Abstract
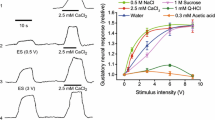
In cats anaesthetized with chloralose and urethane algesic substances were injected intra-arterially into muscles of the left hindlimb and the resulting changes in heart rate and blood pressure recorded. The vagus nerves and both carotid sinus nerves were cut. Injection of KCl regularly induces acceleration of the heart rate and an increase in blood pressure. With bradykinin both accelerations and decelerations were observed (with or without accompanying pressor or depressor responses respectively). Injection of serotonin was rather ineffective in producing heart rate or blood pressure changes but subsequent injections of either KCl or bradykinin gave rise to enhanced acceleration and pressor responses. In the discussion it will be proposed that the diverse responses are due to differences in the composition of the afferent volleys elicited, probably because besides stimulating nociceptors these algesic substances activate to a varying extent non-nociceptive muscular fine afferent units of different modality and various central actions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burch GE, De Pasquale NP (1962) Bradykinin, digital blood flow, and the arteriovenous anastomoses. Circ Res 10:105–115
Fisher ML, Nutter DO (1974) Cardiovascular reflex adjustments to static muscular contractions in the canine hindlimb. Am J Physiol 226:648–655
Fock S, Mense S (1976) Excitatory effects of 5-hydroxytryptamine, histamine and potassium on muscular group IV afferent units: a comparison with bradykinin. Brain Res 105:459–469
Foreman RD, Schmidt RF, Willis WD (1979) Effects of mechanical and chemical stimulation of fine muscle afferents upon primate spinothalamic tract cells. J Physiol 286:215–231
Franz M, Mense S (1975) Muscle receptors with group IV afferent fibres responding to application of bradykinin. Brain Res 92:369–383
Granit R, Skoglund St, Thesleff St (1953) Activation of muscle spindles by Succinylcholine and Decamethonium. The effect of Curare. Acta Physiol Scand 28:130–160
Guzman F, Braun C, Lim RKS (1962) Visceral pain and the pseudaffective response to intraarterial injection of bradykinin and other algesic agents. Arch Int Pharmacodyn 136:353–384
Hertel HC, Howaldt B, Mense S (1976) Responses of group IV and group III muscle afferents to thermal stimuli. Brain Res 113:201–205
Hník P, Hudlická O, Kučera J, Payne R (1969) Activation of muscle afferents by non-proprioceptive stimuli. Am J Physiol 217:1451–1457
Hong SK, Kniffki KD, Mense S, Schmidt RF, Wendisch M (1979) Descending influences on the responses of spinocervical tract neurones to chemical stimulation of fine muscle afferents. J Physiol 290:129–140
Hunt R (1895) The fall of blood-pressure resulting from the stimulation of afferent nerves. J Physiol 18:381–410
Jänig W (1979) Reciprocal reaction patterns of sympathetic subsystems with respect to various afferent inputs. In: Brooks CMcC, Koizumi K, Sato A (eds) Integrative functions of the autonomic nervous system. University of Tokyo Press, pp 263–274
Jänig W (1981) Reactions of sympathetic neurones to noxious stimulation of skin: new experiments and perspectives. In: Struppler A (ed) Schmerzforschung, Schmerzmessung, Brustschmerz. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 25–37
Kao FF (1963) An experimental study of the pathway involved in exercise hyperpnoea employing cross-circulation technique. In: Cunningham DJC, Lloyd BB (eds) The regulation of human respiration. Blackwell, Oxford, pp 461–502
Kaufman A, Sato A, Sato Y, Sugimoto H (1977) Reflex changes in heart rate after mechanical and thermal stimulation of the skin at various segmental levels. Neuroscience 2:103–109
Kidd GL, Kučera J, Vaillant CH (1971) The influence of the interstitial concentration of K+ on the activity of muscle receptors. Physiol Bohemoslov 20:95–108
Kniffki KD, Mense S, Schmidt RF (1978) Responses of group IV afferent units from skeletal muscle to stretch, contraction and chemical stimulation. Exp Brain Res 31:511–522
Kniffki KD, Mense S, Schmidt RF (1981) Muscle receptors with fine afferent fibers which may evoke circulatory reflexes. Circ Res 48: Supp I, I-25–I-31
Kumazawa T, Mizumura K (1977) Thin-fibre receptors responding to mechanical, chemical, and thermal stimulation in the skeletal muscle of the dog. J Physiol 273:179–194
Lewis T (1942) Pain. The Macmillan Company, New York (reprinted 1944), pp 1–192
Lim RKS, Liu ChN, Guzman F, Braun Ch (1962) Visceral receptors concerned in visceral pain and the pseudaffective response to intrarterial injection of bradykinin and other algesic agents. J Comp Neurol 118:269–293
Liu CT, Huggins RA, Hoff HE (1969) Mechanisms of intra-arterial K+-induced cardiovascular and respiratory responses. Am J Physiol 217:969–973
McCloskey DI, Mitchell JH (1972) Reflex cardiovascular and respiratory responses originating in exercising muscle. J Physiol (Lond) 224:173–186
Mense S (1977) Nervous outflow from skeletal muscle following chemical noxious stimulation. J Physiol 267:75–88
Mense S (1981) Sensitization of group IV muscle receptors to bradykinin by 5-hydroxytryptamine and prostaglandin E2. Brain Res 225:95–105
Mense S, Schmidt RF (1974) Activation of group IV afferent units from muscle by algesic agents. Brain Res 72:305–310
Sato A, Sato Y, Shimada F, Torigata Y (1976) Varying changes in heart rate produced by nociceptive stimulation of the skin in rats at different temperatures. Brain Res 110:301–311
Sato A, Sato Y, Schmidt RF (1977) Autonomic reflexes elicited by stimulation of muscle afferent nerves in the cat. Proc XVIII Int Cong Neuroveg Res, pp 106–108
Sato A, Sato Y, Schmidt RF (1979a) Effects on reflex bladder activity of chemical stimulation of small diameter afferents from skeletal muscle in the cat. Neurosci Lett 11:13–17
Sato A, Sato Y, Schmidt RF (1979b) The effects of somatic afferent activity on the heart rate. In: Brooks CMcC, Koizumi K, Sato A (eds) Integrative functions of the autonomic nervous system. Tokyo University Press, Tokyo, pp 275–282
Sato A, Sato Y, Schmidt RF (1980) Reflex bladder activity induced by electrical stimulation of hind limb somatic afferents in the cat. J Autonomic Nerv Syst 1:229–241
Sato A, Sato Y, Schmidt RF (1981) Heart rate changes reflecting modifications of efferent cardiac sympathetic outflow by cutaneous and muscle afferent volleys. J Autonomic Nerv Syst 4:231–247
Sato A, Schmidt RF (1973) Somatosympathetic reflexes: afferent fibers, central pathways, discharge characteristics. Pysiol Rev 53: 916–947
Tibes U (1977) Reflex inputs to the cardiovascular and respiratory centers from dynamically working canine muscles. Circ Res 41:332–341
Webb-Peploe MM, Brender D, Shepherd JT (1972) Vascular responses to stimulation of receptors in muscle by capsaicin. Am J Physiol 222:189–195
Wildenthal K, Mierzwiak DS, Skinner NS Jr, Mitchell JH (1968) Potassium-induced cardiovascular and ventilatory reflexes from the dog hindlimb. Am J Physiol 215:542–548
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sato, A., Sato, Y. & Schmidt, R.F. Changes in heart rate and blood pressure upon injection of algesic agents into skeletal muscle. Pflugers Arch. 393, 31–36 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00582387
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00582387