Summary
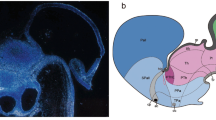
The development of the external zone of the median eminence of the mouse was studied in the electron microscope. The examination follows the development of the embryo from the 15th day of the gestation period and the juvenile growth until 24 days of age.
Single terminals of the tubero-infundibular neurons of the external zone were found to extend to the outer basement membrane of the perivascular space of the portal primary capillary plexus in the 16 day-old embryo. In the 18 day-old embryo a narrow external zone has developed. Organization of the external zone into the adult pattern is accomplished at the age of three to four weeks. Small agranular as well as large granular vesicles are present in the tubero-infundibular nerve terminals even in the 16 day-old embryo.
Changes in the organization of the nerve endings along the outer perivascular basement membrane in relation to the ependymal vascular feet were considered.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Björklund, A., Enemar, A., Falck, B.: Monoamines in the hypothalamo-hypophyseal system of the mouse with special reference to the ontogenetic aspects. Z. Zellforsch.89, 590–607 (1968).
—, Falck, B., Hromek, F., Owman, C., West, K. A.: Identification and terminal distribution of the tubero-hypophyseal monoamine fibre systems in the rat by means of stereotaxic and microspectroflourimetric techniques. Brain Res.17, 1–24 (1970).
Bock, R., aus der Mühlen, K.: Beiträge zur funktionellen Morphologie der Neurohypophyse. I. Über eine “gomori-positive” Substanz in der Zona externa infundibuli beidseitig adrenalektomierter weißer Mäuse. Z. Zellforsch.92, 130–148 (1968).
Clementi, F., Ceccarelli, B., Cerati, E., Demonte, M. L., Felici, M., Motta, M., Pecile, A.: Subcellular localization of neurotransmitters and releasing factors in the rat median eminence. J. Endocr.48, 205–213 (1970).
Corrodi, H., Jonsson, G.: The formaldehyde fluorescence method for the histological demonstration of biogenic amines. A review on the methodology. J. Histochem. Cytochem.15, 65–78 (1967).
Daikoku, S., Sato, T. J. A., Hashimoto, T., Moroshita, H.: Development of the ultrastructures of the median eminence and supraoptic nuclei in rats. Tokushima J. exp. Med.15, 1–15 (1968).
Duffy, P. E., Menefee, M.: Electron microscopic observations of neurosecretory granules, nerve and glial fibers and blood vessels in the median eminence of the rabbit. Amer. J. Anat.117, 251–286 (1965).
Enemar, A.: The structure and development of the hypophysial portal system in the laboratory mouse, with particular regard to the primary plexus. Ark. Zool., II Ser.13, 203–252 (1961a).
- Notes on the histogenesis of the hypophysis of the laboratory mouse, with special reference to its relation to the development of the hypophysial portal system. Kungl. Fysiogr. Sällsk. Handl., N. F.71, Nr.19 (1961b).
Eränkö, O.: The practical histochemical demonstration of catecholamines by formaldehyde-induced fluorescence. J. roy. micr. Soc.87, 259–276 (1967).
Falck, B.: Cellular localization of monoamines. Progr. Brain Res.8, 28–44 (1964).
—, Hillarp, N.- Å., Thieme, G., Torp, A.: Fluorescence of catecholamines and related compounds condensed with formaldehyde. J. Histochem. Cytochem.10, 348–354 (1962).
Fuxe, K.: Cellular localization of monoamines in the median eminence and infundibular stem of some mammals. Z. Zellforsch.61, 710–724 (1964).
—, Hökfelt, T.: Further evidence for the existence of tubero-infundibular dopamine neurons. Acta physiol. scand.66, 245–246 (1966).
— —: Catecholamines in the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland. In: Frontiers in neuroendocrinology, p. 47–96, ed. by W. F. Ganong and L. Martini. New York-London-Toronto: Oxford University Press 1969.
— —: Participation of central monoamine neurons in the regulation of anterior pituitary function with special regard to the neuroendocrine role of tubero-infundibular dopamine neurons. In: Aspects of neuroendocrinology, p. 192–205, eds. W. Bargmann, B. Scharrer. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1970.
Ganong, W. F., Lorentzén, L.: Brain neurohumors and endocrine function. In: Neuroendocrinology, vol.2, p. 583–640, ed. by L. Martini and W. F. Ganong. New York-London: Academic Press 1967.
Hökfelt, T.: In vitro studies on central and peripheral monoamine neurons at the ultrastructural level. Z. Zellforsch.91, 1–74 (1968).
