Abstract
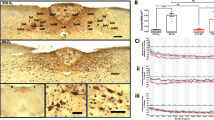
Data on olfactory bulb (OB) development in human fetuses in the stages from the 8th week to birth is provided. Immunohistochemical markers of presynaptic terminals (anti-SNAP-25, synapsin-I, and synaptophysin) were used to evaluate the maturation of the OB. Differentiation of the OB layers begins from the periphery, which indirectly confirms that growth of the olfactory nerve fibers induces not only the anatomical differentiation of the OB but also the differentiation of its functional layers. The sites of the developing glomeruli are revealed using the immunohistochemical procedure prior to the stage in which distinct glomeruli can be identified using a common histological procedure. The OB conductive system demonstrates immunoreactivity with the antibodies to presynaptic proteins at all stages starting with the 10th–11th weeks of fetal development. Four stages of OB development are described. All functional layers of the OB are mature at the 22nd week stage. Further differentiation of the neuroblasts in the OB, including lamina formation of the internal granular layer and the glomerular layer development, and the growth of the OB continue after the 20th–22nd week stage until 38th–40th weeks of fetal development. Patterns of the immunoreactivity with antibodies to SNAP-25, synapsin-I, and synaptophysin at the 38th-40th weeks of prenatal development are fully consistent with those of the adult OB. Complete maturity of the human OB is reached at the 38th–40th week of prenatal development.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Biranowska, J., Dziewiatkowski, J., Ludkiewicz, B., and Morys, J., Developmental changes of synaptic proteins expression within the hippocampal formation of the rat, J. Anat. Embryol., (Berlin), 2002, vol. 206, nos. 1–2, pp. 85–96.
Bossy, J., Development of olfactory and related structures in staged human embryos, Anat. Embryol., 1980, vol. 161, pp. 225–236.
Catsicas, S., Larhammar, D., Blomqvist, A., Sanna, P.P., Milner, R.J., and Wilson, M.C., Expression of a conserved cell-type-specific protein in nerve terminals coincides with synaptogenesis, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 1991, vol. 88, no. 3, pp. 785–789.
Chuah, M.I. and Zheng, D.R., Olfactory marker protein is present in olfactory receptor cells of human fetuses, Neuroscience, 1987, vol. 23, pp. 263–370.
Chuah, M.I. and Zheng, D.R., The human primary olfactory pathway: fine structural and cytochemical aspects during development and in adults, Microsc. Res. Tech., 1992, vol. 23, no. 1, pp. 76–85.
DeCamilli, P., Cameron, R., and Greengard, P., Synapsin I (protein I), a nerve terminal-specific phosphoprotein. I. Its general distribution in synapses of the central and peripheral nervous system demonstrated by immunofluorescence in frozen and plastic sections, J. Cell Biol., 1983, vol. 96, no. 5, pp. 1337–1354.
Doty, R.L., Olfaction in Parkinson’s disease and related disorders, Neurobiol. Dis., 2012, vol. 46, no. 3, pp. 527–552.
Duc, C. and Catsicas, S., Ultrastructural localization of SNAP-25 within the rat spinal cord and peripheral nervous system, J. Comp. Neurol., 1995, vol. 356, no. 1, pp. 152–163.
Fletcher, T.L., Cameron, P., DeCamilli, P., and Banker, G., The distribution of synapsin I and synaptophysin in hippocampal neurons developing in culture, J. Neurosci., 1991, vol. 11, pp. 1617–1626.
Fornasiero, E.F., Bonanomi, D., Benfenati, F., and Valtorta, F., The role of synapsins in neuronal development, Cell. Mol. Life. Sci., 2010, vol. 67, no. 9, pp. 1383–1396.
Goutan, E., Martí, E., and Ferrer, I., Expression of synaptic proteins in the developing rat cerebellum following ionizing radiation, Int. J. Dev. Neurosci., 1999, vol. 17, no. 4, pp. 275–283.
Greenlee, M.H., Roosevelt, C.B., and Sakaguchi, D.S., Differential localization of SNARE complex proteins SNAP-25, syntaxin, and VAMP during development of the mammalian retina, J. Comp. Neurol., 2001, vol. 430, no. 3, pp. 306–320.
Grubb, M.S., Nissant, A., Murray, K., and Lledo, P.M., Functional maturation of the first synapse in olfaction: development and adult neurogenesis, J. Neurosci., 2008, vol. 28, no. 11, pp. 2919–2932.
Hepp, R. and Langley, K., SNAREs during development, Cell. Tissue Res., 2001, vol. 305, pp. 247–253.
Huart, C., Rombaux, P., and Hummel, T., Plasticity of the human olfactory system: the olfactory bulb, Molecules, 2013, vol. 18, no. 9, pp. 11586–11600.
Humphrey, T., The development of the olfactory and accessory olfactory formations in human embryos and fetuses, J. Comp. Neurol., 1940, vol. 73, pp. 431–468.
Ichikawa, M., Kimura-Kuroda, J., Yasui, K., and Kuroda, Y., Expression of synaptophysin during synapse formation between dissociated cortical neurons, Neurosci. Res., 1991, vol. 12, no. 3, pp. 452–458.
Kimura, M., Umehara, T., Udagawa, J., Kawauchi, H., and Otani, H., Development of olfactory epithelium in the human fetus: scanning electron microscopic observations, Congenit. Anom. (Kyoto), 2009, vol. 49, no. 3, pp. 102–107.
