Abstract
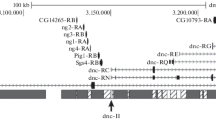
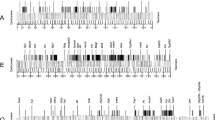
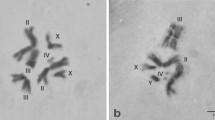
Twelve biotin-labelled recombinant DNA probes were hybridized to polytene chromosomes ofDrosophila melanogaster andD. lebanonesis. Probes were chosen in order to cover the whole chromosomal complement. Six probes correspond to known genes fromD. melanogaster (RpII215, H3−H4, MHC, hsp28/23, hsp83, hsp70), four probes are clones isolated from aD. subobscura library (Xdh, λDsubS3, λDsubG3, λDsubG4) and the remaining two probes correspond to the Adh gene ofD. lebanonensis and to one sequence (262), not yet characterized, from the same species. The chromosomal homologies obtained from the in situ hybridization results allow us to determine that Muller's C and D chromosomal elements are fused in the karyotype ofD. lebanonensis and constitute the large metacentric chromosome. Single pericentric inversions in theE andB elements have generated the medium and small metacentric chromosomes, respectively. No great changes are detected in Muller'sA element, which remains acrocentric. The changes detected in the karyotypic evolution ofD. lebanonensis are frequently observed inDrosophila evolution, as deduced from chromosomal homologies of severalDrosophila species. The results are also consistent with Muller's proposal that chromosomal elements have been conserved during the evolution ofDrosophila.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguadé M (1988) Nucleotide sequence comparison of the rp49 gene region betweenDrosophila subobscura andD. melanogaster. Mol Biol Evol 5: 433–441
Alonso C, Berendes HD (1975) The location of the 5S ribosomal RNA genes inDrosophila hydei. Chromosoma 51: 347–356
Berendes HD, Keyl HG (1967) Distribution of DNA in heterochromatin and euchromatin of polytene nuclei ofD. hydei. Genetics 57: 1–13
Berendes HD, Thijssen WT (1971) Developmental changes in genome activity inDrosophila lebanonensis casteeli Pipkin. Chromosoma 33: 345–360
Bernstein SI, Mogami K, Donady JJ, Emerson CP (1983)Drosophila muscle myosin heavy chain encoded by a single gene in a cluster of muscle mutations. Nature 302: 393–397
Brock HW, Roberts DB (1983) Location of the LSP-1 genes inDrosophila species by in situ hybridization. Genetics 103: 75–92
Carson HL, Yoon JS (1982) Genetics and evolution of HawaiianDrosophila. In: Ashburner M, Carson HL, Thompson Jr JN (eds) The genetics and biology ofDrosophila 3b. Academic Press, pp 298–344
Clayton FE, Guest WC (1986) Overview of chromosomal evolution in the family Drosophilidae. In: Ashburner M, Carson HL, Thompson JN (eds) The genetics and biology ofDrosophila 3e. Academic Press, pp 1–38
Clayton FE, Wheeler MR (1975) A catalog ofDrosophila metaphase chromosome configurations. In: King RC (ed) Handbook of genetics 3. Plenum Press, New York London, pp 471–512
Corces V, Holmgren R, Freund R, Morimoto R, Meselson M (1980) Four heat shock proteins ofDrosophila melanogaster coded within a 12-kilobase region in chromosome subdivision 67B. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77: 5390–5393
Felger I, Pinsker W (1987) Histone gene transposition in the phylogeny of theDrosophila obscura group. Z Zool Syst Evolutforsch 25: 127–140
Holmgren R, Livak K, Morimoto R, Freund R, Meselson M (1979) Studies of cloned sequences from fourDrosophila heat shock loci. Cell 18: 1359–1370
Jokerst RS, Weeks JR, Zerhing WA, Greenleaf AL (1989) Analysis of the gene encoding the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II inDrosophila. Mol Gen Genet 215: 266–275
Juan E, Papaceit M, Quintana A (1990) Nucleotide sequence of the Adh gene ofDrosophila lebanonensis. Nucleic Acids Res 18: 6420
Lakovaara S, Saura A (1972) Location of enzyme loci in chromosomes ofDrosophila willistoni. Experientia 28: 355–356
Levitan M (1982) Therobusta andmelanica groups. In: Ashburner M, Carson HL, Thompson Jr JN (eds) The genetics and biology ofDrosophila 3b. Academic Press, New York, pp 141–192
Loukas M, Kafatos FC (1986) The actin loci in the genusDrosophila: Establishment of chromosomal homologies among distantly related species by in situ hybridization. Chromosoma 94: 297–308
