Summary
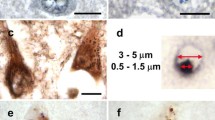
Ballooned neurons are histological features of several neurodegenerative diseases of the central nervous system. We describe the immunocytochemical staining of ballooned neurons in Pick's disease, unclassified dementia, corticonigral degeneration, pigment-spheroid degeneration and Alzheimer's disease. In all of these conditions the ballooned neurons contain phosphorylated epitopes recognized by monoclonal antibodies to neurofilaments, but not epitopes unique to Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles and Pick bodies. The morphological features and immunohistochemical properties of ballooned neurons in these disorders bear resemblance to swollen neurons produced by neurotoxins that impair axoplasmic transport of neurofilaments. This finding, by analogy, suggests that impaired axoplasmic transport of neurofilaments may be a common mechanism in various dementing neurodegenerative diseases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrews JM (1975) The fine structure of the cervical spinal cord, ventral root and brachial plexus in the Wobbler (wr) mouse. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 34:12–27
Brion S, Mikol J, Psimaras A (1973) Recent findings in Pick's disease. In: Zimmermen HM (ed) Progress in neuropathology, vol 2. Grune and Stratton, New York, pp 421–425
Bunney BS, Aghajanian GK (1976) The precise localization of nigral afferents in the rat as determined by a retrograde tracing technique. Brain Res 117:423–435
Case Records of Massachusetts General Hospital (83-1985) (1985) Corticonigral degeneration with neuronal achromasia. N Engl J Med 313:739–748
Clark AW, Manz HJ, White CL, III, Lehman J, Miller D, Coyle JT (1986) Cortical degeneration with swollen chromatolytic neurons: its relationship to Pick's disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 45:268–284
Constantinidis J (1985) Pick dementia: anatomoclinical correlations and pathophysiological considerations. In: Rose FC (ed) Modern approaches to the dementias, part I: etiology and pathophysiology. Karger, Basel, pp 72–97
Dickson DW, Kress Y, Crowe A, Yen S-H (1985) Monoclonal antibodies to Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles. 2. Demonstration of a common antigenic determinant between ANT and neurofibrillary degeneration in progressive supranuclear palsy. Am J Pathol 120:292–303
Dickson DW, Yen S-H, Davies P (1986) Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles (ANT) contain phosphorylated and nonphosphorylated neurofilament (NF) epitopes recognized by monoclonal antibodies. Am J Clin Pathol 85:381 [abstr]
Dooling EC, Schoene WC, Richardson EP Jr (1974) Hallevorden-Spatz syndrome. Arch Neurol 30:70–83
Drager UC, Hofbauer A (1983) Antibodies to heavy neurofilament subunit detect a subpopulation of damaged ganglion cells in the retina. Nature 309:624–626
Engel WK, Kurland LT, Klatzo I (1959) An inherited disease similar to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with a pattern of posterior column involvement: an intermediate form? Brain 82:203–220
Gajdusek DC (1985) Hypothesis: interference with axonal transport of neurofilaments as a common pathogenetic mechanism in certain diseases of the central nervous system. N Engl J Med 312:714–719
Gambetti P, Shecket G, Ghetti B, Hirano A, Dahl D (1983) Neurofibrillary changes in human brain: an immunocytochemical study with a neurofilament antiserum. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 42:69–79
Goldman R, Goldman A, Green K, Jones J, Lieska N, Yang H-Y (1985) Intermediate filaments: possible function as cytoskeletal connecting links between the nucleus and the cell surface. Ann NY Acad Sci 455:1–17
Hirano A, Kurland LT, Sayre GP (1967) Familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. A subgroup characterized by posterior and spinocerebellar tract involvement and hyaline inclusions in the anterior horn cells. Arch Neurol 16:232–243
Hirano A, Donnenfeld H, Sasaki S, Nakani I (1984) Fine structural observations of neurofilamentous changes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 43:461–470