Hökfelt, T.: Electron microscopic studies on peripheral and central monoamine neurons. In: Aspects of neuroendocrinology, p. 79–95, eds. W. Bargmann, B. Scharrer. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1970.
Hyyppä, M.: A histochemical study of the primary catecholamines in the hypothalamic neurons of the rat in relation to the ontogenetic and sexual differentiation. Z. Zellforsch.98, 550–561 (1969).
Kobayashi, H., Oota, Y., Uemura, H., Hirano, T.: Electron microscopic and pharmacologic studies on the rat median eminence. Z. Zellforsch.71, 387–404 (1966).
Kobayashi, T., Kobayashi, T., Yamamoto, K., Kaibara, M., Ajika, K.: Electron microscopic observation on the hypothalamo-hypophyseal system in rats. IV. Ultrafine structure of the developing median eminence. Endocr. jap.15, 337–363 (1968).
— — — — —: Electron microscopic observations of axonal inclusions in rat median eminence. Endocr. jap., Suppl.1, 11–27 (1969).
Lichtensteiger, W., Langemann, H.: Uptake of exogenous catecholamines by monoamine-containing neurons of the central nervous system: uptake of catecholamines by arcuato-infundibular neurons. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther.151, 400–408 (1966).
Loizou, L. A.: The postnatal development of monamine-containing structures in the hypothalamo-hypophyseal system of the albino rat. Z. Zellforsch.114, 234–253 (1971).
Matsui, T.: Fine structure of the median eminence of the rat. J. Fac. Sci. Univ. Tokyo4, 71–96 (1966).
—: Effect of reserpine on the distribution of granulated vesicles in the mouse median eminence. Neuroendocrinology2, 99–106 (1967).
Mazzuca, M.: Structure fine de l'éminence médiane du cobaye. J. Microscop.4, 225–238 (1965).
Monroe, B. G.: A comparative study of the ultrastructure of the median eminence, infundibular stem and neural lobe of the hypophysis of the rat. Z. Zellforsch.76, 405–432 (1967).
Mulder, A. H., Geuze, J. J., Wied, D., de: Studies on the subcellular localization of corticotropin releasing factor (CRF) and vasopressin in the median eminence of the rat. Endocrinology87, 61–80 (1970).
Odake, G.: Fluorescence microscopy of the catecholamine-containing neurons of the hypothalamo-hypophyseal system. Z. Zellforsch.82, 46–64 (1967).
Oota, Y.: Fine structure of the median eminence and pars nervosa of the mouse. J. Fac. Sci. Univ. Tokyo10, 155–168 (1963).
Richardson, K. C.: Electron microscopic identification of autonomic nerve endings. Nature (Lond.)210, 756 (1966).
Rinne, U. K.: Ultrastructure of the median eminence of the rat. Z. Zellforsch.74, 98–122 (1966).
—, Arstila, A. U.: Ultrastructure of the neurovascular link between the hypothalamus and the anterior pituitary gland in the median eminence of the rat. Neuroendocrinology1, 214–227 (1966a).
— —: Electron microscopic evidence on the significance of the granular and vesicular inclusions of the neurosecretory nerve endings in the median eminence of the rat. I. Ultrastructural alterations after reserpine injection. Med. Pharmacol. exp.15, 357–369 (1966b).
Röhlich, P., Vigh, B., Teichmann, I., Aros, B.: Electron microscopy of the median eminence of the rat. Acta biol. Acad. Sci. hung.15, 431–457 (1965).
Sano, Y., Odake, G., Takemoto, S.: Fluorescence microscopic and electron microscopic observations on the tuberohypophyseal tract. Neuroendocrinology2, 30–42 (1967).
Scott, D. E., Knigge, K. M.: Ultrastructural changes in the median eminence of the rat following deafferentation of the basal hypothalamus. Z. Zellforsch.105, 1–33 (1970).
Smith, G. C., Simpson, R. W.: Monoamine fluorescence in the median eminence of foetal, neonatal and adult rats. Z. Zellforsch.104, 541–557 (1970).
Szentágothai, J., Flerkó, B., Mess, B., Halász, B.: Hypothalamic control of the anterior pituitary. Budapest: Akadémiai Kiadó 1962.
Zambrano, D.: On the presence of neurons with granulated vesicles in the median eminence of rat and dog. Neuroendocrinology3, 141–155 (1968).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eurenius, L., Jarskär, R. Electron microscope studies on the development of the external zone of the mouse median eminence. Z.Zellforsch 122, 488–502 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00936083
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00936083