Abstract
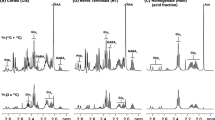
Excitatory amino acid release and neurotoxicity in the ischemic brain may be reduced by endogenously released adenosine which can modulate both glutamate or aspartate release and depress neuronal excitability. The present study reports on the patterns of release of glutamate and aspartate; the inhibitory amino acids GABA and glycine; and of the purine catabolites adenosine and inosine from the rat parietal cerebral cortex during 20 and 60 min periods of middle cerebral artery (MCA) occlusion followed by reperfusion. Aspartate and glutamate efflux into cortical superfusates rose steadily during the period of ischemia and tended to increase even further during the subsequent 40 min of reperfusion. GABA release rose during ischemia and declined during reperfusion, whereas glycine efflux was relatively unchanged during both ischemia and reperfusion. Adenosine levels in cortical superfusates rose rapidly at the onset of ischemia and then declined even though MCA occlusion was continued. Recovery to pre-occulusion levels was rapid following reperfusion. Inosine efflux also increased rapidly, but its decline during reperfusion was slower than that of adenosine.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Choi, D. W. 1991. Calcium and excitotoxic neuronal injury. J. Neurol. Sci. 106:115–122.
Benveniste, H. 1991. The excitotoxin hypothesis in relation to cerebral ischemia. Cerebrovasc. Brain Metab. Rev. 3:213–245.
Siesjo, B. K. 1992. Pathophysiology and treatment of focal cerebral ischemia. Part I. Pathophysiology. J. Neurosurg. 77:169–184.
Pellegrini-Giampietro, D. E., Cherici, G., Alesiani, M., Carla, V., and Moroni, F. 1990. Excitatory amino acid release and free radical formation may cooperate in the genesis of ischemia-induced neuronal damage. J. Neurosci. 10:1035–1041.
Takagi, K., Ginsberg, M. D., Globus, M. Y.-T., Dietrich, W. D., Martinez, E., Kraydieh, S., and Busto, R. 1993. Changes in amino acid neurotransmitters and cerebral blood flow in the ischemic penumbral region following middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat: Correlation with histopathology. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metabol. 13:575–585.
Butcher, S. P., Bullock, R., Graham, D. I., and McCulloch, J. 1990. Correlation between amino acid release and neuropathologic outcome in rat brain following middle cerebral artery occlusion. Stroke 21:1727–1733.
Graham, S. H., Shiraishi, K., Panter, S. S., Simon, R. P., and Faden, A. I. 1990. Changes in extracellular amino acid neurotransmitters produced by focal cerebral ischemia. Neurosci. Lett. 110:124–130.
Hillered, L., Hallstrom, A., Segersvard, S., Persson, L., and Ungerstedt, U. 1989. Dynamics of extracellular metabolites in the striatum after middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat monitored by intracerebral microdialysis. J. Cerebr. Blood Flow Metabol. 9:607–616.
Matsumoto, K., Graf, R., Rosner, G., Shimada, N., and Heiss, W-D. 1992. Flow thresholds for extracellular purine catabolite elevation in cat focal ischemia. Brain Res. 579:309–314.
Matsumoto, K., Graf, R., Rosner, G., Taguchi, J., and Heiss, W-D. 1993. Elevation of neuroactive substances in the cortex of cats during prolonged focal ischemia. J. Cerebr. Blood Flow Metabol. 13:586–594.
Coyle, P. 1982. Middle cerebral artery occlusion in the young rat. Stroke 13:855–859.
Lin, Y., and Phillis, J. W. 1992. Deoxycoformycin and oxypurinol: protection against focal ischemic brain injury in the rat. Brain Res. 571:272–280.
Phillis, J. W., Walter, G. A., and Simpson, R. E. 1991. Release of purines and neurotransmitter amino acids into cerebral cortical perfusates during and following transient ischemia. Int. J. Purine Pyrimid. Res. 2:41–48.
Phillis, J. W., Walter, G. A., and Simpson, R. E. 1991. Brain adenosine and transmitter amino acid release from the ischemic rat cerebral cortex: Effects of adenosine deaminase inhibitor deoxycoformycin. J. Neurochem. 56:644–650.
Buchan, A. M., Yue, D., and Slivka, A. 1992. A new model of temporary focal neocortical ischemia in the rat. Stroke 23:273–279.
Simpson, R. E., O'Regan, M. H., Perkins, L. M., and Phillis, J. W. 1992. Excitatory transmitter amino acid release from the ischemic rat cerebral cortex: Effects of adenosine receptor agonists and antagonists. J. Neurochem. 58:1683–1690.
O'Regan, M. H., Simpson, R. E., Perkins, L. M., and Phillis, J. W. 1992. Adenosine receptor agonists inhibit the release of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) from the ischemic rat cerebral cortex. Brain Res. 582:22–26.
Phillis, J. W., and Sen, S. Oxypurinol attenuates hydroxyl radical production during ischemia/reperfusion injury of the rat cerebral cortex: an ESR study. Brain Res. 628:309–312.
Sen, S., and Phillis, J. W. 1993. Alpha-phenyl-tert-butyl-nitrone (PBN) attenuates hydroxyl radical production during ischemia-reperfusion injury of rat brain: an EPR study. Free Rad. Res. Commun. 19:255–265.
Zini, I., Tomasi, A., Grimaldi, R., Vannini, V., and Agnati, L. F. 1992. Detection of free radicals during brain ischemia and reperfusion by spin trapping and microdialysis. Neurosci. Lett. 138:279–282.
Corradetti, R., Conte, G. L., Moroni, F., Passani, M. B., and Pepeu, G. 1984. Adenosine decreases aspartate and glutamate release from rat hippocampal slices. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 104:19–26.
Phillis, J. W., and Wu, P. H. 1981. The role of adenosine and its nucleotides in central synaptic transmission. Progr. Neurobiol. 16:187–129.
Rudolphi, K. A., Schubert, P., Parkinson, F. E., and Fredholm, B. B. 1992. Neuroprotective role of adenosine in cerebral ischaemia. Trends in Pharm. Sci. 13:439–445.
Rudolphi, K. A., Keil, M., and Hinze, H. J. 1987. Effect of theophylline on ischemically induced hippocampal damage in Mongolian gerbils: a behavioral and histopathological study. J. Cerebr. Blood Flow Metabol. 7:74–81.
Andine, P., Rudolphi, K. A., Fredholm, B. B., and Hagberg, H. 1990. Effect of propentofylline (HWA 285) on extracellular purines and excitatory amino acids in CA1 of rat hippocampus during transient ischemia. Br. J. Pharmacol. 100:814–818.
Miyashita, K., Nakajima, T., Ishikawa, A., and Miyatake, T. 1992. An adenosine uptake blocker, propentofylline, reduces glutamate release in gerbil hippocampus following transient forebrain ischemia. Neurochem. Res. 17:147–150.
Phillis, J. W., Perkins, L. M., and O'Regan, M. H. 1993. Potassium-evoked efflux of transmitter amino acids and purines from rat cerebral cortex. Brain Res. Bull. 31:547–552.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Phillis, J.W., Smith-Barbour, M., O'Regan, M.H. et al. Amino acid and purine release in rat brain following temporary middle cerebral artery occlusion. Neurochem Res 19, 1125–1130 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00965145
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00965145