Kosik KS, Selkoe DJ (1983) Experimental models of neurofilamentous pathology. In: Marotta C (ed) Neurofilaments. University of Minnesota Press, Minneapolis, pp 155–195
Ksiezak-Reding H, Yen S-H (1986) Two monoclonal antibodies recognize Alzheimer's neurofibrillary tangles, neurofilament, and microtubule associated proteins. J Neurochem (in press)
Lieberman AR (1971) The axonal reaction: a review of the principal features of perikaryal responses to axon injury. Int Rev Neurobiol 14:49–124b
Mitsumoto H, Gambetti P (1986) Impaired slow axonal transport in Wobbler mouse neuron disease. Ann Neurol 19:36–43
Moss TH, Lewkowicz SJ (1983) The axon reaction in motor and sensory neurons of mice studied by a monoclonal antibody marker of neurofilament protein. J Neurol Sci 60:267–280
Nukina N, Ihara Y (1986) One of the antigenic determinats of paired helical filaments is related to tau proteins. J Biochem 99:1541–1544
Rasool CG, Selkoe DJ (1985) Sharing of specific antigens by degenerating neurons in Pick's disease and Alzheimer's disease. N Engl J Med 321:700–705
Rebeiz JJ, Kolodny EH, Richardson EP Jr (1968) Corticodentationigral degeneration with neuronal achromasia. Arch Neurol 18:20–33
Rosenfeld J, Dorman ME, Sternberger NH, Sternberger LA, Hoffman PN, Price DL (1985) In situ distribution of phosphorylated and nonphosphorylated neurofilament epitopes following axotomy and neurectomy of sensory neurons. Soc Neurosci Abstr, vol 11, part 1:2
Sayre LM, Autilio-Gambetti L, Gambetti P (1985) Pathogenesis of experimental giant neurofilamentous axonopathies: a unified hypothesis based on chemical modifications of neurofilaments. Brain Res Rev 10:69–83
Seitelberger F, Gross H, Pilz P (1981) Pick's disease: a neuropathologic study. In: Hirano A, Miyoshi K (eds) Neuropsychiatric disorders in the elderly. Igaku-Shoin, New York, pp 87–117
Sternberger LA (1979) Immunocytochemistry, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York, pp 104–169
Sternberger LA, Sternberger NH (1983) Monoclonal antibodies distinguish phosphorylated and nonphosphorylated forms of neurofilaments in situ. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:6126–6130
Sternberger NH, Sternberger LA, Ulrich J (1985) Aberrant neurofilament phosphorylation in Alzheimers disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:4174–4276
Triarhou LC, Norton J, Bugiani O, Ghetti B (1985) Ventral root axonopathy and its relation to neurofibrillary degeneration of lower motor neurons in aluminum-induced encephalomyelopathy. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 11:407–430
Trojanowski JQ, Wakenstein N, Lee V M-Y (1986), Expression of neurofilament subunits in neurons of the central and peripheral nervous system: an immunocytochemical study with monoclonal antibodies. J Neurosci 6:650–660
Ulrich J, Haugh M, Anderton BH, Probst A (1985) Phosphorylated epitopes on Pick bodies (PB) and Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles (NFT) (abstract). J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 44:367
Wang E (1985) Intermediate filament associated proteins. Ann NY Acad Sci 455:32–56
Williams HW (1935) The peculiar cells of Pick's disease: their pathogenesis and distribution in disease. Arch Neurol Psychiatry 34:508–519
Wisniewski HM, Coblentz JM, Terry RD (1972) Pick's disease: a clinical and ultrastructural study. Arch Neurol 26:97–108
Williams RC Jr, Aamodt EJ (1985) Interaction between microtubules and neurofilaments in vitro. Ann NY Acad Sci 455:509–524
Yen S-H, Crowe A, Dickson DW (1985) Monoclonal antibodies to Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles. 1. Identification of polypeptides. Am J Pathol 120:282–291
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dickson, D.W., Yen, S.H., Suzuki, K.I. et al. Ballooned neurons in select neurodegenerative diseases contain phosphorylated neurofilament epitopes. Acta Neuropathol 71, 216–223 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00688042
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00688042