Summary
-
1.
The hemocyanins of 2 spiders (Eurypelma californicum, Cupiennius salei), 2 scorpions (Pandinus pallidus, Androctonus australis), a whipscorption (Mastigoproctus brasilianus) and 2 whipspiders (Tarantula palmata, Trichodamon froesi) were analyzed for subunit heterogeneity by high resolution polyacrylamide electrophoresis (PAGE). For comparison,Limulus polyphemus hemocyanin was subjected to the same analytical scheme.
-
2.
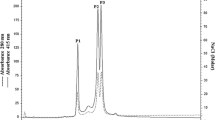
All of the species, except forLimulus (predominantly 60 S-hemocyanin) andCupiennius (16 S- and 24 S-hemocanin) possess only hemocyanin sedimenting in the 33 S to 37 S range. A second, major blood protein was observed in each species, safeMastigoproctus. This second, non-respiratory protein sediments with ca. 16 S, but with about 24 S in the case of the scorption species.
-
3.
Upon incubation with sodium dodecylsulfate (SDS) and β-mercaptoethanol and electrophoresis in polyacrylamide gradients, between 2 and 5 hemocyanin bands are obtained, with average molecular weights between 70,000 and 75,000. The non-respiratory proteins yield two chains in each case, with molecular weights between 95,000 and 130,000.
-
4.
Each hemocyanin could be dissociated at pH 9.6 to yield “native” subunits. By gel filtration, these were separated into monomers (4.5S) and dimers (6 S). No dimers were observed after dissociation ofPandinus and ofLimulus hemocyanin. Only in the case ofCupiennius the dimer is formed by a disulfide bridge. — PAGE of the dissociation mixture shows complex patterns which display 6–7 bands.
-
5.
By preparative isolation of “native” subunits and subsequent analysis in SDS-PAGE, the two patterns of hemocyanin bands could be related to each other, and the total number of different polypeptide chains established with some certainty. It ranges from 5 inCupiennius 16 S-hemocyanin to 8 inAndroctonus hemocyanin and possibly 12 inLimulus hemocyanin. A loose correlation between oligomer size and number of different chains is suggested.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Busselen, P.: The electrophoretic heterogeneity ofCarcinus maenas hemocyanin. Arch. Biochem. Biophys.137, 415–420 (1970)
Goyffon, M., le Fichoux, Y., Lamy, J.: Hétérogénéité du protéinogramme de l'hémolymphe des ScorpionsAndroctonus australis L.,Androctonus mauretanicus Pocock etAndroctonus amoreuxi Aud. et Sav. en gel de polyacrylamide. C.R. Soc. Biol.164, 374–378 (1970)
Goyffon, M., Stockmann, R., Lamy, J.: Valeur taxonomique de l'électrophorèse en disques des protéines de l'hémolymphe chez le Scorpion: étude du genreButhotus (Buthidae). C.R. Acad. Sci. Paris277 D, 61–63 (1973)
Jeffrey, P.D., Shaw, D.C., Treacy, G.B.: Hemocyamin from the Australian freshwater crayfishCherax destructor. Studies of two different monomers and their participation in the formation of multiple hexamers. Biochemistry15, 5527–5533 (1976)
Laemmli, U.K.: Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T 4. Nature (Lond.)227, 680–685 (1970)
Lamy, J., Goyffon, M., Sassé, M., Vachon, M.: L'électrophorése des protéines de l'hémolymphe en gel de polyacrylamide, premier critère biochimique pour l'identification des scorpions. Biochimie53, 249–251 (1971)
Lamy, J., Lamy, J., Baglin, M.-C., Weill, J.: Scorpion hemocyanin subunits: properties, dissociation, association. In: Structure and function of haemocyanin. Bannister, J.V. (ed.), pp. 37–49. Berlin, Heildelberg, New York: Springer 1977
Loewe, R., Linzen, B.: Haemocyanins in spiders. I. Subunits and stability region ofDugesiella californica haemocyanin. Hoppe-Seyler's Z. Physiol. Chem.354, 182–188 (1973)
Markl, J., Schmid, R., Czichos-Tiedt, S., Linzen, B.: Haemocyanins in spiders. III. Chemical and physical properties of the proteins inDugessiella andCupiennius blood. Hoppe-Seyler's Z. Physiol. Chem.357, 1713–1725 (1976)
Markl, J., Markl, A., Hofer, A., Schartau, W., Linzen, B.: Heterogene Untereinheiten bei Arthropodenhämocyaninen. Verh. Dtsch. Zool. Ges.1978, 265 (1978)
Maurer, R.: Disc-Elektrophorese. Berlin: de Gruyter 1968
Melchers, M.: Zur Biologie und zum Verhalten vonCupiennius salei (Keyserling), einer amerikanischen Ctenide. Zool. Jahrb. Abt. Syst. Ökol. Geogr. Tiere91, 1–90 (1963)
Murray, A.C., Jeffrey, P.D.: Hemocyanin from the Australian freshwater crayfish,Cherax destructor. Subunit heterogeneity. Biochemistry13, 3667–3671 (1974)
Roche, A.C., Monsigny, M.: Purification and properties of limulin: a lectin (agglutinin) from hemolymph ofLimulus polyphemus. Biochim. Biophys. Acta371, 242–254 (1974)
Schneider, H.-J., Markl, J., Schartau, W., Linzen, B.: Hemocyanins in spiders. IV. Subunit heterogeneity ofEurypelma (Dugesiella) hemocyanin, and separation of polypeptide chains. Hoppe-Seyler's Z. Physiol. Chem.358, 1133–1141 (1977)
Schutter, W.G., van Bruggen, E.F.J., Bonaventura, J., Bonaventura, C., Sullivan, B.: Structure, dissociation and reassembly ofLimulus polyphemus hemocyanin. In: Structure and function of haemocyanin. Bannister, J.V. (ed.), pp. 13–21. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer 1977
Sugita, H., Sekiguchi, K.: Heterogeneity of the minimum functional unit of the hemocyanins from the spider (Argiope bruennichii), the scorpion (Heterometrus sp.), and the Horseshoe Crab (Tachypleus tridentatus). J. Biochem. (Tokyo)78, 713–718 (1975)
Sullivan, B., Bonaventura, J., Bonaventura, C.: Functional differences in the multiple hemocyanins of the Horseshoe, Crab,Limulus polyphemus L. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA71, 2558–2562 (1974)
Sullivan, B., Bonaventura, J., Bonaventura, C., Godette, G.: Hemocyanin of the Horseshoe Crab,Limulus polyphemus. Structural differentiation of the isolated components. J. Biol. Chem.251, 7644–7648 (1976)
Van Holde, K.E., van Bruggen, E.F.J.: The hemocyanins. In: Subunits in biological systems. Timasheff, S.N., Fasman, G.D., (eds.), pp. 1–53. New York: Marcel Dekker 1971
References
Lamy, J., Lamy, J., Weill, J.: Arthropod hemocyanin structure: isolation of eight subunits in the scorption. Arch. Biochem. Biophys.192 (in press) (1979)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Markl, J., Markl, A., Schartau, W. et al. Subunit heterogeneity in arthropod hemocyanins: I. Chelicerata. J Comp Physiol B 130, 283–292 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00689845
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00689845