Summary
-
1.
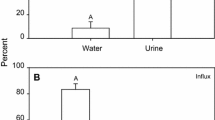
The relative functional surface area of isolated-perfused gills was evaluated by measuring the influx of14C-urea, a passively diffusing molecule.
-
2.
The catecholamines, norepinephrine and epinephrine, increase functional gill surface area and decrease overall branchial vascular resistance.
-
3.
Surface area and resistance effects of adrenergic agonists and blocking agents demonstrated the presence of both α and β adrenergic receptors in rainbow trout gills.
-
4.
Stimulation of α adrenergic receptors increased both functional surface area and branchial vascular resistance, while β adrenergic receptor stimulation increased functional surface area but decreased branchial vascular resistance.
-
5.
Acetylcholine decreased functional gill surface area and increased overall branchial vascular resistance.
-
6.
The data presented strongly indicate that the functional surface area of rainbow trout gills can be regulated by changing perfusion pathway with adjustments in the relative vascular resistance across the different pathways.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahlquist, R. P.: A study of the adrenotropic receptors. Amer. J. Physiol.153, 586–600 (1948)
Ahlquist, R. P.: The adrenergic receptor. J. Pharm. Sci.55, 359–367 (1966)
Ahlquist, R. P.: Adrenergic β-receptor blocking agents. Ann. Rev. Pharmacol.8, 259–272 (1968)
Ahlquist, R. P.: Adrenergic receptors: a personal and practical view. Perspect. Biol. Med.17, 119–122 (1973)
Arnold, A., McAuliff, J. P.: Differentiation of receptors activated by catecholamines. II. Arch. int. Pharmacodyn.193, 287–293 (1971)
Benfey, B. G., Grillo, S. O.: Antagonism of acetylcholine by adrenaline antagonists. Brit. J. Pharmacol.20, 528–533 (1963)
Bettex-Galland, M., Hughes, G. M.: Contractile filamentous material in the pillar cells of fish gills. J. Cell Sci.13, 359–370 (1973)
Cameron, J. N.: Evidence for the lack of by-pass shunting in teleost gills. J. Fish. Res. Board Can.31, 211–213 (1974)
Campbell, G.: Autonomic nervous system. In: Fish physiology, vol. 4, p. 109–132 (Hoar, W. S., Randall, D. J., eds.). New York: Academic Press 1970
Chester Jones, I., Henderson, I. W., Chan, D. K. O., Rankin, J. C.: Steroids and pressor substances in bony fish with special reference to the adrenal cortex and corpuscles of stannius of the eel (Anguilla anguilla L.). Proc. 2nd Int. Congr. Hormonal Steroids, Milan, 1966. Int. Congr. Series, No. 132, p. 136–145 (Martini, L., Franchini, F., Motta, M., eds.). Amsterdam: Excerpta Medica Foundation 1967
Gannon, B. J., Campbell, G., Randall, D. J.: Scanning electron microscopy of vascular casts for the study of vessel connections in a complex vascular bed—the trout gill. 31st Ann. Proc. Electron Microscopy Soc. Amer.31, 442–443 (1973)
Garcia-Romeu, F., Maetz, J.: The mechanism of sodium and chloride uptake by the gills of a fresh-water fish,Carassius auratus. I. Evidence for an independent uptake of soidum and chloride ions. J. Gen. Physiol.47, 1195–1207 (1964)
Gilloteaux, J.: Note sur l'innervation des branchies chezAnguilla anguilla L. Experientia25, 270–271 (1969)
Hughes, G. M.: The dimensions of fish gills in relation to their function. J. Exp. Biol.45, 177–195 (1966)
Hughes, G. M.: Morphometrics of fish gills. Resp. Physiol.14, 1–25 (1972)
Hughes, G. M., Gray, I. E.: Dimensions and ultrastructure of toadfish gills. Biol. Bull.143, 150–161 (1972)
Hughes, G. M., Grimstone, A. V.: The fine structure of the secondary lamellae of the gills ofGadus pollachius. Quart. J. micr. Sci.106, 343–353 (1965)
Johansen, K.: Heart and circulation in gill, skin and lung breathing. Resp. Physiol.14, 193–210 (1972)
Kerstetter, T. H., Kirschner, L. B., Rafuse, D. D.: On the mechanism of sodium ion transport by the irrigated gills of rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). J. Gen. Physiol.56, 342–359 (1970)
Kerstetter, T. H., Kirschner, L. B.: Active chloride transport by the gills of rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). J. exp. Biol.56, 263–272 (1972)
Keys, A., Bateman, J. B.: Branchial responses to adrenaline and pitressin in the eel. Biol. Bull.63, 327–336 (1932)