Loukas M, Kafatos FC (1988) Chromosomal locations of actin genes are conserved between themelanogaster andobscura groups ofDrosophila. Genetica 76: 33–41
Matsuo Y, Yamazaki T (1989) Nucleotide variation and divergence in the histone multigene family inDrosophila melanogaster. Genetics 122: 87–97
Montgomery E, Charlesworth B, Langley CH (1987) A test for the role of natural selection in the stabilization of transposable element copy number in a population ofDrosophila melanogaster. Genet Res 49: 31–41
Muller HJ (1940) Bearings of theDrosophila work on systemstics. In: Huxley J (ed) New systematics. Clarendon Press, Oxford, pp 185–268
O'Connell P, Rosbash M (1984) Sequence, structure and codon preference of theDrosophila ribosomal protein 49 gene. Nucleic Acids Res 12: 5495–5513
Orenic TV, Slusarski DC, Kroll KL, Holmgren RA (1990) Cloning and characterization of the segment polarity gene cubitus interruptus Dominant ofDrosophila. Genes Dev 4: 1053–1067
Patterson JT, Stone WS (1952) Evolution in the genusDrosophila. The Macmillan Company, New York
Pimpinelli S, Santini G, Gatti M (1976) Characterization ofDrosophila heterochromatin. II. C- and N-banding. Chromosoma 57: 377–386
Pipkin SB (1956) Two new species of theDrosophila subgenus Pholadoris and a redescription ofDrosophila hypocausta Osten Sacken. Proc Entomol Soc Wash 58: 251–258
Pipkin SB (1961) Taxonomic relationships within theDrosophila victoria species group, subgenus Pholadoris. Proc Entomol Soc Wash 63: 145–161
Schedl P, Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Steward R, Gehring WJ (1978) Two hybrid plasmids withD. melanogaster DNA sequences complementary to mRNA coding for the major heat shock protein. Cell 14: 921–929
Segarra C, Aguadé M (1992) Molecular organization of the X chromosome in different species of theobscura group ofDrosophila. Genetics 130: 513–521
Steineman UM (1982) Analysis of chromosomal homologies between two species of the subgenus Sophophora:D. miranda andD. melanogaster using cloned DNA segments. Chromosoma 87: 77–88
Steineman UM, Steineman S (1990) Evolutionary changes in the organization of the major LCP gene cluster during sex chromosomal differentiation in the sibling speciesDrosophila persimilis, D. pseudoobscura andD. miranda. Chromosoma 99: 424–431
Steineman UM, Pinsker W, Sperlich D (1984) Chromosome homologies within theDrosophila obscura group probed by in situ hybridization. Chromosoma 91: 46–53
Stone WS (1962) The dominance of natural selection and the reality of superspecies (species groups) in the evolution ofDrosophila. Univ Texas Publ 6205: 507–537
Stuart WD, Bishop JC, Carson HL, Frank MB (1981) Location of the 18/28s ribosomal RNA genes in two HawaiianDrosophila species by monoclonal immunological identification of the RNA-DNA hybrids in situ. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78: 3751–3754
Throckmorton LH (1982) Thevirilis species group. In: Ashburner M, Carson HL, Thompson Jr JN (eds) The genetics and biology ofDrosophila 3b. Academic Press, pp 227–296
Visa N, Marfany G, Vilageliu L, Albalat R, Atrian S, González-Duarte R (1991) The Adh inDrosophila: Chromosomal location and restriction analysis in species with different phylogenetic relationships. Chromosoma 100: 315–322
Wasserman M (1982) Evolution of therepleta group. In: Ashburner M, Carson HL, Thompson Jr JN (eds) The genetics and biology ofDrosophila 3b. Academic Press, New York, pp 61–139
Whiting JH Jr, Pliley MD, Farmer JL, Jeffery DE (1989) In situ hybridization analysis of chromosomal homologies inDrosophila melanogaster andDrosophila virilis. Genetics 122: 99–109
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by: E.R. Schmidt
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Papaceit, M., Juan, E. Chromosomal homologies betweenDrosophila lebanonensis andD. melanogaster determined by in situ hybridization. Chromosoma 102, 361–368 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00661280
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00661280