Summary
-
1.
The use of radioactive and biotinylated oligonucleotide probes has been optimized to detect and analyze byin situ hybridization, neurons expressing neuropeptide genes (vasopressin, oxytocin, somatostatin).
-
2.
In situ hybridization was performed on cryostat-cut sections obtained from tissues perfused with 1% formaldehyde. Radioactive probes were labeled by tailing with35S-dATP and revealed with autoradiography. Biotinylated probes were obtained either by the incorporation of 11-biotin dUTP or by the addition of biotinylated nucleotides to the oligonucleotide during its synthesis. Biotin was revealed with streptavidin alkaline phosphatase and the appropriate substrate.
-
3.
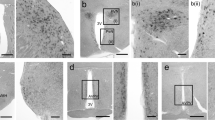
In the adult rat brain, radioactive and biotinylated probes revealed peptidergic neurons. The biotinylated probes provided an optimal cellular and subcellular resolution with a sensitivity similar to that observed with radioactive probes. Staining was selectively restricted to the cytoplasm and to the proximal part of processes.
-
4.
Biotinylated vasopressin probes with 10 biotins added demonstrated magnocellular neurons and parvocellular neurons in the suprachiasmatic nucleus and the bed nucleus stria terminalis.
-
5.
Vasopressin gene expression was studied during ontogeny in the rat fetus and neonate. Vasopressin mRNA was first detectable at gestational day 16 in the supraoptic nucleus in neurons of neuroblastic appearance. An aspect similar to the one present in adult was found at gestational day 19 in magnocellular neurons and at day 3 postnatal in parvocellular neurons.
-
6.
The results confirm that radioactive oligonucleotide probes are efficient tools to investigate neuropeptide gene expression byin situ hybridization and demonstrate that biotinylated oligonucleotides are very efficient and provide a much higher resolution than radioactive probes with a reasonable sensitivity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arai, H., Emson, P. C., Agrawal, S., Christodoulo, C., and Gai, M. (1988). In situ hybridization histochemistry: Localisation of vasopressin mRNA in rat brain using a biotinylated oligonucleotide probe.Mol. Brain Res. 463–69.
Bloch, B., Popovici, T., Le Guellec, D., Normand, E., Chouham, S., Guitteny, A. F., and Böhlen, P. (1986). In situ hybridization for the analysis of gene expression in the endocrine and central nervous system tissues: A three year experience.J. Neurosci. Res. 16183–200.
Bloch, B., Guitteny, A. F., Normand, E., Chouham, S., Le Moine, C., Fouque, B., and Téoule, R. (1989). Histological detection of neuropeptide messenger RNAs with radioactive and biotinylated synthetic oligonucleotides. InWenner-Gren International Symposium Series Macmillan, Basingstoke, pp. 23–29.
Buijs, R. M., Velis, D. N., and Swaab, D. (1980). Ontogeny of vasopressin and oxytocin in the fetal rat: Early vasopressinergic innervation of the fetal brain.Peptides 1315–324.
Davis, L., Banker, G. A., and Steward, O. (1987). Selective dendritic transport of RNA in hippocampal neurons in culture,Nature (London)330477–478.
Funckes, C. L., Minth, C., Deschenes, R., Magaein, M., Tavianini, M., Sheets, M., Collier, K., Weith, H., Aron, D., Ross, B., and Dixon, J. (1983). Cloning and characterization of a mRNA encoding rat preprosomatostatin.Biol. Chem. 258881–887.
Gee, C. E., Chen, C. L., Roberts, J. L., Thompson, R., and Watson, S. J. (1983). Identification of proopiomelanocortin neurones in rat hypothalamus by in situ cDNA hybridization.Nature (London)306374–376.
Guitteny, A. F., Böhlen, P., and Bloch, B. (1988a). Analysis of vasopressin gene expression by in situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry on semi-thin sections.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 361373–1378.
Guitteny, A. F., Fouque, B., Mougin, C., Téoule, R., and Bloch, B. (1988b). Histological detection of messenger RNAs with biotinylated synthetic oligonucleotide probes.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 36563–571.
Guitteny, A. F., Fouqué, B., Téoule, R., and Bloch, B. (1989). Vasopressin gene expression in the normal and Brattleboro rat: A histological analysis in semi-thin sections with biotinylated probes.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 371479–1487.
Hoefler, H., Childers, H., Montminy, M. R., Lechan, R. M., Goodman, R. H., and Wolfe, H. J. (1986). In situ hybridization methods for the detection of somatostatin mRNA in tissue sections using antisense RNA probes.Histochem. J. 18597–604.
Ivell, R., and Richter, D. (1984). Structure and comparison of the oxytocin and vasopressin genes from rat.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 812006–2010.
Larsson, L. I., Christensen, T., and Dalbge, H. (1988). Detection of proopiomelanocortin mRNA by in situ hybridization using a biotinylated oligodeoxynucleotide probe and avidin-alkaline phosphatase histochemistry.Histochemistry 89109–116.
Nojiri, H., Sato, M., and Urano, A. (1985). In situ hybridization of the vasopressin mRNA in the rat hypothalamus by use of a synthetic oligonucleotide probe.Neurosci. Lett. 58101–105.
Normand, E., Popovici, T., Onteniente, B., Fellmann, D., Piatier-Tonneau, D., Auffray, C., and Bloch, B. (1988). Dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra modulate preproenkephalin A gene expression in rat striatal neurons.Brain Res. 43939–46.
Pellegrino, L. J., Pellegrino, A. S., and Cushman, A. (1981).A Sterotaxic Atlas of the Rat Brain, Plenum Press, New York.
Roychoudhury, R., and Wu, R. (1980). Terminal transferase catalyzed addition of nucleotides to 3′ termini of DNA, InMethods in Enzymology, Vol. 65, Academic Press, London, pp. 43–61.
Sinding, C., Robinson, A. G., Seif, S., and Schmid, P. (1980). Neurohypophysial peptides in the developing rat fetus.Brain Res. 195177–186.
Sofroniew, M. V. (1984). Vasopressin, oxytocin and their related neurophysins. InHandbook of Chemical Neuroanatomy A. B. Bjorklund and T. Hokfelt, Eds.), Elsevier, Amsterdam, Vol. 4, pp. 93–113.
Uhl, G. R., Zingg, H. H., and Habener, J. F. (1985). Vasopressin mRNA in situ hybridization: Localization and regulation studied with oligonucleotide cDNA probes in normal and Brattleboro rat hypothalamus.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 825555–5559.
Whitnall, M. H., Key, S., Ben-Barak, Y., Ozato, K., and Gainer, H. (1985). Neurophysin in the hypothalamo-neurohypophysial system. Immunocytochemical studies of the ontogeny of oxytocinergic and vasopressinergic neurons.J. Neurosci. 598–109.
Young, W. S. III, Bonner, T., and Brann, M. (1986). Mesencephalic dopamine neurons regulate the expression of neuropeptide mRNAs in the rat forebrain.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 839827–9831.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bloch, B., Guitteny, A.F., Chouham, S. et al. Topography and ontogeny of the neurons expressing vasopressin, oxytocin, and somatostatin genes in the rat brain: An analysis using radioactive and biotinylated oligonucleotides. Cell Mol Neurobiol 10, 99–112 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00733638
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00733638