Maetz, J., Garcia-Romeu, F.: The mechanism of sodium and chloride uptake by the gills of a fresh-water fish,Carassius auratus. II. Evidence for NH4 +/Na+ and HCO3 −/Cl− exchanges. J. Gen. Physiol.47, 1209–1227 (194)
Morgan, M., Tovell, P. W. A.: The structure of the gill of the trout,Salmo gairdneri (Richardson). Z. Zellforsch.142, 147–162 (1973)
Mott, J. C.: Some factors affecting the blood circulation in the common eel (Anguilla anguilla). J. Physiol. (Lond.)114, 387–398 (1951)
Muir, B. S., Hughes, G. M.: Gill dimensions for three species of tunny. J. exp. Biol.51, 271–285 (1969)
Nakano, T., Tomlinson, N.: Catecholamine and carbohydrate concentrations in rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri) in relation to physical disturbance. J. Fish. Res. Bd. Canada24, 1701–1715 (1967)
Newstead, J. D.: Fine structure of respiratory lamellae of teleostean gills. Z. Zellforsch.79, 396–428 (1967)
Nickerson, M., Hollenberg, N. K.: Blockade of α-adrenergic receptors. In: Physiological Pharmacology, vol. 4, p. 243–305 (Root, W. S., Hofmann, F. G., eds.). New York: Academic Press 1967
Nicol, J. A. C.: Autonomic nervous system in lower chordates. Biol. Rev.27, 1–49 (1952)
Östlund, E., Fänge, R.: Vasodilation by adrenaline and noradrenaline and the effects of some other substances on perfused fish gills. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.5, 307–309 (1962)
Randall, D. J., Baumgarten, D., Malyusz, M.: The relationship between gas and ion transfer across the gills of fish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.41 A, 629–637 (1972)
Randall, D. J., Cameron, J. N.: Respiratory control of arterial pH as temperature changes in rainbow troutSalmo gairdneri. Amer. J. Physiol.225, 997–1002 (1973)
Randall, D. J., Stevens, E. D.: The role of adrenergic receptors in cardiovascular changes associated with exercise in salmon. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.21, 415–424 (1967)
Rankin, J. C., Maetz, J.: A perfused teleostean gill preparation: vascular actions of neurohypophysial hormones and catecholamines. J. Endocr.51, 621–635 (1971)
Reite, O. B.: The evolution of vascular smooth muscle responses to histamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine. I. Occurrence of stimulatory actions in fish. Acta physiol. scand.75, 221–239 (1969)
Richards, B. D., Fromm, P. O.: Patterns of blood flow through filaments and lamellae of isolated-perfused rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri) gills. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.29, 1063–1071 (1969)
Shuttleworth, T. J.: A new isolated perfused gill preparation for the study of the mechanisms of ionic regulation in teleosts. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.43 A, 59–64 (1972)
Sokal, R. R., Rohlf, F. J.: Biometry. San Francisco: W. H. Freeman Co. 1969
Steen, J. B., Kruysse, A.: The respiratory function of teleostean gills. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.12, 127–142 (1964)
Stevens, E. D., Randall, D. J.: Changes of gas concentrations in blood and water during moderate swimming activity in rainbow trout. J. exp. Biol.46, 329–337 (1967a)
Stevens, E. D., Randall, D. J.: Changes in blood pressure, heart rate and breathing rate during moderate swimming activity in rainbow trout. J. exp. Biol.46, 307–315 (1967b)
Wood, C. M.: A critical examination of the physical and adrenergic factors affecting blood flow through the gills of the rainbow trout. J. exp. Biol.60, 241–265 (1974)
Wood, C. M., Randall, D. J.: The influence of swimming activity on sodium balance in the rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). J. comp. Physiol.82, 207–233 (1973)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This research was supported by EPA Training Grant No. T-900331 and EPA Grant R-801034 and by the Michigan Agr. Exper. Sta. Project 122 (Journal article No. 6866). We gratefully acknowledge the technical assistance of Mrs. Esther Brenke.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bergman, H.L., Olson, K.R. & Fromm, P.O. The effects of vasoactive agents on the functional surface area of isolated-perfused gills of rainbow trout. J Comp Physiol B 94, 267–286 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00710640
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00710640