actinomycetes), Moscow: Nauka, 1977.
Wehmeier, U.F., The biosynthesis and metabolism of acarbose in Actinoplanes sp. SE 50/110: a progress report, Biocat. Biotransform., 2003, vol. 21, nos. 4–5, pp. 279–284.
Jokose, K., Ogawa, K., and Ano, T., New α-amylase inhibitor trestatin I. Isolation, characterisation and biological activities of trestatins A, B and C, J. Antibioticus, 1983, no. 36, pp. 1157–1165.
Bonsch, R., Hohmann, K., Kuhn, J., Cerny, V., Hotek, F., and Pendl, J., Verfahren zur Herstellung von Citronensaure und/oder Citraten, DE Patent Appl. no. 19747902, 1999.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © N.Yu. Sharova, 2015, published in Biotekhnologiya, 2015, No. 5, pp. 22–33.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharova, N.Y. Biosynthesis of amylase inhibitor by Streptomycete cultures. Appl Biochem Microbiol 52, 723–732 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S000368381608007X
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S000368381608007X