Abstract
A theoretical investigation of the effect of different parameters on the flow and the temperature fields in a radiofrequency inductively coupled plasma is carried out. The parameters studied are: central injection gas flow rate, total gas flow rate, input power, and the type of plasma gas. The results obtained for argon and nitrogen plasmas at atmospheric pressure indicate that the flow and the temperature fields in the coil region, as well as the heat flux to the wall of the plasma confinement tube, are considerably altered by the changes in the torch operating conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- C p :
-
specific heat at constant pressure
- E θ :
-
electric field intensity
- f :
-
frequency
- F r :
-
radical electromagnetic body force
- g :
-
gravitational acceleration
- H z :
-
magnetic field intensity
- h :
-
enthalpy
- I :
-
coil current
- k :
-
thermal conductivity
- k c :
-
thermal conductivity of quartz
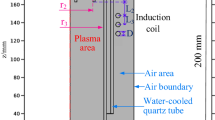
- L 1 :
-
distance from the inlet of the torch to the beginning of the coil
- L 2 :
-
distance from the inlet of the torch to the bottom of the coil
- L T :
-
total length of the plasma confinement tube
- N :
-
number of turns of the coil
- P :
-
local dissipated power
- P 0 :
-
total dissipated (input) power
- Q 1 :
-
central gas flow rate
- Q 2 :
-
plasma gas flow rate
- Q 3 :
-
sheath gas flow rate
- Q 0 :
-
total gas flow rate
- Q r :
-
fraction of the power lost by radiation
- Q w :
-
fraction of the power lost by heat conduction to the wall
- Q g :
-
fraction of the power carried by the exit plasma gas
- q w :
-
local heat flux to the wall
- r :
-
radial position
- r 1 :
-
inside radius of the central tube
- r 2 :
-
outside radius of the central tube
- r 3 :
-
radius of the plasma gas tube
- R 0 :
-
inside radius of the plasma confinement tube
- R c :
-
coil radius
- R 0 :
-
local radiation loss
- T :
-
temperature
- V r :
-
radial velocity component
- V z :
-
axial velocity component
- w :
-
thickness of the quartz tube
- z :
-
axial position
- ρ :
-
density
- μ :
-
viscosity
- ζ :
-
permeability of free space
- ω :
-
=2πf
- χ :
-
phase angle
- ψ :
-
stream function
- σ :
-
electrical conductivity
- η :
-
percentage of the total power
References
P. Fauchais and J. M. Baronnet,Pure Appl. Chem. 52, 1669–1705 (1980).
D. Benenson, and H. S. Kwok,Pure Appl. Chem. 54, 1157–1180 (1982).
M. I. Boulos,IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. PS-4, 28–39 (1976).
M. I. Boulos, R. Gagné, and R. M. Barnes,Can. J. Chem. Eng.,58, 367–375, 381 (1980).
J. Mostaghimi, P. Proulx, and M. I. Boulos,J. Numerical Heat Transfer, in press (1984).
C. Borgianni, M. Capitelli, F. Cramarossa, L. Triolo, and Molinari,Combust. Flame 13, 181–194 (1969).
M. I. Boulos,IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. PS-6, 93–106 (1978).
M. W. Blades and G. Horlick,Spectrochim. Acta Part B 36, 881–900 (1981).
N. Furuta and G. Horlick,Spectrochim. Acta Part B,37, 53–64 (1982).
R. Gagné, “Etude de modélisation d'un plasma à induction généré à haute fréquence,” Master of Science thesis, University of Sherbrooke (1980).
R. M. Barnes and R. G. Schleicher,Spectrochim. Acta Part B 30, 109–134 (1975).
R. M. Barnes and S. Nikdel,J. Appl. Phys. 47, 3929–3934 (1976).
R. M. Barnes and R. G. Schleicher,Spectrochim. Acta Part B 36, 81–101 (1981).
R. C. Miller and R. J. Ayen,J. Appl. Phys. 40, 5260–5273 (1969).
S. V. Patankar,Numerical Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow, McGraw-Hill, New York (1980).
J. L. Lewis, “The motion of particles entrained in a plasma jet,” Ph.D. Thesis, McGill University (1971).
D. L. Evans and R. S. Tankin,Phys. Fluids 10, 1137–1144 (1967).
R. S. Devoto,Phys. Fluids 9, 1230–1240 (1966).
M. Capitelli, E. Ficocelli, and E. Molinari,Equilibrium Compositions and Thermodynamic Properties of Mixed Plasmas, Instituto di Chimica Grenerale e Inorganica, Università degli Studi-Bari (1969).
C. Gorse, Contribution au calcul des propriétés de transport des plasmas des mélanges argon-hydrogène et argon-azote,” Ph.D. dissertation, University of Limoges (1975).
W. D. Barfield, J.Q.S.R.T.,17, 471 (1977).
E. Pfender, “Electric arcs and arc gas heaters” inGaseous Electronics, M. N. Hirsh and H. J. Oskam, eds., eds., Vol. 1, Academic, New York (1978), p. 362.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mostaghimi, J., Proulx, P. & Boulos, M.I. Parametric study of the flow and temperature fields in an inductively coupled r.f. plasma torch. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 4, 199–217 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00566841
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00566841