Knaus, P., Betz, H., and Rehm, H., Expression of synaptophysin during postnatal development of the mouse brain, J. Neurochem., 1986, vol. 47, no. 4, pp. 1302–1304.
Kulakovskaya, V.S., Observations on the sense of taste and smell in newborns, Zhur. Izuch. Ran. Det. Vozr., 1929, vol. 9, no. 1, pp. 15–20.
Leclerc, N., Beesley, P.W., Brown, I., Colonnier, M., Gurd, J.W., Paladino, T., and Hawkes, R., Synaptophysin expression during synaptogenesis in the rat cerebellar cortex, J. Comp. Neurol., 1989, vol. 280, no. 2, pp. 197–212.
Lin, D.M. and Ngai, J., Development of the vertebrate main olfactory system, Curr. Opin. Neurobiol., 1999, vol. 9, pp. 74–78.
Mason, C.A., Axon development in mouse cerebellum: embryonic axon forms and the expression of synapsin I, Neuroscience, 1987, vol. 19, pp. 1319–1333.
Mennella, J.A., Jagnow, C.P., and Beauchamp, G.K., Prenatal and postnatal flavor learning by human infants, Pediatrics, 2001, vol. 107, no. 6, p. E88.
Moran, DT., Rowley, J.C. 3rd, Jafek, B.W., and Lovell, M.A., The fine structure of the olfactory mucosa in man, J. Neurocytol., 1982, vol. 11, no. 5, pp. 721–746.
Muller, F. and O’Rahilly, R., Olfactory structures in staged human embryos, Cells Tissues Organs, 2004, vol. 178, pp. 93–116.
Nadarajah, B. and Parnavelas, J.G., Mode of neuronal migration in the developing cerebral cortex, Nat. Rev. Neurosci., 2002, vol. 3, pp. 423–443.
Nieuwenhuys, R., The Central Nervous System of Vertebrates, Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 1998, vol. 3.
Oyler, G.A., Polli, J.W., Wilson, M.C., and Billingsley, M.L., Developmental expression of the 25-kDa synaptosomal-associated protein (SNAP-25) in rat brain, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci USA, 1991, vol. 88, no. 12, pp. 5247–5251.
Pearson, A.A., The development of the olfactory nerve in man, J. Comp. Neurol., 1941, vol. 75, pp. 199–217.
Pearson, A.A., The development of the olfactory nerve, the nervus terminalis, and the vomeronasal nerve in man, Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol., 1942, vol. 51, no. 2, pp. 317–332.
Petten, B.M., Embriologiya cheloveka (Human Embryology), Moscow: Medgiz, 1959.
Pyatkina, G.A., The development of human olfactory receptors, Tsitologiya, 1982, vol. 24, no. 1, pp. 11–16.
Rakic, P., Mode of cell migration to the superficial layers of fetal monkey neocortex, J. Comp. Neur., 1972, vol. 145, no. 1, pp. 61–84.
Salasar, I., Quintiero, P.S., Lombardero, M., Aleman, N., and Fernandez de Troconiz, P., The prenatal maturity of the accessory olfactory bulb in pigs, Chem. Senses, 2004, vol. 29, no. 1, pp. 3–11.
Schaal, B., Marlier, L., and Soussignan, R., Human foetuses learn odours from their pregnant mother’s diet, Chem. Senses, 2000, vol. 25, pp. 729–737.
Sidor-Kaczmarek, J., Labuda, C., Litwinowicz, B., Spodnik, J.H., Kowian-ski, P., Dziewiatkowski, J., and Moryś, J., Developmental expression of SNAP-25 protein in the rat striatum and cerebral cortex, Folia Morphol. (Warsz), 2004, vol. 63, no. 3, pp. 285–288.
Sollner, T., Bennett, M.K., Whiteheart, S.W., Scheller, R.H., and Rothman, J.E., A protein assembly-disassembly pathway in vitro that may correspond to sequential steps of synaptic vesicle docking, activation, and fusion, Cell, 1993, vol. 75, no. 3, pp. 409–418.
Takahashi, S., Iwanaga, T., Takahashi, Y., Nakano, Y., and Fujita, T., Neuron-specific enolase, neurofilament protein and S-100 protein in the olfactory mucosa of human fetuses. An immunohistochemical study, Cell. Tissue. Res., 1984, vol. 238, no. 2, pp. 231–234.
Tao-Cheng, J.H., Du, J., and McBain, C.J., SNAP-25 is polarized to axons and abundant along the axolemma: an immunogold study of intact neurons, J. Neurocytol., 2000, vol. 29, no. 1, pp. 67–77.
Valverde, F., Santacana, M., and Heredia, M., Formation of an olfactory glomerulus: morphological aspects of development and organization, Neuroscience, 1992, vol. 49, pp. 255–275.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © A.S. Kharlamova, V.M. Barabanov, S.V. Saveliev, 2015, published in Ontogenez, 2015, Vol. 46, No. 3, pp. 174–185.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kharlamova, A.S., Barabanov, V.M. & Saveliev, S.V. Development of human olfactory bulbs in prenatal ontogenesis: An immunochistochemical study with markers of presynaptic terminals (anti-SNAP-25, synapsin-I, and synaptophysin). Russ J Dev Biol 46, 137–147 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1062360415030054
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1062360415030054