Summary
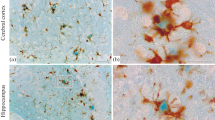
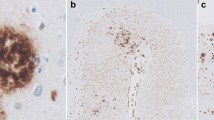
Biotinyl derivatives of several lectins and avidin-horseradish peroxidase were used to study the localization of glycoconjugates in amyloid plaques and in neuritic tangles in brains of patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD), Downs syndrome (DS) and Gerstmann-Sträussler syndrome (GSS). The lectins tested recognize the following residues: β-d-galactosyl [Ricinus communis agglutinin 120, (RCA-1) and peanut agglutinin, (PNA)]; α-d-galactosyl [Griffonia simplicifolia agglutinin (GSA)]; α-d-mannosyl>α-d-glucosyl [concanavalin A (Con A) andLens culinaris agglutinin (LcH)];N-acetyl- andN-glycolylneuraminic acid [Limax flavus agglutinin (LFA) andLimulus polyphemus agglutinin (LPA)];N-acetyl-glucosaminyl and sialyl [wheat germ agglutinin (WGA)];N-acetyl-d-galactosaminyl [Helix pomatia agglutinin (HPA) andDolichos biflorus agglutinin (DBA)] and α-l-fucosyl [Ulex europeus agglutinin (UEA-1)]. The majority of lectins listed above bind preferentially to the peripheral area of AD plaques, whereas in plaques of DS they are mainly bound to central amyloid core. In neurofibrillary tangles of AD brains only residues recognized by WGA and HPA or DBA were found, whereas in DS brains, in addition to above mentioned, β-d-galactose (RCA-1) and sialic acid (LFA) were also present. In brain microblood vessels the strongest reaction in endothelia appeared with UEA-1 and RCA-1, indicating the abundance of α-l-fucosyl and β-d-galactosyl residues. In AD brains deposits of amyloid were noted in the wall of some blood vessels, where monosaccharide residues recognized by RCA-1, GSA, UEA and WGA but not by Con A and LFA were present. However, our studies of some organs (liver, kidney, heart and testes) of patients with generalized amyloidosis revealed a lack of these sugar residues. It indicates, that the composition of amyloid present in brains of AD is different to that in other organs in generalized amyloidosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bolton DC, Meyer RK, Prusiner SB (1985) Scrapie PrP27-30 is a sialoglycoprotein. J Virol 53:596–606
Cohen AS (1986) High resolution ultrastructure, immunology and biochemistry of amyloid. In: Mandema E, Ruinen L, Scholten JH, Cohen AS (eds) Amyloidosis. Excerpta Medica Foundation, Amsterdam, pp 149–171
De Armond SJ, McKinley MP, Barry RA, Braunfeld M, McColloch JR, Prusiner SB (1985) Identification of prion amyloid filaments in scrapie-infected brain. Cell 41:221–235
Gerhart DE, Elonis MS, Drewes LR (1986) Light and electron microscopic localization ofd-galactosyl residues in capillary endothelial cells of the canine cerebral cortex. J Histochem Cytochem 34:641–648
Graham RC, Karnovsky MJ (1966) The early stages of absorption of injected horseradish peroxidase in the proximal tubules of the mouse kidney: ultrastructural cytochemistry by a new technique. J Histochem Cytochem 14:291–302
Holthöfer H, Virtanen T, Kariniemi AL, Hormia M, Linder E, Miettinen A (1982)Ulex europeus I lectin as a marker for vascular endothelium in human tissues. Lab Invest 47: 60–66
Masters CL, Simms G, Weinman NA, Multhaup G, McDonald BL, Beyreuther K (1985) Amyloid plaque core protein in Alzheimer's disease and Down Syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:4245–4249
Muir H, Cohen AS (1968) Mucopolisaccharides as components of amyloid. In: Mandema E, Ruinen L, Scholten JH, Cohen AS (eds) Amyloidosis. Excerpta Medica Foundation, Amsterdam, pp 280–285
Oyamada M, Mori M (1985) Immunohistochemical demonstration of tubulin and actin in rat hepatocytes in situ using a perfusion extraction fixation procedure. J Histochem Cytochem 33:1197–1204
Schmitz-Moormann P (1968) Chemical composition of amyloid. In: Mandema E, Ruinen L, Scholten JH, Cohen AS (eds) Amyloidosis. Excerpta Medica Foundation, Amsterdam, pp 286–290
Stiller D, Katenkamp D (1975) Histochemistry of amyloid. Gustav Fischer, Jena, pp 19–40
Szumanska G, Vorbrodt AW, Wisniewski HM (1986) Lectin histochemistry of scrapie amyloid plaques. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 69:205–212
Vorbrodt AW (1986) Changes in the distribution of endothelial surface glycoconjugates associated with altered permeability of brain microblood vessels. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 70:103–111
Vorbrodt AW, Dobrogowska DH, Lossinsky AS, Wisniewski HM (1986) Ultrastructural localization of lectin receptors on the luminal and abluminal aspects of brain micro-blood vessels. J Histochem Cytochem 34:251–261
Wisniewski HM, Mertz GS (1985) Neuropathology of the aging brain and dementia of the Alzheimer type. In: Gaitz CM, Samorajski T (eds) Aging 2000: Our health care destiny, vol 1. Springer, New York Berlin Heidelberg Tokyo, pp 231–243
Wisniewski HM, Iqbal K, Grundke-Iqbal I, Rubenstein R, Wen GY, Merz PA, Kascsak R, Kristensson K (1986) Amyloid in Alzheimer's disease and unconventional viral infections. In: International Symposium on Dementia and Amyloid, Neuropathology [Suppl 3] (in press)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported in part by grant no. AG 04220-03 from the National Institute of Aging, NIH
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Szumanska, G., Vorbrodt, A.W., Mandybur, T.I. et al. Lectin histochemistry of plaques and tangles in Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol 73, 1–11 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00695495
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00695495