Summary
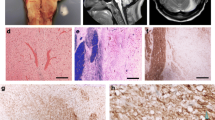
23 cases of central pontine myelinolysis (CPM) were investigated histopathologically. According to the degree of glial reaction, two groups could be distinguished—those of early (8 cases) and late (15 cases) phases.
In the early phase, oligodendroglial cells presented various signs of degeneration particularly coagulation necrosis or karyorrhexis. In the late phase, no obvious oligodendroglial degeneration was found.
Good correlation existed between the degree of demyelination and that of degeneration or loss of oligodendrocytes.
In areas of demyelination, neurons presented various nonspecific changes in all early phase cases; in addition, multifocal acute anoxic damage of nerve cells was found in 4 early phase cases (50%). In the late phase, spheroids and retrograde neuronal degeneration or nonspecific changes were observed, but no anoxic damage.
Astrocytes frequently showed nuclear swelling and, in some late phase cases, slight cellular increase without fibrillar gliosis. According to these findings, acute oligemic anoxia, happening but once, is suggested to cause CPM.
Structural peculiarities of the pontine base were studied morphometrically in 2 normal control cases; the findings support a hypothesis of the possibility of a “vascular steal”-phenomenon which may cause oligodendroglial damage in case of sudden hypotension. Reasons for the specific localisation of CPM in the pontine base are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Berry, K., Olszewski, J.: Central pontine myelinolysis. Neurology (Minneap.)13, 531–537 (1963)
Blinkov, S. M., Glezer, I. I.: Das Zentralnervensystem in Zahlen und Tabellen. Jena: G. Fischer 1968
Castaigne, P., Buge, A., Cambier, J., Escourolle, R., Rancurel, G.: La maladie de Marchiafava-Bignami: Étude anatomoclinique de dix observations. Rev. neurol.125, 179–196 (1971)
Finlayson, M. H., Snider, S., Oliva, L. A., Gault, M. H.: Cerebral and pontine myelinolysis. Two cases with fluid and electrolyte imbalance and hypotension. J. neurol. Sci.18, 399–409 (1973)
Goebel, H. H., Herman-Ben Zur, P.: Central pontine myelinolysis. Brain95, 495–504 (1972)
Haltia, M., Sourander, P., Svennerholm, L.: Chronic sclerosing Panencephalitis. I. A histological and lipid-histochemical study. Acta neuropath. (Berl.)14, 284–292 (1970)
Holdorff, B., Cervos-Navarro, J.: Die Pathologie der inneren pontomesencephalen Venen. Radiologie11, 465–471 (1971)
Jellinger, K.: Protrahierte Formen der posttraumatischen Encephalopathie. Beitr. gerichtl. Med.23, 65–118 (1965)
Jellinger, K., Seitelberger, F.: Pseudosystematische Läsionen bei “atypischen” Encephalitiden. Acta neuropath. (Berl.)8, 185–209 (1967)
Lampert, P. W., Sims, J. K., Kniazeff, A. J.: Mechanism of demyelination in JHM virus encephalomyelitis. Electron microscopic studies. Acta neuropath. (Berl.)24, 76–85 (1973)
Landers, J. W., Chason, J. L., Samuel, V. N.: Central pontine myelinolysis. Neurology (Minneap.)15, 968–971 (1965)
Lapresle, J., Milhaud, M.: Lesions du système nerveux central après arrêt circulatoire. Presse mèd.70, 429–432 (1962)
Monteiro, L.: La Myélinolyse du Centre du Pont dans le Cadre d'un Nouveau Syndrome Histopathologique de Topographie Systématisée. A Propos d'un Cas Anatomo-clinique. J. neurol. Sci.13, 293–314 (1971)
Paguirigan, A., Lefken, E. B.: Central pontine myelinolysis. Neurology (Minneap.)19, 1007–1011 (1969)
Seitelberger, F., Gross, H.: Zur Neuropathologie des Alkoholismus. In: Arbeitstagung über Alkoholismus, Hrsg. K. Krypsin-Exner, S. 12–30. Wien: Schreib- und Karteibüro E. Werner 1962
Seitelberger, F., Gross, H.: Zur organischen Hirnschädigung des Alkoholkranken. Die Läsion der Brücke bei alkoholbedingten Encephalopathien (zentrale pontine Myelinolyse; diffuse pontine Dystrophie). In: Klinik und Therapie des Alkoholismus, Symposium über den Alkoholismus, S. 109–138. Wien: Verlag der Wiener Medizinischen Akademie 1968
Seitelberger, F., Jonasch, G.: Zentrale pontine Myelinolyse nach Schädeltrauma. Klinischanatomische und pathogenetische Studie. Dtsch. Z. Nervenheilk.197, 28–41 (1970)
Sherins, R. J., Verity, M. A.: Central pontine myelinolysis associated with acute haemorrhagic pancreatitis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat.31, 583–588 (1968)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Okeda, R. Centrale pontine Myelinolyse. Acta Neuropathol 27, 233–246 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00687633
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00687633